Trinidad Orisha
|
Read other articles:

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 2005 Sun Belt Conference men's basketball tournament – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) College basketball tournament 2005 Sun Belt Conference men's basketball tournamentClassificationDivision ISeason2004–05Teams...
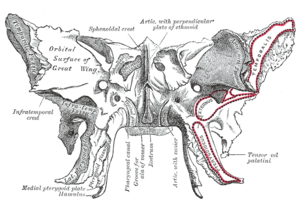
Large part of the skull front behind the eye socketThis article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Greater wing of sphenoid bone – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)Greater wing of sphenoid boneFigure 1: Sphenoid bone, upper surface...

Manuel Almunia Almunia con la maglia del West Ham nel 2011 Nazionalità Spagna Altezza 193 cm Peso 86 kg Calcio Ruolo Portiere Termine carriera 27 agosto 2014 Carriera Squadre di club1 1997-1999 Osasuna B44 (-?)1999-2000→ Cartagonova3 (-6)2000-2001 Sabadell25 (-21)[1]2001 Celta Vigo0 (0)2001-2002→ Eibar35 (-19)2002-2003→ Recreativo Huelva2 (-4)2003-2004→ Albacete24 (-27)2004-2011 Arsenal109 (-99)2011→ West Ham Utd4 (-3...

Stéphane Gatignon Stéphane Gatignon en avril 2013. Fonctions Maire de Sevran 18 mars 2001 – 15 mai 2018(17 ans, 1 mois et 27 jours) Élection 18 mars 2001 Réélection 16 mars 2008 30 mars 2014 Prédécesseur Jacques Oudot (RPR) Successeur Stéphane Blanchet Conseiller régional d'Île-de-France 21 mars 2010 – 18 décembre 2015(5 ans, 8 mois et 27 jours) Élection 21 mars 2010 Biographie Date de naissance 25 août 1969 (54 ans) Lieu de naissance Argen...

Election 1857 Vermont gubernatorial election ← 1856 September 1, 1857 (1857-09-01) 1858 → Nominee Ryland Fletcher Henry Keyes Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 26,719 12,869 Percentage 67.0% 32.3% Governor before election Ryland Fletcher Republican Elected Governor Ryland Fletcher Republican Elections in Vermont Federal government Presidential elections 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 ...

Brazilian footballer (born 2000) In this Portuguese name, the first or maternal family name is Lemos and the second or paternal family name is Martins. Tetê Tetê with Shakhtar Donetsk in 2021Personal informationFull name Mateus Cardoso Lemos Martins[1]Date of birth (2000-02-15) 15 February 2000 (age 24)[1]Place of birth Alvorada, BrazilHeight 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in)Position(s) Attacking midfielder, wingerTeam informationCurrent team GalatasarayNumber 20Yo...

这是马来族人名,“莫哈末·雅辛”是父名,不是姓氏,提及此人时应以其自身的名“慕尤丁”为主。 尊敬的丹斯里拿督哈芝慕尤丁·莫哈末雅辛馬來語:Muhyiddin Mohd YassinMahiaddin bin Md Yasin(注册名)国会议员PSM; SPMJ; SHMS; SPSA; SPMP; SUNS; SPDK; DP; PNBS; SMJ; BSI (I); PIS (I)2021年的慕尤丁 第8任马来西亚首相任期2020年3月1日—2021年8月20日君主國家元首蘇丹阿都拉副职依斯迈沙比里前任马...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Chichester. Salah satu sudut kota Chichester Chichester ialah sebuah kota yang didirikan pada masa Kekaisaran Romawi di West Sussex, selatan Inggris. Jalanan kota ini memiliki tata silang, diwarisi dari masa Romawi. Dari monumen 'Cross'ke utara, timur, selatan, dan barat. Chichester memiliki sebuah katedral, dipersembahkan untuk Santo Ricardus dari Chichester. Atap Chichester Cathedral' dibakar dan dibangun kembali pada abad-abad terakhir. Chichester terkenal akan C...

Wilmington merupakan nama kota di Amerika Serikat. Kota ini terletak di Kabupaten New Hanover, negara bagian North Carolina, Amerika Serikat. Pada tahun 2006, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebanyak 100.000 jiwa (kota), 300.000 jiwa (metro) dan memiliki kepadatan penduduk 2.069,3 jiwa/km². Wali kotanya ialah Bill Saffo. Kota kembar Dandong, Tiongkok Doncaster, Britania Raya Bridgetown, Barbados Pranala luar Situs resmi Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Amerika Serikat ini adalah sebua...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) سوبك حتب الثالثسوبك حتب الثالث يعبد ساتت. الثقب الأوسط عندما كان يستخدم كحجر للطحن بعد فترة طويلة من النح...

