Vakhsh (river)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

هذه المقالة عن معالم المسجد الأقصى. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أقصى (توضيح). معالم المسجد الأقصى هي المصليات والمآذن والقباب والأبواب والمدارس والأروقة والبوائك والمنابر والمصاطب والمحاريب والأسبلة ومعالم أخرى، ويتضمن المسجد الأقصى من المصليات المسقوفة سبعة مساجد هي: الجا�...

Current delegationMarco Rubio (R)Rick Scott (R) Florida was admitted to the Union on March 3, 1845, and elects its U.S. senators to class 1 and class 3. Florida's U.S. Senate seats were declared vacant in March 1861, due to its secession from the Union. They were filled again in July 1868. The state is currently represented by Republicans Marco Rubio (serving since 2011) and Rick Scott (serving since 2019). Duncan U. Fletcher was Florida's longest-serving senator (1909–1936). Florida is on...

Ka'bah di Masjidil Haram, situs paling suci dalam Islam.[1] Situs suci dalam Islam sebagian besar terletak di Jazirah Arab dan Syam.[2] Sementara urutan kesucian sebagian besar tempat biasanya bervariasi tergantung pada cabang Islam, namun ada kesepakatan semua cabang arus utama agama yang menegaskan tiga kota memiliki tingkat kesucian tertinggi, yakni Masjidil Haram di Makkah (termasuk Ka'bah), Masjid Nabawi di Madinah, dan Masjid al-Aqsa di Yerusalem, semuanya dianggap oleh ...

SukorejoKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan SukorejoNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKabupatenPonorogoPemerintahan • Camat-Populasi • Total52.340 jiwaKode Kemendagri35.02.15 Kode BPS3502160 Luas59,58 km²[1]Desa/kelurahan18 Sukorejo adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Ponorogo, Provinsi Jawa Timur, Indonesia. Kecamatan ini berjarak sekitar 17 kilometer[2] dari ibu kota Kabupaten Ponorogo ke arah barat laut. Pusat pemerintahannya berada di desa Sukorej...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (June 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The topic of this article may not meet Wikip...

1941 battle of the Second Sino-Japanese War You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (October 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Japanese article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting...

This article is about the town in Shizuoka, Japan. There are towns, all now dissolved, with the same name (吉田町) in four other prefectures in Japan, see Yoshida, Ehime, Yoshida, Kagoshima, Yoshida, Niigata, Yoshida, Saitama, Yoshida, Hiroshima. Town in JapanYoshida 吉田町TownYoshida Town hall FlagSealLocation of Yoshida in Shizuoka PrefectureYoshida Coordinates: 34°46′N 138°15′E / 34.767°N 138.250°E / 34.767; 138.250CountryJapanRegionChūbuTōkaiPr...
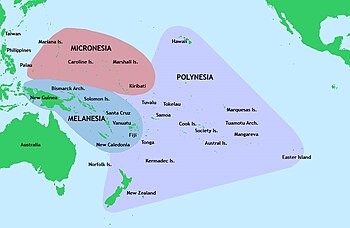
Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang pribumi Kepulauan Pasifik. Untuk pribumi lainnya, lihat Pribumi (disambiguasi). Tiga subkawasan besar di Oseania. Penduduk Pasifik (bahasa Inggris: Pacific Islander) adalah istilah yang digunakan untuk menyebut penduduk Kepulauan Pasifik. Kawasan Lihat pula: Kepulauan Pasifik Menurut Encyclopædia Britannica, Penduduk Pasifik menetap di tiga kawasan yang terbagi menjadi: Polinesia Pulau yang tersebar di segitiga kawasan timur-tengah Samudra Pasifik. Segitiga...

Pour un article plus général, voir Championnats d'Europe d'athlétisme. 1 500 mètres aux championnats d'Europe d'athlétisme Le Britannique Steve Cram remporte le titre européen du 1 500 m en 1982 et 1986.Généralités Sport Athlétisme1 500 mètres Organisateur(s) AEA Éditions 25e en 2022 Catégorie Championnats d'Europe Palmarès Tenant du titre Jakob Ingebrigtsen (2022)Laura Muir (2022) Plus titré(s) Steve Cram, Mehdi Baala et Jakob Ingebrigtsen (2) Nuria Fernández et La...

Lego theme Lego The Powerpuff GirlsSubjectThe Powerpuff GirlsLicensed fromCartoon NetworkAvailability2018–2019Total sets2[1]CharactersBlossom, Bubbles, Buttercup, Donny the Unicorn, Mojo Jojo, Octi and Princess MorbucksOfficial website Lego The Powerpuff Girls (stylized as LEGO The Powerpuff Girls) was a Lego theme based on the Cartoon Network television series of the same name created by Craig McCracken. It was licensed from Cartoon Network.[2] Before the launch o...

