St. Louis Blues–Philadelphia Flyers brawl
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
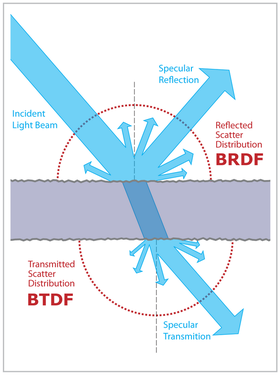
Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Fungsi Sebaran Hamburan Cahaya Dwiarah (bahasa Inggris : bidirectional scattering distribution function (BSDF)) hingga kini belum memiliki pengertian yang jelas. Istilah ini diduga dipakai pertama kali oleh Bartell, Dereniak, dan Wolfe pada tahun...

SMK Puja BangsaInformasiJenisSwastaAkreditasiAKepala SekolahDika Dwi Wibowo, S.KomJurusan atau peminatanTeknik komputer dan jaringan, Teknik Otomotif, Akuntansi, Akuntansi dan Keuangan Lembaga, Otomatisasi Tata Kelola PerkantoranRentang kelasX-XIIKurikulumK13-RevAlamatLokasiJln. Dr. Setia Budi No. 37 Karang Asih RT :05 RW: 06 Desa :karang Asih, Kabupaten Bekasi, Jawa Barat, IndonesiaTel./Faks.021-8900914Koordinat6°15'2S 107°9'10ESitus webwww.pujabangsa.sch.idMotoMotoIman, Il...

Kirgizstan padaOlimpiadeKode IOCKGZKONKomite Olimpiade Nasional Republik KirgizstanMedali 0 3 3 Total 6 Penampilan Musim Panas1996200020042008201220162020Penampilan Musim Dingin19941998200220062010201420182022Penampilan terkait lainnya Kekaisaran Rusia (1900–1912) Uni Soviet (1952–1988) Tim Persatuan (1992) Kirgizstan telah tampil dalam enam Olimpiade Musim Panas dan lima Olimpiade Musim Dingin sebagai negara merdeka dan telah memenangkan empat medali. Negara tersebut sebel...

Military Headdress Colonel Richard D. Clarke, a former commanding officer of the U.S. Army's 75th Ranger Regiment, wearing a tan beret. The tan beret, also known as a beige beret, has been adopted as official headgear by several special operations forces as a symbol of their unique capabilities. Afghan National Army Afghan National Army Special Forces members were awarded a tan beret after successfully completing ANA Special Forces Qualification and serving honorably for two deployment cycles...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «Confederación Deportiva Olímpica Alemana» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesPuedes avisar al redactor principal pegando lo siguiente en su página de discusión: {{sust:Aviso referencias|Confederación Deportiva Olímpica Alemana}} ~~~~Uso de esta plantilla: {{Referencias|t={{sust:CURRENTTIMESTAMP}}}} Alemania en los Juegos Olímpicos Bandera de A...

Cuisine of Telangana, India This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Telangana cuisine – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series on theTelangana culture History• History of Telangana • Economy of Telangana •...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Dalam nama Korean ini, nama keluarganya adalah Lee. Lee Ye-chanInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Lee Ye-chanTanggal lahir 1 Mei 1996 (umur 28)Tempat lahir South KoreaTinggi 170 m (557 ft 9 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub ...

Terusan SuezSpesifikasi teknisPanjang120,11 mil (193,30 km)Lintang maksimum775 m (2.542 ft 8 in) Terusan Suez (bahasa Arab: قناة السويس, Qanā al-Suways), di sebelah barat Semenanjung Sinai, merupakan terusan kapal sepanjang 193 km yang terletak di Mesir, menghubungkan Pelabuhan Said (Būr Sa'īd) di Laut Tengah dengan Suez (al-Suways) di Laut Merah. Terusan Suez diresmikan tahun 1869[1] dan dibangun atas prakarsa insinyur Prancis yang bernama Fe...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Culture of Ukraine – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Ukrainian Baroque, St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery in KyivA map showing various regional styles of Ukrainian embroideryA Zaporozhian...

Presiden Venezuela (bahasa Spanyol: Presidente de Venezuela) adalah sebutan politis untuk kepala negara dan kepala pemerintahan Venezuela. Masa jabatan presiden yang berlaku sekarang adalah enam tahun dengan kemungkinan untuk satu kali lagi langsung dipilih kembali, dan dengan jaminan konstitusional untuk menyelenggarakan referendum setiap saat pada masa tiga tahun terakhir dari masa jabatan presiden itu. Sebutan Presiden mencakup hanya orang-orang yang diambil sumpahnya untuk menduduki jabat...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2015) عبد الملك العباسي معلومات شخصية تعديل مصدري - تعديل عبد الملك بن صالح بن علي بن عبد الله بن العباس أمير من بني العباس، ولاه الهادي إمرة الموصل سنة 169 هــ...

