Spuyten Duyvil Bridge
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Daging ham Ham adalah bagian daging babi yang berasal dari bagian kaki belakang. Ham dibuat di seluruh dunia, termasuk beberapa makanan khas daerah, meskipun istilah ini memiliki penggunaan yang lebih luas dan dapat digunakan untuk merujuk pada daging babi yang telah dibentuk kembali. Selain itu, ada banyak memiliki produk perlindungan ham secara geografis, seperti Prosciutto di Parma di Eropa, dan Smithfield ham di Amerika Serikat. Merek yang dilindungi Belgia Jambon d'Ardenne - Wallonia, Be...

Ada usul agar artikel ini digabungkan dengan MNC Vision Networks. (Diskusikan) Vision PrimeLogo Vision PrimeDiluncurkan14 April 2012JaringanMNC ChannelsPemilikMNC Sky Vision (2012-2019)MNC Vision Networks (2019-sekarang)SloganTerbaik Untuk IndonesiaNegaraIndonesiaKantor pusatMNC Studios Tower II Lantai 3-5, Jl. Raya Perjuangan, Kebon Jeruk, Jakarta Barat, IndonesiaNama sebelumnyaMNC Drama (15 April 2012-19 Juni 2015)Drama Channel (20 Juni 2015-31 Desember 2019)MenggantikanMovie Channel (30 Me...

2010 Newark mayoral election ← 2006 May 11, 2010[1] 2014 → Candidate Cory Booker Clifford J. Minor Party Nonpartisan Nonpartisan Popular vote 22,745 13,570 Percentage 59.1% 35.3% Mayor before election Cory Booker Democratic Elected Mayor Cory Booker Democratic Elections in New Jersey Federal government U.S. President 1788-89 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 18...

John Franklin EndersJohn Franklin Enders's bronze bust at the Polio Hall of FameLahir(1897-02-10)10 Februari 1897West Hartford, ConnecticutMeninggal8 September 1985(1985-09-08) (umur 88)Waterford, ConnecticutKebangsaanAmerika SerikatAlmamaterUniversitas YaleDikenal ataspoliomyelitis virusPenghargaanNobel Fisiologi atau Kedokteran, 1954 John Franklin Enders (10 Februari 1897 – 8 September 1985) ialah mikrobiolog Amerika Serikat yang bersama Thomas H. Weller dan Frederick ...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

South Korean TV series or program Five FingersPromotional posterGenreRomanceMusicWritten byKim Soon-okDirected byChoi Hyeong-hunStarringJu Ji-hoonChae Shi-raJi Chang-wookJin Se-yeonComposerHa Geun-youngCountry of originSouth KoreaOriginal languageKoreanNo. of episodes30ProductionExecutive producerKang Shin-hyoProducerLee Myung-sukProduction locationKoreanRunning time70 minutesProduction companyJidam Inc. (formerly Yein E&M)Original releaseNetworkSBS TVReleaseAugust 18 (2012-08-18)&#...

For other novels, see Flood (disambiguation) § Literature. The Flood First editionAuthorIan RankinCountryScotlandLanguageEnglishPublisherPolygonPublication date1986Media typePrint (Hardback & Paperback)Pages188 ppISBN0-948275-09-X The Flood is the first novel by crime writer Ian Rankin. Plot summary Mary Miller has always been an outcast. As a child, she fell into the hot burn - a torrent of warm chemical run-off from the local coal mine - and her hair turned white. Initially s...

Part of a series onCannabis ArtsCulture 420 (chan) Books Magu (deity) Names Religion Judaism Latter-day Saints Sikhism Smoke-in Spiritual use Sports Stoner film Stoner rock Terms Chemistry Cannabinoid receptors Cannabinoid receptor type 1 Cannabinoid receptor type 2 Cannabinoids 2-AG 2-AGE, Noladin ether AEA CBC CBL CBD CBDV CBG CBN CBV NADA THC THCV Virodhamine Synthetic cannabinoids AM-2201 CP-55940 Dimethylheptylpyran HU-210 HU-331 JWH-018 JWH-073 JWH-133 Levonantradol SR144528 WIN 55,212...
本條目被提議拆分為「中国与联合国」和「台湾入联议题」。(討論) (2023年9月18日) 中国 → 联合国会员国会员正式会员始于1945年 (1945)创始会员国:( 中華民國)1971年 (1971)轉移席位:( 中华人民共和国)安理会席位常任理事国常驻代表傅聪 中國與聯合國的關係始於1945年聯合國籌建之初,中、美、英、蘇並稱第二次世界大戰戰勝國四巨頭,且是聯合國宣言...

Action or behavior that violates social norms Deviant redirects here. For other uses, see Deviant (disambiguation). Part of a series onSociology History Outline Index Key themes Society Globalization Human behavior Human environmental impact Identity Industrial revolutions 3 / 4 / 5 Social complexity Social environment Social equality Social equity Social power Social stratification Social structure Social cycle theory Perspectives Conflict theory Critical theory Structural functionalism Posi...

Island in the Philippines Calayan IslandCalayan IslandLocation within the PhilippinesGeographyCoordinates19°19′37″N 121°27′57″E / 19.32694°N 121.46583°E / 19.32694; 121.46583ArchipelagoBabuyan IslandsAdjacent toBalintang ChannelLuzon StraitArea196 km2 (76 sq mi)[1]Highest elevation499 m (1637 ft)[1]Highest pointMount CalayanAdministrationPhilippinesRegionCagayan ValleyProvinceCagayanMunicipalityCalayanBaran...

