St. Marks Light
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. This is a list of people who identify as pansexual and who are the subjects of articles on the English Wikipedia.Figure skater, Amber Glenn Rapper, Angel Haze Former gymnast, Danell Leyva Comedian, painter and television presenter, Joe Lycett Singer-songwriter, Declan McKenna Video game writer and former journalist, Alanah Pearce Name Birt...

Drăgăneşti-OltKotaNegara RumaniaProvinsiOltStatusKotaPemerintahan • Wali kotaSorin Ionel Ghiţă (Partidul National Liberal)Luas • Total78,88 km2 (3,046 sq mi)Populasi (2002) • Total12.195Zona waktuUTC+2 (EET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+3 (EEST) Drăgăneşti-Olt adalah kota yang terletak di provinsi Olt, Rumania selatan, di tepi sungai Olt pada ketinggian sekitar 100 meter (330 ft). Pada tahun 2002, kota ini memilik...

Kanvas. Kanvas adalah media lukis yang memiliki pori-pori yang telah ditutup cat dasar berwarna putih. Media ini lebih sering digunakan untuk melukis dengan cat minyak karena cat minyak butuh ketebalan dalam pewarnaan dan kadang butuh metode palet yang membutuhkan terknik kontruksi pada bidang lukisnya. Palet pada umumnya sudah memiliki kerangka yang berbentuk persegi dan ada pula yang masih berbentuk gulungan tanpa kerangka. Referensi Mayer Ralph: The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techn...

Kunming昆明Stasiun Kereta KunmingLokasiDistrik Guandu, Kunming, YunnanTiongkokKoordinat25°1′3″N 102°43′15″E / 25.01750°N 102.72083°E / 25.01750; 102.72083OperatorBiro Kereta Kunming Kementerian Perkeretaapian TiongkokJumlah peron6Informasi lainKode stasiun Kode TMIS: 48197[1] Kote Telegraf: KMM Kode Pinyin: KMI KlasifikasiStasiun Kereta Kelas 1SejarahDibuka1966Sunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Stasiun Kereta Ku...

أفغانستان، هي دولة تقع في آسيا الوسطى تحدها من كل من طاجكستان وأوزبكستان وتركمانستان من الشمال وإيران من الغرب والصين من الشرق فيما تحدها باكستان من الجنوب. ومعنى كلمة أفغانستان هو أرض الأفغان. وكانت المنطقة هدفا لكثير من الشعوب الغازية والفاتحين منذ القدم، منذ عهد المقد�...

Munisipalitas di Roraima, Brasil Berikut ini adalah daftar dari munisipalitas negara bagian di Roraima (RR), Brasil. Mesoregion Microregion # Munisipalitas Norte de Roraima Boa Vista 1 Alto Alegre 2 Amajari 3 Boa Vista (Ibu kota negara bagian) 11 Pacaraima Nordeste de Roraima 4 Bonfim 5 Cantá 10 Normandia 15 Uiramutã Sul de Roraima Caracarai 6 Caracaraí 8 Iracema 9 Mucajaí Sudeste de Roraima 7 Caroebe 12 Rorainópolis 13 São João da Baliza 14 São Luiz lbsMunisipalitas di Brasil menurut...

PemberitahuanTemplat ini mendeteksi bahwa artikel bahasa ini masih belum dinilai kualitasnya oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa dan ProyekWiki terkait dengan subjek. Terjadi [[false positive]]? Silakan laporkan kesalahan ini. 14.00, Selasa, 9 April, 2024 (UTC) • hapus singgahan Sebanyak 1.304 artikel belum dinilai Artikel ini belum dinilai oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Hala...

American politician Alfred Dockery Alfred Dockery (December 11, 1797 – December 3, 1873) was an American Congressional Representative from North Carolina.[1] Early life and career Alfred Dockery was born near Rockingham, North Carolina.[2] He attended the public schools and engaged in planting. Dockery was a member of the North Carolina House of Commons in 1822. He was also the father of Oliver Hart Dockery, who was born in 1830. Dockery was a member of the State constitutio...

В этом списке картографические проекции рассортированы по виду поверхности проектирования. Традиционно выделяют три категории проекций: цилиндрические, конические и азимутальные. Некоторые проекции трудно отнести к какой-либо из этих трёх категорий. С другой стороны, ...

