William J. Ripple
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Arwana perak Osteoglossum bicirrhosum Status konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN49830060 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasActinopteriOrdoOsteoglossiformesFamiliOsteoglossidaeGenusOsteoglossumSpesiesOsteoglossum bicirrhosum lbs Arwana silver (Osteoglossum bicirrhosum) adalah ikan air tawar bertulang yang berasal dari Amerika Selatan, yang termasuk famili Osteoglossidae. Biasanya, arwana silver dipelihara di akuarium, tapi ikan ini merupakan ikan predator dan membutuhkan tangki yang besar. ...

Provinsi Hitachi (常陸国code: ja is deprecated , hitachi no kuni) adalah nama provinsi lama Jepang dengan wilayah yang sekarang menjadi prefektur Ibaraki. Hitachi berbatasan dengan provinsi Iwashiro, Iwaki, Shimousa, dan provinsi Shimotsuke. Menurut hasil penggalian arkeologi, ibu kota dan kuil resmi berada di dekat kota Ishioka sekarang. Bangunan utama kuil berada agak jauh di sebelah timur di kota Kashima. Pada zaman Sengoku, wilayah Hitachi dibagi-bagi kepada beberapa orang daimyo. Ist...

Ar-RawabiLingkunganNegaraArab SaudiProvinsiProvinsi MakkahPemerintahan • Wali kotaHani Abu Ras[1] • Gubernur kotaMish'al Al-SaudKetinggian12 m (39 ft)Zona waktuUTC+3 (AST) • Musim panas (DST)ASTKode pos(5 kode digit dimulai dari 23; e.g. 23434)Kode area telepon+966-12Situs webwww.jeddah.gov.sa/english/index.php Ar-Rawabi adalah sebuah permukiman padat penduduk di kota Jeddah di Provinsi Makkah, tepatnya di sebelah barat Arab Saudi.[3&#...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Sliyeg, Indramayu – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTORSliyegKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa BaratKabupatenIndramayuPemerintahan • CamatENDANG ISMIATI, S.STP., M.Si.P...

جيوفاني تيديسكو معلومات شخصية الميلاد 13 مايو 1972 (العمر 51 سنة)باليرمو الطول 1.70 م (5 قدم 7 بوصة) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية إيطاليا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي بيركيركارا المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 1990–1993 ريجينا 74 (6) 1993–1995 فيورنتينا 47 (2) 1995–1997 فوجيا 63 (5) 1997–1...

American alternative metal band 10 Years10 Years performing at The Pearl Room in Mokena, IllinoisBackground informationOriginKnoxville, Tennessee, U.S.GenresAlternative metalprogressive metalpost-grungenu metalYears active1999–presentLabelsUniversalPalehorse/ILG (Warner)Mascot[1]MembersJesse HasekBrian VodinhLuke NareyMatt WantlandChad GrennorPast membersMike UnderdownAndy ParksLewis Big Lew CosbyRyan CollierRyan Tater JohnsonChad HuffKyle MayerWebsite10yearsmusic.com 10 Years ...

Provinsi Święty Krzyż provinsi di Polandia flag of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (en) Coat of arms of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship (en) Dinamakan berdasarkanŚwiętokrzyskie Mountains (en) Tempat <mapframe>: Judul Poland/Świętokrzyskie.map .map bukan merupakan halaman data peta yang sah Negara berdaulatPolandia NegaraPolandia Ibu kotaKielce Pembagian administratifKielce County (en) Końskie County (en) Opatów County (en) Ostrowiec County (en) Włoszczowa County (en) Busko Count...

Oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide RutileGeneralCategoryOxide mineralsFormula(repeating unit)TiO2IMA symbolRt[1]Strunz classification4.DB.05Crystal systemTetragonalCrystal classDitetragonal dipyramidal (4/mmm) H-M symbol: (4/m 2/m 2/m)Space groupP42/mnmUnit cella = 4.5937 Å, c = 2.9587 Å; Z = 2IdentificationColorBrown, reddish brown, blood red, red, brownish yellow, pale yellow, yellow, pale blue, violet, rarely grass-green, grayish black; black if high i...

Запрос «Пугачёва» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Алла Пугачёва На фестивале «Славянский базар в Витебске», 2016 год Основная информация Полное имя Алла Борисовна Пугачёва Дата рождения 15 апреля 1949(1949-04-15) (75 лет) Место рождения Москва, СССР[1]...

