9th Infantry Division "Pasubio"
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Liga 3 Aceh 2021Logo Liga 3 Aceh 2021Tanggal penyelenggaraan4 Desember 2021 - 8 Januari 2021Tempat penyelenggaraan6 stadionJumlah peserta27 tim sepak bolaJuara bertahanPersidiJuaraPSBL[1](gelar ke-1)Tempat keduaGalacticos FCTempat ketigaPSLSTempat keempatPersipKualifikasi untukLiga 3 2021 Putaran nasionalJumlah pertandingan63Jumlah gol187 (2.97 per pertandingan)Pencetak gol terbanyak8 golAl Muzanni[2](PSLS)← 2019 20222023 → Liga 3 Aceh 2021 adalah edisi ketiga dari musim L...

The 12th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) was held during 17–25 April 1923 in Moscow. The congress elected the 12th Central Committee. It was attended by 408 delegates with deciding votes and 417 with consultative votes, representing 386,000 party members.[1] This was the last congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks) (RCP(b) during Vladimir Lenin's leadership, though Lenin was unable to attend due to illness.[1][2] Agenda L.Kamenev an...

For the FM radio station in Huntington, Texas, United States, see KSML-FM. Radio station in Diboll, TexasKSMLDiboll, TexasBroadcast areaLufkin-NacogdochesFrequency1260 kHzBrandingPower 103-7ProgrammingFormatUrban contemporary gospel and urban adult contemporaryOwnershipOwnerKasa Family Limited PartnershipSister stationsKRBA, KSML-FM, KYBIHistoryFirst air dateMarch 3, 1986Former call signsKAFX (1986-1986)KDFX (1989-1996)Call sign meaningSuper Mix Lufkin (former branding)Technical informationFa...

برنامج الأمم المتحدة للمستوطنات البشرية برنامج الأمم المتحدة للمستوطنات البشرية شعار برنامج الأمم المتحدة للمستوطنات البشرية الاختصار (بالإنجليزية: UN Habitat)، و(بالإنجليزية: UN-Habitat)، و(بالفرنسية: ONU-Habitat) المقر الرئيسي نيروبي، كينيا تاريخ التأسيس 1978؛ من...

Sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guidelines for companies and organizations. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted.Find sources: Inter-American Division...

RulesAlbum studio karya The Whitest Boy AliveDirilis3 Maret 2009GenreMinimalist Pop, indie popLabelBubbles RecordsKronologi The Whitest Boy Alive Dreams(2006)Dreams2006 Rules(2009) Rules adalah album studio kedua dari The Whitest Boy Alive. Album ini direkam ketika mereka sedang menjalankan promo tour di Meksiko. Seluruh lagu di album ini telah beredar secara ilegal di internet sejak Januari 2009. Daftar lagu “Keep a Secret” “Intentions” “Courage” “Timebomb” “Rollercoast...

Portuguese football referee This biography of a living person includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately, especially if potentially libelous or harmful. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) In this Portuguese name, the first or mat...

Artikel ini perlu diterjemahkan dari bahasa Inggris ke bahasa Indonesia. Artikel ini ditulis atau diterjemahkan secara buruk dari Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Jika halaman ini ditujukan untuk komunitas bahasa Inggris, halaman itu harus dikontribusikan ke Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. Lihat daftar bahasa Wikipedia. Artikel yang tidak diterjemahkan dapat dihapus secara cepat sesuai kriteria A2. Jika Anda ingin memeriksa artikel ini, Anda boleh menggunakan mesin penerjemah. Namun ingat, mohon tidak men...

Voce principale: Piacenza Calcio 1919. Piacenza FCStagione 1999-2000 Sport calcio Squadra Piacenza Allenatore Luigi Simoni, poi Daniele Bernazzani e Maurizio Braghin Presidente Stefano Garilli, poi Fabrizio Garilli Serie A18º (retrocesso in Serie B) Coppa ItaliaOttavi di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Roma (32)Totale: Roma (36) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Di Napoli (4) StadioLeonardo Garilli Media spettatori10 763[1] 1998-1999 2000-2001 Si invita a seguire il modello...

Mazda BT-50Ford RangerInformasiProdusenMazdaMasa produksi2006–sekarangBodi & rangkaKelasTruk pikapMobil terkaitFord Ranger2007-2019Isuzu D-Max 2019-sekarangKronologiPendahuluMazda B-SeriesPenerusMazda BT-50 (berbasis Isuzu D-Max) Mazda BT-50 (J97M) adalah truk pikap yang diproduksi oleh Mazda sejak 2006. Ford juga menjual versi sejenis dari BT-50 yang dinamai Ford Ranger dan SUV Ford Everest. Generasi kedua Ranger didesain oleh Ford Australia, dengan Mazda juga menjualnya dengan nama BT...

