WOLB
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Palestina padaOlimpiadeBendera PalestinaKode IOCPLEKONKomite Olimpiade PalestinaSitus webwww.poc.ps (dalam bahasa Arab)Medali 0 0 0 Total 0 Penampilan Musim Panas1996200020042008201220162020 Palestina diwakili pada Komite Olimpiade Internasional oleh Komite Olimpiade Palestina. Komite Olimpiade Palestina telah mengirim tim pada setiap Olimpiade Musim Panas sejak 1996 dengan kode negara PLE.[1] Palestina diakui sebagai anggota Dewan Olahraga Asia sejak 1986, dan Komite O...

Mazmur 43 (Penomoran Septuaginta: Mazmur 42) adalah mazmur ke-2 dalam bagian ke-2 Kitab Mazmur di Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama dalam Alkitab Kristen.[1][2] Teks Naskah sumber utama: Masoretik, Septuaginta dan Naskah Laut Mati. Pasal ini terdiri dari 5 ayat. Dalam sejumlah naskah Ibrani, mazmur ini disambung di belakang Mazmur 42, nyanyian pengajaran Bani Korah.[3] Dalam versi Terjemahan Baru dari Lembaga Alkitab Indonesia, mazmur ini diberi judul Kerinduan kepada...

American politician (1862–1927) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Ambrose Everett Burnside StephensMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Ohio's 2nd districtIn officeMarch 4, 1919 – February 12, 1927Preceded by...

Squad 38Poster promosiGenrePembalasanKriminalDitulis olehkoSutradaraHan Dong-hwaPemeranMa Dong-seokSeo In-gukSooyoungNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. episode16ProduksiProduser eksekutifPark Ho-sikProduserHwang Joon-hyukDurasi65 menitRumah produksiStudio DragonDistributorOCNRilis asliJaringanOCNFormat gambar1080iFormat audio2 channels Dolby DigitalRilis17 Juni (2016-06-17) –06 Agustus 2016 (2016-08-06) Squad 38[2][3] (Hangul: 38사기동�...
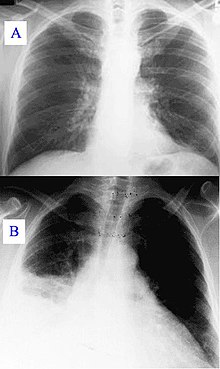
Pneumonia as seen on chest x-ray. A: Normal chest x-ray. B: Abnormal chest x-ray with shadowing from pneumonia in the right lung (left side of image). Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) or nosocomial pneumonia refers to any pneumonia contracted by a patient in a hospital at least 48–72 hours after being admitted. It is thus distinguished from community-acquired pneumonia. It is usually caused by a bacterial infection, rather than a virus.[1][2] Hospital acquired pneumonia is ...

American bishop and academic This article is about the 19th-century American bishop. For the Brisbane Bears player, see Matthew Simpson (footballer). For other people with similar names, see Matt Simpson. Matthew SimpsonBornJune 21, 1811 (1811-06-21)Cadiz, OhioDiedJune 18, 1884(1884-06-18) (aged 72)Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaNationalityAmericanOccupationPastorSignature Matthew Simpson (June 21, 1811 – June 18, 1884) was an American bishop of the Methodist Episcopal Church, elec...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Canal Nostalgia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Television channel Canal NostalgiaCountrySpainNetworkTVEProgrammingLanguage(s)SpanishPicture format576i (4:3 SDTV)OwnershipOwnerRTVESis...

Thomas HardyLahir2 Juni 1840Stinsford, Dorset, InggrisMeninggal11 Januari 1928PekerjaanNovelis, cerpenis, penyairKebangsaanInggrisAliran sastraNaturalisme Thomas Hardy, OM (2 Juni 1840 – 11 Januari 1928) adalah seorang novelis, cerpenis, dan penyair Inggris yang termasuk gerakan naturalisme. Sebagian besar karyanya, berlatar di daerah semi-imajiner bernama Wessex, diwarnai deskripsi puitis dan fatalisme. Bibliografi Prosa Hardy membagi novel-novel dan kumpulan cerita pend...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Lisa A. Riyanto – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Lisa A. RiyantoLahirElizabeth Dani Putri A Riyanto6 September 1975 (umur 48)Jakarta,IndonesiaPekerjaanpenyanyiSuami/istriRichardus...