American sports car by the Chevrolet division of General Motors (GM) This article is about the sports car. For other uses, see Corvette (disambiguation). Motor vehicle Chevrolet Corvette2021 Chevrolet Corvette C8OverviewManufacturerChevrolet (General Motors)Production1953–presentModel years1953–19821984–present1953–1962 (C1)1963–1967 (C2)1968–1982 (C3)1984–1996 (C4)1997–2004 (C5)2005–2013 (C6)2014–2019 (C7)2020–present (C8)AssemblyUnited States:Flint, Michigan 1953S...

Аппалачская музыка Истоки народная музыка Время и место возникновения XVIII век, Аппалачи, США Производные блюграсс, кантри Медиафайлы на Викискладе Струнный народный ансамбль The Bog Trotters Band, Вирджиния, 1937 год Аппалачская музыка (от англ. Appalachian music) — это музыка р�...

2013 Philippine House of Representatives elections ← 2010 May 13, 2013 (2013-05-13) 2016 → All 293 seats to the House of Representatives of the Philippines147 seats needed for a majorityCongressional district elections Party % Seats +/– Liberal 37.56 109 +62 NPC 17.08 42 +13 UNA 11.17 8 +8 NUP 8.55 24 +24 Nacionalista 8.41 18 −7 Lakas 5.24 14 −92 Bukidnon Paglaum 0.36 1 +1 Kambilan 0.34 1 +1 KABAKA 0.34 1 0 Unang Sigaw 0.34 1 +1 KBL 0.34 1 0 UNEGA 0...
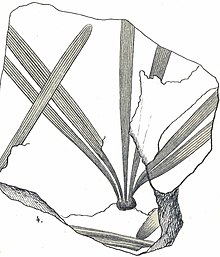
Extinct order of plants CzekanowskialesTemporal range: Late Triassic–Maastrichtian PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Fossil leaves of Phoenicopsis angustifolia Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Spermatophytes Clade: Gymnospermae Order: †CzekanowskialesPant, 1957 Genera Czekanowskia (leaves) Phoenicopsis (leaves) Solenites (leaves) Sphenarion (leaves) Arctobaiera (leaves) Leptostrobus (ovulate cone) Brinkia (ovulate cone) Ixostrobus (male cone) Synonyms L...

Russian strategic bomber aircraft Tu-95 Tu-95MS Bear H RF-94130 off Scotland in 2014 Role Strategic heavy bomberType of aircraft National origin Soviet Union Manufacturer Aviakor Design group Tupolev First flight 12 November 1952; 71 years ago (1952-11-12) Introduction 1956 Status In service Primary users Russian Aerospace ForcesSoviet Air Forces (historical) Soviet Navy (historical) Ukrainian Air Force (historical) Produced 1952–1993 Number built >500 Variants Tup...

English football manager (born 1977) Sam Collins Collins as manager of York City in 2018Personal informationFull name Sam Jason Collins[1]Date of birth (1977-06-05) 5 June 1977 (age 46)[2]Place of birth Pontefract, EnglandHeight 6 ft 3 in (1.91 m)[3]Position(s) Centre backYouth career000–1994 Huddersfield TownSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1994–1999 Huddersfield Town 37 (0)1999–2002 Bury 82 (2)2002–2006 Port Vale 135 (11)2005–2006 → ...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Local football club in the Horsham District Football League, Australia An editor has performed a search and found that sufficient sources exist to establish the subject's notability. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Harrow Balmoral Football Netball Club – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this ...

Species of bat Little black serotine Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Chiroptera Family: Vespertilionidae Genus: Eptesicus Species: E. andinus Binomial name Eptesicus andinus(J.A. Allen, 1914) The little black serotine (Eptesicus andinus) is a species of insectivorous vesper bat.[2] It is found in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela, Bolivia and Brazil...

Load-dragging structure Cheyenne family using a horse-drawn travois, 1890. A travois (/ˈtrævwɑː/; Canadian French, from French travail; also travoise or travoy) is an A-frame structure that was used to drag loads over land, most notably by the Plains Indians of North America.[1] Construction and use Travois designs used by the Blackfoot people The basic construction consists of a platform or netting mounted on two long poles, lashed in the shape of an A-frame; the frame was dragge...

Protected area in South AustraliaWhidbey Isles Conservation ParkSouth AustraliaIUCN category Ia (strict nature reserve)[1] Golden Island seen from Almonta BeachWhidbey Isles Conservation ParkNearest town or cityCoffin Bay.Coordinates34°43′37.6″S 135°09′33″E / 34.727111°S 135.15917°E / -34.727111; 135.15917Established16 March 1967[2]Area2.48 km2 (1.0 sq mi)[3]Managing authoritiesDepartment for Environment and WaterSee ...