Alessandro Chiesa
|
Read other articles:

Jahit kerut adalah teknik menjahit dekoratif yang melibatkan menjahit banyak baris kain yang terkumpul.[1] Jahit kerut mengurangi ukuran kain asli dengan menambahkan tekstur pada kain dekoratif yang dihasilkan.[2] Tampilan dekat jahitan kerut pada blus Dalam menjahit, jahit kerut adalah dua baris atau lebih kumpulan yang digunakan untuk menghiasi bagian-bagian pakaian, biasanya bagian lengan, korset, atau kuk . Istilah ini juga terkadang digunakan untuk menyebut lipatan yang t...

Droit des personnes en France Personnalité juridique Types de personnalités : Personne physique, personne morale (voir droit des sociétés) Acquisition de la personnalité : Naissance, conception Perte de la personnalité : Absence, Disparition, Mort Individualisation de la personne (état civil) : Domicile, Sexe, Nationalité, Nom Caractères de la personnalité : Indisponibilité, imprescriptibilité Droit des incapacités Protection des mineurs Majorité civile...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Sejarah Kekaisaran Romawi – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan...

PausGabriel V dari AleksandriaPaus Aleksandria ke-88 & Patriarkh Tahta St. MarkusAwal masa jabatan1409Masa jabatan berakhir1427PendahuluMatiusPenerusYohanes XIInformasi pribadiLahirMesirWafat1427MesirMakamGereja Perawan Suci (Babilonia El-Darag)KewarganegaraanMesirDenominasiKristen Ortodoks KoptikKediamanGereja Perawan Maria (Haret Zuweila) Paus Gabriel V dari Alexandria adalah Paus Aleksandria ke-88 & Patriarkh Tahta St. Markus. Paus Gabriel menamai pendahulunya Matius I.[1] ...

Untuk senapan serbu, lihat Valmet M82. Untuk senapan runduk aksi-baut, lihat Parker Hale M82. M82 Barrett M82A1 dilengkapi dengan alat bidik optik AN/PVS-10 siang/malam Jenis Senapan anti materiel Negara asal Amerika Serikat Sejarah pemakaian Masa penggunaan 1989–sekarang Digunakan oleh Lihat Pengguna Sejarah produksi Perancang Ronnie Barrett Tahun 1980 Produsen Barrett Firearms Manufacturing Biaya produksi $8,900[1] Diproduksi 1982–sekarang Varian M82A1,...

Korean Buddhist monk (590–658) This article is about the Buddhist monk. For the village in Iran, see Jajang, Iran. For the noodle dish, see Jajangmyeon. For the sauce used in the noodle dish, see Sweet bean sauce. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Jajang – news · newspapers · books · scholar �...
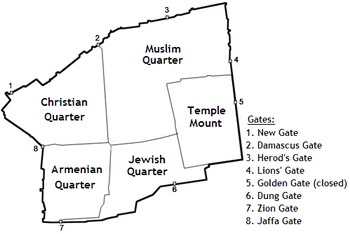
Gate of the Old City of Jerusalem Jaffa GateJaffa GateLocation in Old JerusalemGeneral informationTown or cityOld City (Jerusalem)Coordinates31°46′35.5″N 35°13′39.7″E / 31.776528°N 35.227694°E / 31.776528; 35.227694 Old City Gates Jaffa Gate (Hebrew: שער יפו, romanized: Sha'ar Yafo; Arabic: باب الخليل, romanized: Bāb al-Khalīl, Hebron Gate) is one of the seven main open gates of the Old City of Jerusalem. The name Jaffa Gate is cu...

Re di Francia - Capetingi Ugo Capeto (~940-996) Figli Roberto II Roberto II (972-1031) Figli Enrico I Roberto I di Borgogna Enrico I (1008/1010-1060) Figli Filippo I Ugo I di Vermandois Filippo I (1052-1108) Figli Luigi VI Luigi VI (1081-1137) Figli Luigi VII Enrico Costanza Luigi VII (1120-1180) Figli Maria di Champagne Alice Margherita Adele Filippo II Agnese, contessa del Vexin Filippo II (1165-1223) Figli Luigi VIII Filippo Hurepel di Clermont Luigi VIII (1187-1226) Figli Luigi IX Robert...

Artikulationsställen Labiala Bilabiala Labiodentala Linguolabiala Koronala Interdentala Dentala Retroflexa Alveolara Postalveolara Alveolopalatala Dorsala Palatala Labiopalatala Velara Labiovelara Uvulara Faryngala Epiglottala Glottala Se även: artikulationssätt · Kategori:Konsonantljud Den här sidan kan innehålla fonetisk information skriven med IPA, som kan krångla i vissa webbläsare. Hjälp. Redigera den här mallen Den här artikeln behöver källhänvisningar för att kunn...

