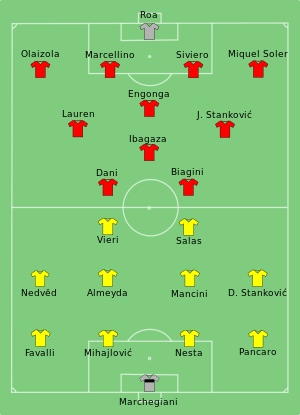
1999 UEFA Cup Winners' Cup final
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kantor Bataviaasch Nieuwsblad, Batavia. Bataviaasch Nieuwsblad ([Surat Kabar Batavia] Error: {{Lang-xx}}: text has italic markup (help)) adalah salah satu surat kabar harian terdepan dan terbesar di Hindia Belanda Berkantor pusat di Batavia (sekarang Jakarta), surat kabar ini dibaca di seluruh nusantara. Kantor beritanya didirikan oleh wartawan dan penulis Belanda P.A.Daum pada tahun 1885 dan terus berdiri sampai 1957. Koran yang inovatif dan populer ini sangat kritis terhadap pemerintah kolo...

العلاقات الباربادوسية الليتوانية باربادوس ليتوانيا باربادوس ليتوانيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الباربادوسية الليتوانية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين باربادوس وليتوانيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية �...

A state firearm has been designated by ten states in the United States: Alaska, Arizona, Utah, Indiana, Kentucky, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Tennessee, Texas, and Missouri. States In March 2011, Utah adopted the M1911 pistol as its state firearm. This gun was designed by Ogden, Utah native John Browning. The adoption was supported by Republican Utah State Representative Carl Wimmer, who said, It does capture a portion of Utah's history and even bigger than that, it captures a portion of Am...

20twentyCompany typePrivateIndustryBankingFounded2001[1]Defunct2006[2]FateBankruptcyHeadquartersCape Town, South AfricaArea servedSouth AfricaKey peopleChristo Davel (CEO)ProductsRetail bankingNumber of employees~100 (2006)[3]Websitewww.20twenty.com 20Twenty was an online South African retail bank that specialised in no frills digital banking. It focused on offering low transaction costs with low interest rates on loans whilst offering higher interest rates on savings...

Peta negara-negara yang berbentuk federasi (berwarna hijau).Bagian dari seri PolitikBentuk dasar dari pemerintahan Struktur kekuatan Konfederasi Federasi Hegemoni Kerajaan Negara kesatuan Sumber kekuatan Demokrasi Langsung Perwakilan Semi lainnya Kerajaan Mutlak Konstitusi Oligarki Aristokrasi Junta militer Kleptokrasi Plutokrasi Stratokrasi Timokrasi Otokrasi Otoritarianisme Despotisme Diktatur (Kediktatoran) Totalitarianisme Republik Parlementer Presidensial Semi presidensial Lainnya A...
Ulmen is a Mapudungun word meaning rich man. In Mapuche society, the wealthy men were usually the loncos and would often be the influential leaders of their rehue and aillarehue. If skilled in war, like the military leader Caupolicán, they were sometimes elected toqui. Sources Juan Ignacio Molina (1809). The Geographical, Natural, and Civil History of Chili Volume 2. London: Longman, Hurst, Rees, and Orme. This South American history-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expan...