American businessman (1875–1966) Alfred P. SloanAlfred P. Sloan in 1937BornAlfred Pritchard Sloan Jr.(1875-05-23)May 23, 1875New Haven, Connecticut, U.S.DiedFebruary 17, 1966(1966-02-17) (aged 90)New York City, U.S.EducationBrooklyn Polytechnic Institute,[1] Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyKnown forPresident & CEO of General MotorsSpouseIrene Jackson Alfred Pritchard Sloan Jr. (/sloʊn/ SLOHN; May 23, 1875 – February 17, 1966) was an American busine...

Egyptian pharaoh SemerkhetSemempses, MempsesAlabaster vase of Semerkhet, the inscription reads King Iry-Nebty visits the house-of-the-pleased-king, oil jars for it, National Archaeological Museum (France)PharaohReign8½ years, ca. 2920 BCPredecessorAnedjibSuccessorQa'aRoyal titulary Horus name Hor-SemerkhetḤr-smr.ẖtCompanion of the divine communityAlternative:Companion of the gods[1] Abydos King List Iry?/Semsu?iry?/smsw? Turin King ListSemsemsmsmThe elder of Horus Prenomen ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Capriata (disambigua). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento architettura è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti più precisamente. Segui i...

SuspiriaDakota Johnson in una scena del filmLingua originaleinglese, tedesco Paese di produzioneItalia, Stati Uniti d'America Anno2018 Durata152 min Rapporto1,85:1 Genereorrore, drammatico, storico RegiaLuca Guadagnino SoggettoDario Argento, Daria Nicolodi (personaggi) SceneggiaturaDavid Kajganich ProduttoreLuca Guadagnino, David Kajganich, Francesco Melzi d'Eril, Marco Morabito, Gabriele Moratti, William Sherak, Silvia Venturini Fendi, Bradley J. Fischer Produttore esecutivoCarlo...

Rosena Allin-KhanAllin-Khan pada 2019 Menteri Kabinet Bayangan untuk Kesehatan MentalPetahanaMulai menjabat 6 April 2020PemimpinKeir StarmerPendahuluBarbara Keeley (Kesehatan Mental dan Pelayanan Sosial)PenggantiPetahanaMenteri Bayangan untuk OlahragaMasa jabatan9 Oktober 2016 – 14 Januari 2020PemimpinJeremy CorbynPendahuluClive EffordPenggantiCatherine WestAnggota Parlemenuntuk TootingPetahanaMulai menjabat 16 Juni 2016PendahuluSadiq KhanPenggantiPetahanaMayoritas14,307 (2...

Cultural Center in Guatemala City, GuatemalaTeatro Nacional Centro Cultural Miguel Ángel AsturiasGeneral informationTypeCultural CenterLocationGuatemala City, GuatemalaCompleted1973OpenedJune 16, 1978Design and constructionArchitect(s)Efraín RecinosWebsiteCentro Cultural “Miguel Ángel Asturias” - Portal MCD The Centro Cultural Miguel Ángel Asturias, commonly called Teatro Nacional, is a cultural center in Guatemala City, Guatemala. It is located in the Centro Cívico (Civic Center) of...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Бастер (значения). Не следует путать с с городом Бас-Тер — административным центром Французской Гваделупы. ГородБастерBasseterre 17°17′54″ с. ш. 62°44′03″ з. д.HGЯO Страна Сент-Китс и Невис История и география Основан...

グリフォン(Griffon )はイギリスのロールス・ロイスが開発、生産した航空機用レシプロエンジンである[1]。 マーリンを元に爆撃機用として開発され、ボア 6in×ストローク 6+5/8in(φ152.5mm×167.6 mm)の排気量2,240立方インチ (36,700 cc)に拡大したが、寸法も重量もさほど増加しなかったため戦闘機用としても重宝され、第二次世界大戦後期に活躍した[1]。元�...

Mexican actor In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Sendel and the second or maternal family name is Santealla. Sergio SendelBornArnoldo Sergio Santaella Sendel (1966-11-04) November 4, 1966 (age 57)Mexico City, MexicoOccupationActorSpouse Marcela Rodriguez (m. 1996; div. 2012)Children2 Arnoldo Sergio Santaella Sendel (born November 4, 1966) is a Mexican actor, known for playing antagonistic roles in Mexican tel...