Questa voce sull'argomento aeroporti del Regno Unito è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Aeroporto di Newcastle upon Tyneaeroporto Codice IATANCL Codice ICAOEGNT Nome commercialeNewcastle Airport DescrizioneTipoCivile GestoreNewcastle International Airport Ltd Stato Regno Unito PosizioneWoolsington Base Jet2 Ryanair TUI UK Altitudine81 m s.l.m. Coordinate55°02′15″N 1°41′30″W / 55.0375°N 1.691667°W...

This article is written like a story. Please help rewrite this article to introduce an encyclopedic style and a neutral point of view. (January 2018) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message)Not to be confused with Topass, the South Asian translators for the Br...

1973 American filmThe Werewolf of WashingtonDVD coverDirected byMilton Moses GinsbergWritten byMilton Moses GinsbergProduced byNina SchulmanStephen A. MillerStarringDean StockwellBiff McGuireClifton JamesMichael DunnCinematographyRobert M. BaldwinEdited byMilton Moses GinsbergMusic byArnold FreedDistributed byDiplomatRelease date February 20, 1973 (1973-02-20) Running time90 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguagesEnglishHungarian The Werewolf of Washington is a 1973 horror comedy ...

Voce principale: Guerra civile in Afghanistan#Cronologia storica. Guerra civile afghana (1996-2001)parte della guerra civile afghanaLa suddivisione dell'Afghanistan nel 1996Datasettembre 1996 - ottobre 2001 LuogoAfghanistan Esitosituazione di stallo risolta poi dal successivo intervento statunitense Schieramenti Stato islamico dell'Afghanistan: Alleanza del Nord Supporto da: Iran India Stati Uniti Emirato islamico dell'Afghanistan (Talebani) Al-QāʿidaSupporto da: Pakist...

2013 January February March April May June July August September October November December From left, clockwise: Edward Snowden becomes internationally famous for leaking classified NSA wiretapping information; Typhoon Haiyan kills over 6,000 in the Philippines and Southeast Asia; the Rana Plaza collapse in Bangladesh kills over 1,000 people; the streak from the Chelyabinsk meteor that rocketed across the Russian morning sky; protests occur amid the coup d'état that overthrew President Moha...

Overview of the events of 1953 in architecture List of years in architecture (table) … 1943 1944 1945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950 1951 1952 1953 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 1963 … Buildings and structures Art Archaeology Architecture Literature Music Philosophy Science +... The year 1953 in architecture involved some significant events. Events Gordon Ryder and Peter Yates form an architectural practice based in Newcastle upon Tyne in the north of England. Buildings and stru...

構造地質学や岩石学におけるへき開については「en:Cleavage (geology)」をご覧ください。 へき開(劈開、へきかい、英: cleavage)とは、結晶や岩石の割れ方がある特定方向へ割れやすいという性質のこと。鉱物学、結晶学用語である。宝石の加工や、工学の分野で重要な性質の1つ。 概要 岩石を構成する造岩鉱物は結晶構造由来の結晶面をもつ。この面では原子間の結合�...

Regional airline of the United States Mesa Airlines IATA ICAO Call sign YV ASH AIR SHUTTLE Founded1980; 44 years ago (1980)[1]Commenced operationsOctober 12, 1980; 43 years ago (1980-10-12)[1]AOC #MASA036A[2]HubsCincinnatiHouston–IntercontinentalWashington–DullesFrequent-flyer programMileage Plus (United)AllianceStar Alliance (United)Fleet size69Destinations200Parent companyMesa Air Group, Inc.HeadquartersPhoenix, Arizona, U...

Governo Fanfani II Stato Italia Presidente del ConsiglioAmintore Fanfani(DC) CoalizioneDC, PSDI LegislaturaIII Legislatura Giuramento2 luglio 1958 Dimissioni26 gennaio 1959 Governo successivoSegni II16 febbraio 1959 Zoli Segni II Il Governo Fanfani II è stato il tredicesimo esecutivo della Repubblica Italiana, il primo della III legislatura. È rimasto in carica dal 2 luglio 1958[1][2] al 16 febbraio 1959[3] per un totale di 229 giorni, ovvero 7 mesi e 14 giorni....

ملعب إيبوروا البلديمعلومات عامةالمنطقة الإدارية إيبار البلد إسبانيا التشييد والافتتاحالافتتاح 1947الافتتاح الرسمي 14 سبتمبر 1947 المقاول الرئيس إيبار الاستعمالالرياضة كرة القدم المستضيف نادي إيبارالمالك بلدية إيبارالإدارة بلدية إيبارمعلومات أخرىالطاقة الاستيعابية 6,3...

City and municipality in South Holland, Netherlands City and municipality in South Holland, NetherlandsDordrecht DordtCity and municipalityAugustijnenkampHistoric city centreBleijenhoekCity hall FlagCoat of armsLocation in South HollandDordrechtLocation within the NetherlandsShow map of NetherlandsDordrechtLocation within EuropeShow map of EuropeCoordinates: 51°47′45″N 04°40′42″E / 51.79583°N 4.67833°E / 51.79583; 4.67833CountryNetherlandsProvinceSouth Holl...