聖湖鎮(葡萄牙語:Lagoa Santa),是巴西的城鎮,位於該國東南部,由米納斯吉拉斯州負責管轄,始建於1738年12月17日,面積232平方公里,海拔高度759米,2010年人口52,526,人口密度每平方公里226.41人。 參考資料 Riedel, Agusto. Brandt's Tomb in Lagoa Santa. World Digital Library. [2013-12-26]. (原始内容存档于2016-03-12). 这是一篇與巴西相關的地理小作品。您可以通过编辑或修订扩�...

Division of NBCUniversal NBC Sports GroupCompany typeDivisionIndustryTelevisionFounded2011; 13 years ago (2011)HeadquartersStamford, Connecticut, United StatesKey peoplePete Bevacqua (chairman)ParentNBCUniversal Media GroupDivisionsGolf ChannelTelemundo DeportesNBC SportsNBC Sports DigitalNBC Sports FilmsNBC Sports RadioNBC Sports Regional NetworksSubsidiariesNBC Olympics LLCNBC Sports Ventures LLCWebsitenbcsportsgrouppressbox.com NBC Sports Group is a division of NBCUnivers...

Julián Castro 16º Segretario della Casa e dello Sviluppo UrbanoDurata mandato28 luglio 2014 –20 gennaio 2017 PresidenteBarack Obama PredecessoreShaun Donovan SuccessoreBen Carson Sindaco di San AntonioDurata mandato1º giugno 2009 –22 luglio 2014 PredecessorePhil Hardberger SuccessoreIvy Taylor Dati generaliPartito politicoDemocratico UniversitàUniversità di StanfordUniversità di Harvard Firma Julián Castro (San Antonio, 16 settembre 1974) è un poli...

鉄腕アトム > 鉄腕アトム (アニメ第1作) 1980–1981年作品「鉄腕アトム (アニメ第2作)」とは異なります。 大泉アニメゲートに設置されている「ねりまアニメ年表」の一コマ。 鉄腕アトム (アニメ第1作)(てつわんアトム)では手塚治虫原作の漫画『鉄腕アトム』のアニメ第1作目を解説する。 フジテレビ系列にて、1963年1月1日から1966年12月31日まで放送。全193話。一部...

2-dimensional art style without gradations in shade or hue For the related printmaking techniques, see Engraving, Etching, Woodcut, and Lithography. Example of line art (published in The Survey, October 1917–March 1918). Line art or line drawing is any image that consists of distinct straight lines or curved lines placed against a background (usually plain). Two-dimensional or three-dimensional objects are often represented through shade (darkness) or hue (color). Line art can use lines of ...

Culinary traditions of Sweden Swedish meatballs with cream sauce, mashed potatoes, broccoli, and lingonberry jam Part of a series on theCulture of Sweden History Prehistory 800–1521 Kalmar Union 1523–1611 Rise to become Great Power Swedish Empire Great Northern War Age of Liberty Coup of 1756 December Crisis (1768) Revolution of 1772 Gustavian era Coup of 1809 Sweden–Norway union Famine of 1867–1869 Modernization Industrialization World War I World War II timeline 1945–1967 1967–1...

LeonardoLogo Sede centrale a Roma, piazza Monte Grappa, 4 Stato Italia Forma societariaSocietà per azioni Borse valoriBorsa Italiana: LDO ISINIT0003856405 Fondazione18 marzo 1948 a Roma Sede principaleRoma GruppoDipartimento del Tesoro (Azionista di controllo) Persone chiave Stefano Pontecorvo, Presidente Roberto Cingolani, Amministratore Delegato e Direttore Generale Lorenzo Mariani, Condirettore Generale SettoreDifesa, aerospazio e sicurezza Prodotti Elettronica, difesa e sistemi ...

India-Nauru bilateral relations in the Commonwealth This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Bilateral relationsIndia-Nauru relation...

Dutch-born Australian geneticist Peter VisscherFRS FAAVisscher in 2018BornPeter Martin VisscherNetherlandsNationalityAustralianAlma materUniversity of EdinburghKnown forQuantitative geneticsScientific careerFieldsGenetics[1]InstitutionsQueensland Institute of Medical ResearchUniversity of QueenslandThesisEstimation of genetic parameters in dairy cattle using an animal model and implications for genetic improvement (1991)Doctoral advisorBill Hill[2] Websitere...

Territorial settlement following the Second Balkan War For other treaties signed in Bucharest, see Treaty of Bucharest (disambiguation). This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Treaty of Bucharest 1913 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2011) Treaty of BucharestBorde...