ColbertIl Colbert ormeggiato a Bordeaux nel 2006Descrizione generale Tipoincrociatore antiaereo (CAA)incrociatore missilistico (CLM) Classeunica In servizio con Marine nationale IdentificazioneC 611 Ordine1953 CantiereBrest Impostazione17 maggio 1954 Varo24 marzo 1956 Entrata in servizio5 maggio 1959 Ammodernamento1970-1972 IntitolazioneJean-Baptiste Colbert Fuori servizio24 maggio 1991 Destino finaledemolita nel 2018 Caratteristiche generaliDislocamento11.300 t Lunghezza184,47 m Lar...
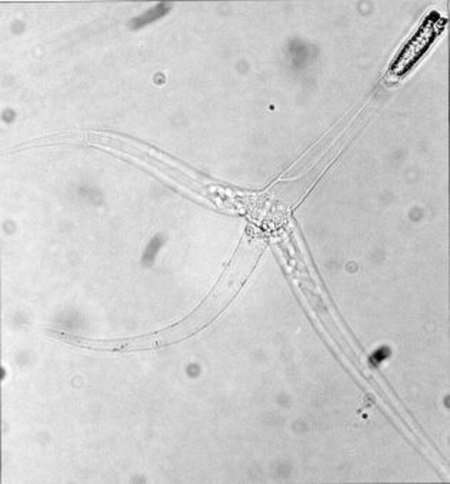
Myxozoa Myxobolus cerebralis TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumCnidariaSubfilumMyxozoa Grassé, 1970 Subkelas Myxosporea Malacosporea lbs Myxozoa (etimologi: bahasa Yunani: μύξα myxa lendir atau mukus[1] + vokal tematik o + ζῷον zoon hewan[2]) adalah kelas hewan yang bersifat akuatik dan parasit yang termasuk dalam filum Cnidaria. Lebih dari 1.300 spesies telah dideskripsikan[3] dan banyak yang memiliki siklus hidup dua inang, melibatkan ikan dan cacing annelida a...

State park in Bristol County, Massachusetts Fall River Heritage State ParkLocation in MassachusettsShow map of MassachusettsFall River Heritage State Park (the United States)Show map of the United StatesLocationFall River, Bristol, Massachusetts, United StatesCoordinates41°42′20″N 71°9′38″W / 41.70556°N 71.16056°W / 41.70556; -71.16056Area14 acres (5.7 ha)[1]Established1985Governing bodyMassachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreati...

Electronic test instrument that measures multiple signals from a circuit This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Logic analyzer – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Logic analyzer A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that ca...

Губерния Российской империиПолтавская губерния Герб 49°34′28″ с. ш. 34°34′07″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Российская империя Адм. центр Полтава История и география Дата образования 1802 год Дата упразднения 1 августа 1925 года Площадь 43 844,0 вёрст2 (49 894 км2) Население Население ...

1947 massacres of Sikhs and Hindus in Rawalpindi 1947 Rawalpindi massacresSkeletal remains of people burned to death at Thamali during the Rawalpindi massacresDateMarch 1947LocationRawalpindi Division, Punjab, British IndiaCaused byMuslim mobsGoalsMassacrereligious persecutionethnic cleansingsexual violenceforced conversionsMethodsRiotingpogromarsonrapeParties Muslim mobs Hindus and Sikhs Lead figures Muslim League National Guards CasualtiesDeath(s)2,000 – 7,000 The 1947 Rawalpindi massacre...

Rumah rakyat Okinawa yang umumnya bergenteng merah Arsitektur Okinawa atau Arsitektur Ryukyu dalah jenis arsitektur yang berkembang di wilayah Prefektur Okinawa, Jepang. Arsitektur Okinawa berkembang bersamaan dengan pengaruh-pengaruh arsitektur Tionghoa, Jepang dan Asia Tenggara. Sejarah Arsitektur purba Okinawa pertama kali muncul pada Periode Gundukan Kerang (2000 SM - 1000 SM) berupa rumah lubang (pit dwelling). Dua jenis rumah lubang telah ditemukan di Okinawa, jenis pertama berupa luban...

Distrik Kannur CannanoreDistrik Dari atas, searah jarum jam:Senja di Danau Vayalapra, Hidangan Thalassery, Benteng St. Angelo, Teluk Mappila, Pantai Muzhappilangad, dan Bandar Udara Internasional Kannur.Koordinat: 11°52′08″N 75°21′20″E / 11.8689°N 75.35546°E / 11.8689; 75.35546Negara IndiaNegara bagianKeralaDinamai berdasarkanDesa Kanathur;Kannan (Kresna) dan ur (tempat)Markas besarKannurPemerintahan • District CollectorS. Chandrasekar, IAS...