Evening daily tabloid newspaper published in Newport The South Wales ArgusSouth Wales Argus front page in July 2007TypeDaily newspaperFormatTabloidOwner(s)NewsquestPublisherNewsquest Media (Southern) Ltd.EditorGavin ThompsonFounded1892[1]Headquarters1st Floor, Chartist Tower, Upper Dock Street, Newport NP20 1DWCirculation3,623 (as of 2023)[2]Websitesouthwalesargus.co.uk The South Wales Argus is a daily tabloid newspaper published in Newport, South Wales. The Argus is distr...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) •&...
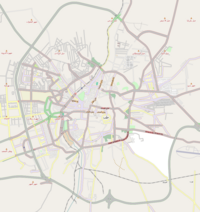
لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع حلب (توضيح). حلب حلب معالم مدينة حلب ساحة السبع بحرات •قلعة حلبمبنى القصر البلدي •مئذنة المسجد الأموي •ساعة باب الفرجمحطة بغداد (محطة القطار) •الحديقة العامةبيوت في حلب القديمة من القلعة حلبشعار حلب عاصمة الثقافة الإسلامية خريطة مد�...

Nature reserves in Australia Grey Box ReserveBoothtown Reserve, just south of the contiguous Grey Box ReserveTypeNature reserveLocationGreystanes, New South Wales, AustraliaCoordinates33°49′33″S 150°55′53″E / 33.825713°S 150.9313571°E / -33.825713; 150.9313571Area6.5 hectares (16 acres)Operated byCumberland City CouncilStatusClosed for public The Grey Box Reserve, or Greystanes Grey Box Reserve, is a small nature reserve situated in the suburb of Greys...

Street in Mumbai; metonym for Indian finance Dalal StreetDalal Street SignOtherWebsitewww.dsij.in Dalal Street (Hindi: dalāl path, Marathi: dalāl gallī), known as the Wall Street of Mumbai,[1] in turn described as the New York of India,[2] is the metonym for the financial markets of India, the Indian financial services industry of the country as a whole, or the actual financial district itself. It is located in the Financial District of Fort in Mumbai and is the address of ...

Capital and largest city of Kenya This article is about the city in Kenya. For the county which it resides, see Nairobi City County. For other uses, see Nairobi (disambiguation). Consolidated city-county in KenyaNairobiConsolidated city-countyClockwise from top: central business district; a giraffe walking in Nairobi National Park; Parliament of Kenya; Nairobi City Hall; and the Kenyatta International Convention Centre FlagCoat of armsNickname: The Green City in the SunNairobiLocation wi...

Yaroslavl ЯрославльKota[1]Church of Elijah the Prophet in Yaroslavl BenderaLambang kebesaranPeta lokasi Yaroslavl YaroslavlLokasi YaroslavlTampilkan peta RusiaYaroslavlYaroslavl (Yaroslavl Oblast)Tampilkan peta Yaroslavl OblastKoordinat: 57°37′0″N 39°51′0″E / 57.61667°N 39.85000°E / 57.61667; 39.85000Koordinat: 57°37′0″N 39°51′0″E / 57.61667°N 39.85000°E / 57.61667; 39.85000NegaraRusiaSubjek federalYarosl...

1968 United States Grand Prix Race detailsDate October 6, 1968Official name XI United States Grand PrixLocation Watkins Glen Grand Prix Race CourseWatkins Glen, New YorkCourse Permanent road courseCourse length 3.78 km (2.35 miles)Distance 108 laps, 408.2 km (253.8 miles)Weather Temperatures reaching a maximum of 20 °C (68 °F);wind speeds up to 14.82 km/h (9.21 mph)[1]Pole positionDriver Mario Andretti Lotus-FordTime 1:04.20Fastest lapDriver Jackie Stewart Matra...
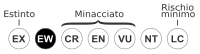
Questa voce sull'argomento solanales è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Come leggere il tassoboxStramonio arboreoStato di conservazioneEstinto in natura[1] Classificazione APG IVDominioEukaryota RegnoPlantae (clade)Angiosperme (clade)Mesangiosperme (clade)Eudicotiledoni (clade)Eudicotiledoni centrali (clade)Superasteridi (clade)Asteridi (clade)Euasteridi (clade)Lamiidi OrdineSolanales FamigliaSolanaceae SottofamigliaSolanoideae Tr...

Brazilian fencer (born 1996) Henrique MarquesMarques (front) at the 2016 Summer OlympicsPersonal informationFull nameHenrique Tavian Pereira MarquesBorn (1996-09-24) 24 September 1996 (age 27)São PauloSportSportFencing Medal record Men's fencing Representing Brazil Pan American Games 2019 Lima Team foil 2023 Santiago Team foil Pan American Championships 2016 Panama Team 2017 Montreal Team 2018 Habana Team 2019 Toronto Team 2022 Asuncion Team South American Games 2018 Cochabam...
