Western Australian Herbarium
|
Read other articles:

Coit AlbertsonAlbertson dari sebuah iklan untuk The Carter Case (1919)LahirEdward Coit Albertson(1880-10-14)14 Oktober 1880Reading, Pennsylvania, Amerika SerikatMeninggal13 Desember 1953(1953-12-13) (umur 73)Los Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatMakamInglewood Park CemeteryNama lainC. Albertson Cort Albertson E. Coit AlbertsonPekerjaanPemeran Edward Coit Albertson (14 Oktober 1880 – 13 Desember 1953) adalah seorang pemeran panggung dan film Amerika Serikat. Albert...

Saudi royal, government official, and poet (1925–1985) In this Arabic name, the surname is Al Saud. Abdul Muhsin bin Abdulaziz Al SaudGovernor of Medina ProvinceTenure1965 – 1985PredecessorMuhammad bin Abdulaziz Al SaudSuccessorAbdul Majeed bin AbdulazizMonarchKing FaisalKing KhalidKing FahdMinister of InteriorTenure1960 – 1961PredecessorMusaid bin Abdul RahmanSuccessorFaisal bin Turki IMonarchKing SaudBorn1925Riyadh, Sultanate of NejdDied11 May 1985 (aged 59–60)Riyadh, Saudi...

Untuk novel berjudul sama tahun 2014, lihat Aruna & Lidahnya (novel). Aruna & LidahnyaPoster resmiSutradaraEdwinProduser Muhammad Zaidy Meiske Taurisia Ditulis olehTitien WattimenaBerdasarkanAruna & Lidahnyaoleh Laksmi PamuntjakPemeran Dian Sastrowardoyo Nicholas Saputra Hannah Al Rasyid Oka Antara Penata musik Ken Jenie Mar Galo SinematograferAmalia T. S.PenyuntingW. IchwandiardonoPerusahaanproduksi Palari Films Go-Studio CJ Entertainment Phoenix Films Ideosource Entertainm...

Untuk edisi terakhir, lihat Miss Universe 2022. Untuk edisi akan datang, lihat Miss Universe 2023. Miss UniverseTanggal pendirian28 Juni 1952; 71 tahun lalu (1952-06-28)TipeKontes kecantikanKantor pusat New York, Amerika SerikatBidangKontes kecantikanBahasa resmi InggrisTokoh pentingAnne Jakrajutatip (Pemilik)Amy Emmerich (CEO) (Presiden)MotoBeautifully ConfidentOrganisasi indukJKN Global GroupSitus webwww.missuniverse.com Miss Universe adalah kontes kecantikan internasional yang diselen...
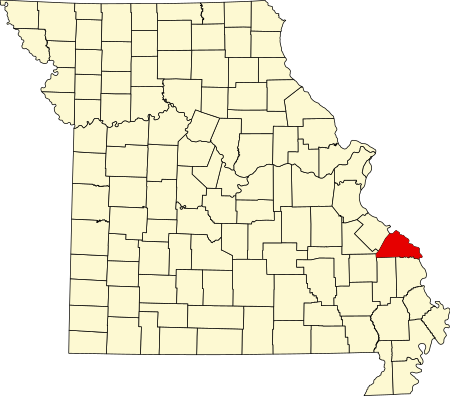
Church in Missouri, United StatesSt. Rose of Lima Mission, Roman Catholic Church (Silver Lake, Missouri)37°41′01″N 89°59′24″W / 37.68361°N 89.99000°W / 37.68361; -89.99000Location13370 Hwy 32, Silver Lake, MissouriCountryUnited StatesDenominationCatholic ChurchHistoryFormer name(s)Holy InnocentsFounded1850sConsecrated1879ArchitectureGroundbreaking1877Completed1879AdministrationArchdioceseArchdiocese of St. LouisDeanerySte. Genevieve St. Rose of Lima Mission...

Couvent franciscain de Wurtzbourg Façade de l'église conventuelle Présentation Culte Catholicisme Type Couvent Rattachement Frères mineurs conventuels Début de la construction 1221 Géographie Pays Allemagne Land Bavière Ville Wurtzbourg Coordonnées 49° 47′ 28″ nord, 9° 55′ 51″ est Géolocalisation sur la carte : Bavière Géolocalisation sur la carte : Allemagne modifier Le couvent franciscain de Wurtzbourg, dédié au Recouvrem...

Tokyu Corporation東急株式会社 Création 2 septembre 1922[1] Fondateurs Keita Gotō Forme juridique Kabushiki gaisha Action Bourse de Tokyo (9005)[2] Siège social 5-6 Nanpeidai-chō, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo 150-8511 Japon Activité Holding Filiales Izukyu Holdings (d)Tokyu Hotels (d)[3]Mauna Lani Bay Hotel & Bungalows (d)Réseau ferré de la Tōkyū (d)Tokyu Bus (d)[4]Tokyu Department Store (en)Tokyu Store (d)Tokyu Lifia (d)[5] Site web www.tokyu.co.jp Chiffre d'affaires 931,3 milli...