安倍晋太郎安倍晋太郎(攝於1987年4月21日) 日本第112、113任外務大臣任期1982年11月27日—1986年7月22日总理中曾根康弘前任櫻内義雄继任倉成正 日本第42任通商產業大臣任期1981年11月30日—1982年11月27日总理鈴木善幸前任田中六助(日语:田中六助)继任山中貞則 日本第41任内閣官房長官任期1977年11月28日—1978年12月7日总理福田赳夫前任園田直继任田中六助(日语�...

American filmsby year 1890s 1890–1899 1900s 1900 1901 1902 1903 19041905 1906 1907 1908 1909 1910s 1910 1911 1912 1913 19141915 1916 1917 1918 1919 1920s 1920 1921 1922 1923 19241925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930s 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940s 1940 1941 1942 1943 19441945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950s 1950 1951 1952 1953 19541955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会白俄罗斯代表團白俄罗斯国旗IOC編碼BLRNOC白俄羅斯共和國奧林匹克委員會網站www.noc.by(英文)(俄文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員103參賽項目17个大项旗手开幕式:Mikita Tsmyh(游泳)和Hanna Marusava(射箭)[1]闭幕式:Ilya Palazkov(现代五项)[2]獎牌榜...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 1975–76 Football League First Division – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021)1975–76 season of Football League First Division Football league seasonFootball League First DivisionSeason1975–76ChampionsLiverpool9th titleRele...

American journalist and educator Gene Swann GrahamBorn(1924-08-26)August 26, 1924Murray, KentuckyDiedMay 24, 1982(1982-05-24) (aged 57)OccupationJournalistNationalityAmericanEducationBachelor of Science, 1948Alma materMurray State CollegeNotable awardsPulitzer Prize for National Reporting 1962 Spouse Martha Fentress (m. 1945)ChildrenSusan Marie, Betty Jane, and Philip Gene Gene Swann Graham (August 26, 1924 – May 24, 1982) was an American journalist ...

Augusta LindbergLindberg pada 1906.LahirAugusta Wilhelmina Blomstedt17 Maret 1866Stockholm, SwediaMeninggal3 Desember 1943 (usia 77)PekerjaanPemeran Augusta Lindberg (née Blomstedt; 17 Maret 1866 – 3 Desember 1943) adalah seorang pemeran panggung Swedia. Lindberg juga tampil dalam film-film bisu, seperti film epik sejarah tahun 1925 Charles XII.[1] Ia menikahi pemeran August Lindberg dan merupakan ibu dari penulis Stina Bergman dan sutradara Per Lindberg. Filmog...

Voce principale: Società Sportiva Lazio. SS LazioStagione 1934-1935Una formazione della Lazio 1934-35 Sport calcio Squadra Lazio Allenatore Walter Alt Presidente Eugenio Gualdi Serie A5º Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Ferraris IV (30) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Piola (21) Stadiodel Partito Nazionale Fascista 1933-1934 1935-1936 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Società Sportiva Lazio nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione...

Ini adalah daftar katedral di Meksiko. Katedral Bunda Maria Yang Dikandung Tanpa Noda, Campeche Katedral Metropolitan Salib Suci, Bunda Maria dari Regla dan Santo Fransiskus dari Assisi, Chihuahua Katedral Santa Perawan Maria yang Terberkati Yang Dikandung Tanpa Noda Hingga ke Surga, Kota Meksiko Katedral Bunda dari Monterrey, Monterrey Katedral Santo Yakobus, Saltillo Katedral Santo Yusuf dari Nazaret, Toluca Katedral Bunda dari Guadalupe, Zamora de Hidalgo Katolik Katedral Gereja Katolik di...
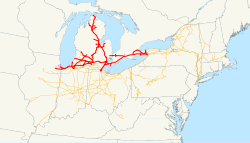
密歇根中央铁路公司Michigan Central Railroad1918年的密歇根中央铁路公司(紅色)和 紐約中央鐵路公司(橙色)區域密歇根州、印第安納州、伊利諾伊州、安大略省繼承紐約中央鐵路公司軌距4英尺8 1⁄2英寸(1,435毫米)密歇根中央鐵路公司(英語:Michigan Central Railroad;報告記號:MC)最初成立於 1846 年,目的是在密歇根州的底特律和聖約瑟夫之間提供鐵路服務。該鐵路公司�...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une rencontre de football et l’Europe. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Finale de la Ligue des champions 1995-1996 Stade Olympique de Rome hôte de la finale. Contexte Compétition Ligue des champions 1995-1996 Date 22 mai 1996 Stade Stade olympique Lieu Rome, Italie Affluence 67 000 spectateurs Résultat Ajax Amsterdam 1 – 1 ap Juventus FC Tirs au ...

