USS Mount Vernon (AP-22)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Peta infrastruktur dan tata guna lahan di Komune Lardy. = Kawasan perkotaan = Lahan subur = Padang rumput = Lahan pertanaman campuran = Hutan = Vegetasi perdu = Lahan basah = Anak sungaiLardyNegaraPrancisArondisemenÉtampesKantonÉtréchyAntarkomuneCC de l'ArpajonnaisKode INSEE/pos91330 / Lardy merupakan sebuah kota dan komune di département Essonne, di region Île-de-France di Prancis. Demografi Menurut sensus 1999, penduduknya berjumlah...

Menara lonceng di Keabasan Luxeuil Keabasan Luxeuil (pengucapan bahasa Prancis: [lyksœj]), Abbaye Saint-Pierre et Saint-Paul, adalah salah satu biara tertua di Bourgogne, terletak di tempat yang sekarang menjadi departemen Haute-Saône di Franche-Comté, Prancis. Didirikan pada tahun 590 oleh Santo Kolumbanus[1] bersama dengan Santo Deikolus, di situs Luxovium kuno, sebuah kota penting di zaman Romawi dan benar-benar hancur oleh invasi barbar. Saracen menjarah keabasan pada tahu...

Current delegationBrian Schatz (D)Mazie Hirono (D) Hawaii was admitted to the Union on August 21, 1959, and elects U.S. senators to classes 1 and 3. Seven people including only one Republican have served as a U.S. senator from Hawaii. The state's current U.S. senators are Democrats Brian Schatz and Mazie Hirono. Hawaii's class 1 seat is the only one in the United States that has always been held by an ethnic minority.[citation needed] Its class 3 seat is the only one in the United St...

American mayor and silversmith Thomas Aspinwall DavisMayor of BostonIn officeFebruary 27, 1845[1][2] – November 22, 1845[2]Preceded byMartin BrimmerSucceeded byJosiah Quincy Jr. Personal detailsBornThomas Aspinwall DavisDecember 11, 1798Brookline, Massachusetts, United StatesDiedNovember 22, 1845(1845-11-22) (aged 46)Political partyNative American PartyOccupationBusinessman, politician Thomas Aspinwall Davis (December 11, 1798 – November 22, 1845) was...

University housing The Augustinianum College (Italian: Collegio Augustinianum) is a college founded in Milan, Italy in 1933 by Agostino Gemelli, in order to offer the opportunity to study at Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore to the most capable among the resident students, providing a bed during their university studies.[1] Notable alumni Giuseppe Dossetti Amintore Fanfani[2] Giovanni Maria Flick Luigi Gui Mario Mauro Ciriaco De Mita[3] Paolo Prodi Romano Prodi[...

Jodoh RomantisGenre Drama Roman PembuatSinemArtSkenarioAdra P DanielSutradaraIndrayanto KurniawanPemeran Nabila Syakieb Marcel Chandrawinata Syarmi Amanda Agus Kuncoro Ana Pinem Eeng Saptahadi Lagu pembukaEngkau oleh NidjiLagu penutupEngkau oleh NidjiNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode10ProduksiProduserLeo SutantoDurasi60 MenitRumah produksiSinemArtDistributorSurya Citra MediaRilis asliJaringanSCTVRilis05 Februari (2007-02-05) –09 April 2007&#...
French physician and neurologist (1840–1919) Hippolyte Bernheim. Hypnosis Applications Animal magnetism Hypnotherapy Stage hypnosis Self-hypnosis Hypnosurgery Origins/History History of hypnosis Royal Commission on Animal Magnetism Key figures Theodore Xenophon Barber Deirdre Barrett Hippolyte Bernheim Gil Boyne James Braid John Milne Bramwell William Joseph Bryan Jean-Martin Charcot Émile Coué Dave Elman Milton H. Erickson James Esdaile John Elliotson Sigmund Freud Erika Fromm Ernest Hil...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori peruviani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Jhoel Herrera Nazionalità Perù Altezza 177 cm Peso 72 kg Calcio Ruolo Difensore Squadra Juan Aurich Carriera Squadre di club1 2001 Sporting Cristal4 (0)2002-2003 Cor. Bolognesi FC39 (2)2004-2005 Unión Huaral43 (1)2005-2006 Universitario39 (2)2007 Alianza Lima11 (0)2007...

Ponzone commune di Italia Tempat Negara berdaulatItaliaRegion di ItaliaPiedmontProvinsi di ItaliaProvinsi Alessandria NegaraItalia Ibu kotaPonzone PendudukTotal1.007 (2023 )GeografiLuas wilayah69,03 km² [convert: unit tak dikenal]Ketinggian629 m Berbatasan denganCartosio Cavatore Grognardo Molare Morbello Pareto Sassello Tiglieto Urbe Cassinelle Malvicino Montechiaro d'Acqui SejarahHari liburpatronal festival Informasi tambahanKode pos15010 Zona waktuUTC+1 UTC+2 Kode telepon0144 I...

County-level city in Shandong, People's Republic of ChinaQufu 曲阜市KufowCounty-level cityQufu's south gateLocation in JiningQufuLocation in ShandongShow map of ShandongQufuQufu (China)Show map of ChinaCoordinates (Qufu municipal government): 35°34′55″N 116°59′10″E / 35.5819°N 116.9862°E / 35.5819; 116.9862CountryPeople's Republic of ChinaProvinceShandongPrefecture-level cityJiningArea • County-level city815 km2 (315 sq mi)...