Olimpiade Musim Dingin XXIIITuan rumahPyeongchang, Korea SelatanMotoPassion. Connected.(bahasa Korea: 하나된 열정., Hanadoen Yeoljeong)Jumlah negara92Jumlah atlet2,922 (1,680 laki-laki and 1,242 perempuan)Jumlah disiplin102 di 7 cabang olahraga (15 disiplin)Pembukaan9 Februari 2018Penutupan25 Februari 2018Dibuka olehPresiden Moon Jae-inKaldronKim Yun-aStadionStadion Olimpiade PyeongchangMusim Dingin ← Sochi 2014 Beijing 2022 → Musim Panas ← Rio 2016 Tokyo 2020 ͛...

Not to be confused with the 1982 animated film of the same name, see Mobile Suit Gundam#Films. This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 2003 video gameMobile Suit Gundam: Encounters in SpaceNTSC-U cover artDeveloper(s)BecPublisher(s)BandaiComposer(s)Tadayoshi MakinoYasuharu TakanashiTakanori Ar...

Questa voce sull'argomento giocatori di polo è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Andrés Gazzotti Nazionalità Argentina Polo Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Giochi olimpici 1 0 0 Vedi maggiori dettagli Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Andrés Gazzotti (Chacabuco, 30 maggio 1896 – 1984) è stato un giocatore di polo argentino. Ha vinto la medaglia d'oro nel polo ai Giochi olimpici di Berlino 1936. Altri pr...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

مرتضى الحسيني الشيرازي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1964 - 1384 هـكربلاء، العراق الإقامة كربلاء، العراق مواطنة العراق الأولاد مصطفى · محمد جواد · مهدي الحياة العملية التعلّم حوزة الرسول الأعظم، الكويت.حوزة قم، إيران المهنة رجل دين المواقع الموقع موقع «التقى»...

المقاومة الشعبية مشارك في الحرب الأهلية اليمنية (2015) الوضع في اليمن. تحت سيطرة جماعة الحوثي وأنصار صالح تحت سيطرة المقاومة الشعبية والجيش الموالي للرئيس هادي مناطق نفوذ وسيطرة القاعدة وأنصار الشريعة سنوات النشاط 2015-الآن قادة حمود سعيد المخلافي (تعز) حس�...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) نادي المصيف الرياضي السعودي الاسم الكامل نادي المصيف الرياضي السعودي تأسس عام 10 شوال 1404 هجري - 9 يوليو 1984 مي�...

High school in Texas, United States Benbrook Middle-High SchoolAddress201 OvercrestFort Worth, Texas 76126United StatesCoordinates32°39′52″N 97°29′09″W / 32.6645°N 97.4857°W / 32.6645; -97.4857InformationTypePublic secondary schoolSchool districtFort Worth Independent School DistrictPrincipalRichard PenlandTeaching staff96.78 (on an FTE basis)[1]Grades6-12[1]Enrollment1532 (2021-22)[1]Student to teacher ratio15.83[1]Websiteww...

Member Bank of Federal Reserve Federal Reserve Bank of AtlantaFederal Reserve SealHeadquartersHeadquarters1000 Peachtree St NE Atlanta, Georgia, USAEstablishedMay 18, 1914 (110 years ago) (1914-05-18)PresidentRaphael BosticCentral bank of Sixth District Alabama Florida GeorgiaParts of: Louisiana Mississippi Tennessee Websitewww.atlantafed.orgThe Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta is one of 12 regional banks that make up the Federal Rese...

Chief justice of the United States from 1801 to 1835 For other people named John Marshall, see John Marshall (disambiguation). John MarshallPortrait by Henry Inman, c. 18324th Chief Justice of the United StatesIn officeFebruary 4, 1801 – July 6, 1835[1]Nominated byJohn AdamsPreceded byOliver EllsworthSucceeded byRoger B. Taney4th United States Secretary of StateIn officeJune 13, 1800 – March 4, 1801PresidentJohn AdamsPreceded byTimothy PickeringSucceeded byJames ...

Hermandad del Descendimiento (Córdoba) LocalizaciónPaís EspañaLocalidad CórdobaSede canónica Parroquia de San José y Espíritu SantoDatos generalesFundación 1937Titulares Santísimo Cristo del Descendimiento Nuestra Señora del Buen Fin Nuestra Señora de los Dolores y el Rayo María Santísima del RefugioPasos 2Hermano Mayor Manuel Aguilera VillanuevaTúnica Rojo y BlancoProcesionesDía y hora Viernes SantoDuración 6 horas[editar datos en Wikidata] La Primitiva ...
