Phenylethanolamin-N-Methyltransferase (PNMTase) ist das Enzym, das Noradrenalin zu Adrenalin methyliert und daher unentbehrlich für die Biosynthese dieses Hormons. PNMTase wird in Wirbeltieren produziert. Im Menschen ist sie in den Nebennieren und im Nervensystem, aber auch im Herz zu finden.[1][2]
Die Produktion der PNMTase wird durch hormonelle und neurologische Stimuli wie beispielsweise Stress kontrolliert.[3][4]
Katalysierte Reaktion
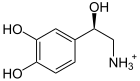 + S-Adenosyl-Met ⇔
+ S-Adenosyl-Met ⇔
⇔  + S-Adenosyl-Hom
+ S-Adenosyl-Hom
Noradrenalin wird (wie andere Phenylethanolamin-Derivate) zu Adrenalin umgewandelt. Als Methylgruppendonor fungiert S-Adenosylmethionin.
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ UniProt P11086
- ↑ Kuroko Y, Yamazaki T, Tokunaga N, et al: Cardiac epinephrine synthesis and ischemia-induced myocardial epinephrine release. In: Cardiovasc. Res. 74. Jahrgang, Nr. 3, Juni 2007, S. 438–44, doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.02.018, PMID 17448453.
- ↑ Wong DL: Epinephrine biosynthesis: hormonal and neural control during stress. In: Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 26. Jahrgang, Nr. 4–6, 2006, S. 891–900, doi:10.1007/s10571-006-9056-6, PMID 16645894.
- ↑ Evinger MJ, Mathew E, Cikos S, et al: Nicotine stimulates expression of the PNMT gene through a novel promoter sequence. In: J. Mol. Neurosci. 26. Jahrgang, Nr. 1, 2005, S. 39–55, doi:10.1385/JMN:26:1:039, PMID 15968085.