Piala Interkontinental 1995 Ajax Grêmio 0 0 Ajax menang 4-3 lewat adu penaltiTanggal28 November 1995StadionStadion Olimpiade Tokyo, TokyoPemain Terbaik Danny Blind (Ajax)WasitDavid Elleray (Inggris)Penonton47,129← 1994 1996 → Piala Interkontinental 1995 adalah sebuah pertandingan sepak bola pada 28 November 1995 antara Ajax Amsterdam dari Belanda, juara Liga Champions UEFA 1994-95 melawan Gremio dari Brasil, juara Copa Libertadores 1995. Laga dimainkan di Stadion Olimpiade Tokyo,...

Nikolaus Selnecker Nikolaus Selnecker (Hersbruck, 5 dicembre 1532 – Lipsia, 24 maggio 1592) è stato un teologo e organista tedesco, uno degli autori della Formula della Concordia con Jakob Andreae e Martin Chemnitz. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Note 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Nikolaus Selnecker nacque a Hersbruck in Baviera, Germania. Suo padre lo trasferì a Norimberga mentre era ancora un bambino. Da giovane fu un organista presso la cappella di Kaiserburg. ...

Standardized set of Chinese characters Traditional ChineseScript type Logographic Published Taiwan: (19791982)Hong Kong: (1986) DirectionLeft-to-right (modern)Top-to-bottom, columns right to left (historical)Official scriptTaiwanHong KongMacauLanguagesChinese languagesRelated scriptsParent systemsOracle bone scriptSmall seal scriptClerical scriptRegular scriptTraditional ChineseSister systems Simplified characters Kanji Hanja Chữ Nôm Zhuyin Khitan large script Khitan small script Sawndip I...

Italia Sport Ginnastica artistica Federazione FGI Confederazione UEG Colori azzurro Soprannome Azzurri Direttore Tecnico Giuseppe Cocciaro Giochi olimpici Partecipazioni 25 (esordio: 1906) Miglior risultato Oro Medaglie 25 Mondiali Partecipazioni ? Miglior risultato Oro Medaglie 52 Europei Partecipazioni ? Miglior risultato Oro Medaglie 40 (di cui 24 junior) La nazionale di ginnastica artistica maschile dell'Italia è la squadra maschile di ginnastica artistica che rappresenta l'Italia nelle...

Wife of Martin Van Buren Hannah Van BurenPersonal detailsBornHannah Hoes(1783-03-08)March 8, 1783Kinderhook, New York, United StatesDiedFebruary 5, 1819(1819-02-05) (aged 35)Albany, New York, United StatesSpouse Martin Van Buren (m. 1809)ChildrenAbraham Van Buren II, John Van Buren, Martin Van Buren Jr., Smith Thompson Van Buren Hannah Hoes Van Buren (born Hoes; March 8, 1783 – February 5, 1819) was the wife of the eighth President of the United States, M...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...

Japanese bimonthly magazine by Shueisha This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Cobalt magazine – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) CobaltThe February 2006 cover of Cobalt,featuring art by Reine Hibiki.EditorYayoi TamuraCatego...

Jim CrockettDonnées généralesNationalité AméricainNaissance 10 août 1944CharlotteDécès 3 mars 2021 (à 76 ans)Charlottemodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata James Allen Crockett Jr., né le 10 août 1944 et mort le 3 mars 2021, est promoteur américain de catch. De 1973 à 1989, il était propriétaire de la Jim Crockett Promotions (JCP), une entreprise de catch affiliée à la National Wrestling Alliance (NWA). De 1976 à 1987, Jim Crockett Promotions détente aussi l'...

Peterborough–Lincoln lineThe line heads away from Lincoln toward SleafordOverviewStatusOperationalOwnerNetwork RailLocaleEast MidlandsTerminiPeterboroughLincolnStations6ServiceTypeHeavy railSystemNational RailOperator(s)East Midlands RailwayLondon North Eastern RailwayRolling stockClass 156 Super SprinterClass 158 Express Sprinter Class 800 AzumaTechnicalLine length24 mi (39 km)Number of tracksTwoTrack gauge4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gaugeElectrif...

For other uses, see How Are You (disambiguation). 1986 single by The KinksHow Are YouSingle by The Kinksfrom the album Think Visual B-sideKilling Time (UK)Working at the Factory (US)Released22 December 1986RecordedJanuary 1986 and June–August 1986 at Konk Studios, LondonGenreRockLength4:27LabelMCA / Davray Music Ltd.Songwriter(s)Ray DaviesProducer(s)Ray DaviesThe Kinks singles chronology Rock 'n' Roll Cities (1986) How Are You (1986) Lost and Found (1987) How Are You is the seventh track on...

Clinic at Northwestern University Dental School. (1903) The Northwestern University Dental School closed in 2001, 110 years after opening in 1891.[1][2] Its first dean was Edgar Swain. According to the trustees, the mentioned financial stresses and reputation as reasons for the closure of the program. History The school was initially located on South State Street and then eventually moved into the new Medical School buildings on South Dearborn and East 24th in 1893. In 1895, N...

巴西工党Partido Trabalhista Brasileiro巴西工党标志领袖罗伯托·杰斐逊成立1981年11月3日解散2023年11月9日併入民主復興黨(英语:Democratic Renewal Party (Brazil))总部SAS, Qd. 1, Bloco M, Ed. Libertas, Loja 101Brasilia, Brazil党员(2021年11月)1,075,750意識形態現在:社会保守主义民族保守主义经济自由主义巴西民族主义右翼民粹主义瓦加斯主义军国主义反共主义歷史上:自由保守主義第三條道路工�...