Buddha Besar Ushiku(牛久大仏code: ja is deprecated )Rupang Ushiku DaibutsuKoordinat35°58′57″N 140°13′13″E / 35.98250°N 140.22028°E / 35.98250; 140.22028Koordinat: 35°58′57″N 140°13′13″E / 35.98250°N 140.22028°E / 35.98250; 140.22028LokasiUshiku, Ibaraki, JepangPerancangŌtani KōshōTipepatungMaterialperungguTinggi patung: 100 meter (330 ft) termasuk fondasi: 120 meter (390 ft) Tanggal selesai1993 Ushiku Dai...

Norwegian jazz band Jaga JazzistJaga Jazzist at Tauron Nowa Muzyka 2014 in Katowice, PolandBackground informationOriginTønsberg, NorwayGenresJazztronicaacid jazzjazz fusionavant-garde jazzexperimental rockpost-rockYears active1994–presentLabelsSmalltown Supersound, Ninja TuneMembersMartin HorntvethLars Horntveth Marcus ForsgrenEven Ormestad Andreas Mjøs Line Horntveth Øystein Moen Erik JohannessenPast membersMathias EickHarald Frøland Ivar Chr. Johansen / RaviJonas Bendiksen Lars Wabø ...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) كأس أمريكا الجنوبية 1967معلومات عامةموسم لـ كوبا أمريكا الرياضة كرة القدم البلد الأوروغواي المكان ملعب سنتي...

1980 television film directed by Richard Loncraine This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Blade on the FeatherDeep Cover U.S. VHS coverWritten byDennis PotterDirected byRichard LoncraineStarringTom ContiDonald PleasenceDenholm ElliottKika MarkhamPhoebe Nicholl...

Election 1911 United States Senate election in New Jersey ← 1905 January 24–25, 1911 1916 → Resolution of the New Jersey Legislature Nominee James E. Martine Edward C. Stokes John W. Griggs Party Democratic Republican Republican Electoral vote 47 21 5 Percentage 59.5% 26.6% 6.3% Senator before election John Kean Republican Elected Senator James Edgar Martine Democratic Elections in New Jersey Federal government U.S. President 1788-89 1792 1796 1800 1804 180...
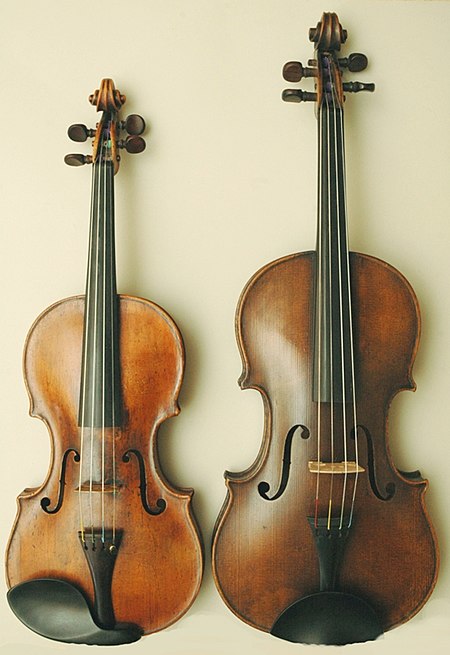

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Alto. Alto Classification Instrument à cordes Famille Instrument à cordes frottées Instruments voisins Violon, violoncelle, contrebasse, octobasse Tessiture Œuvres principales Symphonie concertante pour violon et alto de Mozart - Sonata per la Grand Viola de Paganini - Harold en Italie de Berlioz - Sonate Arpeggione de Schubert - Märchenbilder de Schumann Instrumentistes bien connus Liste d'altistes Facteurs bien connus Antonio Stradivari - Niccolò Ama...

Kobe神戸— Đô thị quốc gia —神戸市 · Kobe City[1] Từ trái qua: Khu phố Tàu Nankimachi, Cầu Akashi-Kaikyo, Tháp cảng Kobe, Bầu trời đêm ở Kobe từ đỉnh Maya Hiệu kỳBiểu trưngVị trí của Kobe trong tỉnh HyōgoKobe Tọa độ: 34°41′B 135°12′Đ / 34,683°B 135,2°Đ / 34.683; 135.200 Quốc giaNhật BảnTỉnhHyōgoĐặt tên theoKanbe Thủ phủCh�...

Germanische Ratsversammlung – Relief der Marc-Aurel-Säule zu Rom Phantasie-Rekonstruktion von 2003 eines Thingplatzes in Gulde bei Stoltebüll, Schleswig-Holstein Als Thing (rechtschreiblicher Tagung von 1901 entsprechend auch Ting) oder Ding (altnordisch und neuisländisch þing, dänisch, norwegisch und schwedisch ting; oberdeutsch auch Thaiding von ahd. taga-ding[1]) wurden Volksversammlungen (Volksthing) und Gerichtsversammlungen nach germanischen Rechten bezeichnet. Der ...

Campionati mondiali di trampolino elasticoSport Trampolino elastico FederazioneFIG OrganizzatoreFederazione Internazionale di Ginnastica TitoloCampione mondiale Cadenzaannuale StoriaFondazione1964 Edizione in corsoCampionati mondiali di trampolino elastico 2018 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale I Campionati mondiali di trampolino elastico sono una competizione sportiva organizzata dalla Federazione Internazionale di Ginnastica (FIG), con cadenza annuale, in cui si assegnano i titoli m...