Trade union federation in Hong Kong Not to be confused with the Hong Kong Confederation of Trade Unions. Hong Kong Federation of Trade Unions 香港工會聯合會AbbreviationFTUPresidentNg Chau-peiChairmanKingsley WongSecretary-GeneralMa Kwong-yuFounded17 April 1948; 76 years ago (1948-04-17)Headquarters12 Ma Hang ChungRoad, Tokwawan,Kowloon, Hong KongMembership (2020) 420,000+Ideology Socialism (HK) Socialist patriotism Conservatism (HK) Political positionLeft-wingNat...
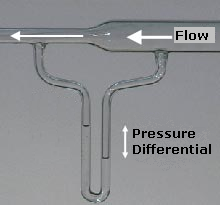
此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2020年4月24日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:伯努利定律 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 氣體流入文丘里計。減少流體壓力而增加動能,由圖中兩管水的高度差可以看...
Chronologies Données clés 900 901 902 903 904905 906 907 908 909Décennies :870 880 890 900 910 920 930Siècles :VIIIe IXe Xe XIe XIIeMillénaires :-IIe -Ier Ier IIe IIIe Calendriers Romain Chinois Grégorien Julien Hébraïque Hindou Hégirien Persan Républicain modifier Les années 900 couvrent la période de 900 à 909. Événements Le monde vers 900 Vers 900 : établissement des Toltèques au Mexique. Leur arrivée marque le déb...

1990 single by Status QuoThe Anniversary WaltzCover artwork for Part One. The artwork for Part Two is coloured red.Single by Status Quofrom the album Rocking All Over the Years Released 17 September 1990 (1990-09-17) (Part One) 3 December 1990 (1990-12-03) (Part Two) Length10:38Label Vertigo Phonogram Songwriter(s)VariousProducer(s)Pip WilliamsStatus Quo singles chronology Little Dreamer (1989) The Anniversary Waltz (1990) Can't Give You More (1991) The Anniversa...

Promozione 1953-1954 Competizione Promozione Sport Calcio Edizione 2ª Organizzatore FIGCLeghe Regionali Luogo Italia Cronologia della competizione 1952-1953 1954-1955 Manuale Nella stagione 1953-1954, la Promozione era il quinto livello del calcio italiano, il primo livello regionale. Suddiviso in tanti gironi regionali, è l'antesignano dell'attuale Eccellenza. Per ottenere la promozione in IV Serie non era sufficiente vincere il campionato. La Federazione, nel valutare i titoli spor...

Terza Divisione 1934-1935 Competizione Terza Divisione Sport Calcio Edizione 13ª Organizzatore FIGC e Direttori di Zona Luogo Italia Formula Gironi A/R e finali regionali Cronologia della competizione 1933-1934 1935-1936 Manuale La Terza Divisione 1934-1935 è stata il torneo regionale inferiore di quell’edizione del campionato italiano di calcio, il più basso in assoluto. La gestione di questo campionato era affidata ai Direttori di Zona, che li organizzavano autonomamente, con la...

La civilisation romaine a laissé de nombreuses traces monumentales et archéologiques dans les régions autrefois soumises à Rome. La solidité des constructions a permis à un certain nombre d'entre elles de résister aux assauts du temps et des hommes, parfois grâce à des détournements fonctionnels qui ont évité qu'elles ne soient considérées que comme des carrières de pierre faciles à exploiter - ce qui fut assez souvent le cas. Cette liste de monuments romains recense les monum...

この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2022年5月) 独立記事作成の目安を満たしていないおそれがあります。(2022年5月)出典検索?: GxG – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp ...

King of Bavaria from 1848 and 1864 For the earlier elector, see Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Maximilian II of Bavaria – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Maximilian IIMaximilian...

German-French canon regular and theologian Hugh of Saint VictorHugh of Saint VictorBornc. 1096Probably the Duchy of SaxonyDied11 February 1141Abbey of Saint-Victor, ParisEraMedieval philosophyRegionWestern philosophySchoolScholasticism Hugh of Saint Victor (c. 1096 – 11 February 1141) was a Saxon canon regular and a leading theologian and writer on mystical theology. Life As with many medieval figures, little is known about Hugh's early life. He was probably born in the 1090s. His hom...