آيت ناصر وعلي تقسيم إداري البلد المغرب الجهة بني ملال خنيفرة الإقليم أزيلال الدائرة بزو الجماعة القروية تنانت المشيخة آيت ناس الجبل السكان التعداد السكاني 375 نسمة (إحصاء 2004) • عدد الأسر 59 معلومات أخرى التوقيت ت ع م±00:00 (توقيت قياسي)[1]، وت ع م+01:00 (توقيت صيفي)[1...
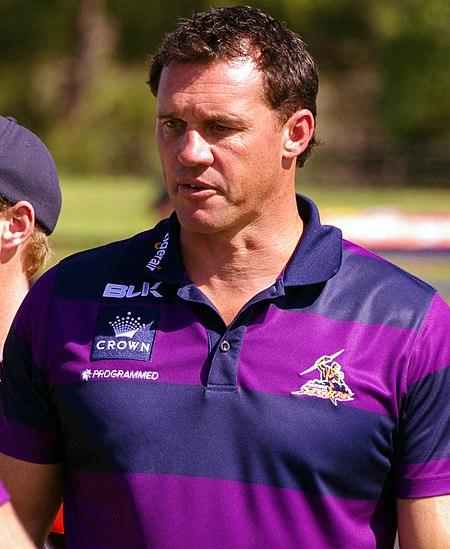

Pro RL coach and former Australia international rugby league footballer Matt AdamsonPersonal informationFull nameMatthew AdamsonBorn (1972-08-14) 14 August 1972 (age 51)Taree, New South Wales, AustraliaPlaying informationHeight195 cm (6 ft 5 in)Weight107 kg (16 st 12 lb)PositionFullback, Wing, Second-row Club Years Team Pld T G FG P 1991 Parramatta Eels 1 0 0 0 0 1993–01 Penrith Panthers 157 28 2 0 116 2002–04 Leeds Rhinos 72 9 0 0 36 2005 C...

Customary law concept within international law The ius gentium or jus gentium (Latin for law of nations) is a concept of international law within the ancient Roman legal system and Western law traditions based on or influenced by it. The ius gentium is not a body of statute law nor a legal code,[1] but rather customary law thought to be held in common by all gentes (peoples or nations) in reasoned compliance with standards of international conduct.[2] Following the Christianiz...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento oggetti non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Urna funeraria romana. I secolo, Museo archeologico regionale di Palermo. Urna cineraria dalla necropoli di Casinalbo (MO) Urna funeraria con le ceneri di Sigmund Freud (1856 – 1939). Un'urna funeraria (anche chiamata urna cineraria, dal latino cinis, -eris, ce...

Golfo de México. Golfo de Alaska. Golfo de Botnia. Un golfo es una abertura geográfica costera desde un océano o un mar hacia la masa terrestre, encerrada por cabos de tierra.[1] Típicamente presentan una abertura más estrecha que la de una bahía; aunque esto no es observable en todas las áreas geográficas así nombradas, se entiende que las bahías son de menor extensión.[2] El término golfo se usó tradicionalmente para grandes cuerpos de agua salada navegables y muy...

1951 Italian filmWithout a FlagDirected byLionello De FeliceWritten byFranco Brusati Jacopo Comin Lionello De Felice Luigi Freddi Giorgio Prosperi Nantas SalvalaggioProduced byLuigi FreddiStarringMassimo Serato Paolo Stoppa Walter RillaCinematographyMario CraveriEdited byMario SerandreiMusic byRenzo RosselliniProductioncompanyElfo FilmDistributed byENICRelease date October 1951 (1951-10) Running time121 minutesCountryItalyLanguageItalian Without a Flag (Italian: Senza bandiera) is a...