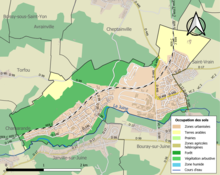
Peta infrastruktur dan tata guna lahan di Komune La Baffe. = Kawasan perkotaan = Lahan subur = Padang rumput = Lahan pertanaman campuran = Hutan = Vegetasi perdu = Lahan basah = Anak sungaiLa Baffe merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Vosges yang terletak pada sebelah timur laut Prancis. Lihat pula Komune di departemen Vosges Referensi INSEE lbsKomune di departemen Vosges Les Ableuvenettes Ahéville Aingeville Ainvelle Allarmont Ambacourt Ameuv...

سيريوس سام 4 (بالإنجليزية: Serious Sam 4) ملف:Serious Sam 4.jpg المطور كروتيم الناشر ديفولفر ديجيتال الموزع ستيم، وجوجل ستاديا، وبلاي ستيشن ستور، ومتجر مايكروسوفت[1]، وغوغ دوت كوم المصمم Davor HunskiDavor Tomičić المخرج Davor Hunski الكاتب Jonas KyratzesVerena Kyratzes المنتج Davor Hunski الموسيق...

Coal-fired power plant in Jefferson County, Alabama James H. Miller Jr. Electric Generating PlantCountryUnited StatesLocationWest Jefferson, AlabamaCoordinates33°37′55″N 87°03′38″W / 33.63194°N 87.06056°W / 33.63194; -87.06056 (James H. Miller Jr. Electric Generating Plant)StatusOperationalCommission dateUnit 1 - 1978Unit 2 - 1985 Unit 3 - 1989Unit 4 - 1991Owner(s)Alabama Power CompanyThermal power station Primary fuelCoalPower&#...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang the 2009 film. Untuk the 2000 Showtime film, lihat Seventeen Again. 17 AgainPoster bioskopSutradaraBurr SteersProduserAdam ShankmanJennifer GibgotDitulis olehJason FilardiKeenan DonahuePemeranMatthew Perry Zac EfronLeslie MannThomas LennonSterling KnightMichelle TrachtenbergPenata musikRolfe KentSinematograferTim SuhrstedtPenyuntingPadraic McKinleyPerusahaanproduksiOffspring EntertainmentDistributorNew Line CinemaTanggal rilis Australia9 April 200...

This page is an archive of past discussions. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. Article on Brain stem death Could a neurologically trained editor, preferably from the UK, take a look at this article and its discussion page, please? It is, at present, just a polemic by an author pushing a very specific minority viewpoint and needs either a complete rewrite or a merge into the main brain-death...

Ministro de Economía y Finanzas del Perú Gran sello de la República del Perú José Arista Arbildo Desde el 13 de febrero de 2024Ámbito PerúTitular de Ministerio de Economía y Finanzas del PerúSede LimaDesignado por Presidente del Perú (en coordinación con la PCM)Creación 1 de marzo de 1969Primer titular Francisco Morales BermúdezSitio web www.mindef.gob.pe[editar datos en Wikidata] El ministro de Economía y Finanzas del Perú es el encargado del Ministerio de Econo...

中華民國 中華民國政府与政治系列条目 政府(沿革) 憲法 中華民國憲法(憲政史) 中華民國憲法增修條文 正副總統直接選舉與罷免 國會全面選舉與罷免 國民大會(已停止運作) 一府五院 總統 總統:賴清德 副總統:蕭美琴 總統府 秘書長:潘孟安 資政 國策顧問 戰略顧問 國史館 中央研究院 國家安全會議 主席:賴清德 副主席:蕭美琴 秘書長:吳釗燮 國家安全局 行政...

Diese Liste umfasst die Schweizer Botschafter im Vereinigten Königreich. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Missionschefs 2 Siehe auch 3 Literatur 4 Weblinks 5 Einzelnachweise Missionschefs Schweizer Botschaft, 16-18 Montagu Place im Londoner Stadtteil Marylebone Schweiz Schweizer Botschafter in London[1] Name Amtsbeginn Amtsende Charles-Daniel Bourcart (1860–1940) – Generalkonsul 20. Februar 1891 7. Februar 1896 Charles-Daniel Bourcart (1860–1940) – Ministerresident 7. Februar 1896 21. De...

The Boat Race 1995 Jadwal 1 April 1995 Balapan putra Juara Cambridge Selisih 4 lengths Catatan waktu 18 menit 4 detik Total kemenangan Cambridge-Oxford 72 - 68 Wasit Balapan lainnya Juara putri Cambridge Juara cadangan Goldie Balapan sebelumnya 1994 Balapan selanjutnya 1996 The Boat Race ke-141 diselenggarakan pada 1 April 1995. Ajang olahraga tahunan ini melombakan cabang olahraga dayung berdampingan antara dua tim dari Universitas Oxford dan Universitas Cambridge di jalur Sungai Thames. Ca...

Main article: 1988 United States presidential election 1988 United States presidential election in North Carolina ← 1984 November 8, 1988 1992 → Nominee George H. W. Bush Michael Dukakis Party Republican Democratic Home state Texas Massachusetts Running mate Dan Quayle Lloyd Bentsen Electoral vote 13 0 Popular vote 1,237,258 890,167 Percentage 57.97% 41.71% County Results Congressional District Results Bush 50–60% 60�...

