Space Travel (video game)
| |||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Arnaud Montebourg Menteri Pembaruan IndustriMasa jabatan16 Mei 2012 – 25 Agustus 2014PresidenFrançois HollandePerdana MenteriJean-Marc AyraultManuel Valls PendahuluÉric BessonPenggantiEmmanuel Macron Informasi pribadiLahir30 Oktober 1962 (umur 61)Clamecy, PrancisPartai politikPartai SosialisPasangan serumahAudrey Pulvar (2010–2012)Alma materUniversitas Pantheon-SorbonneInstitut Pembelajaran Politik, ParisSunting kotak info • L • B Arnaud Montebourg (pengucapa...
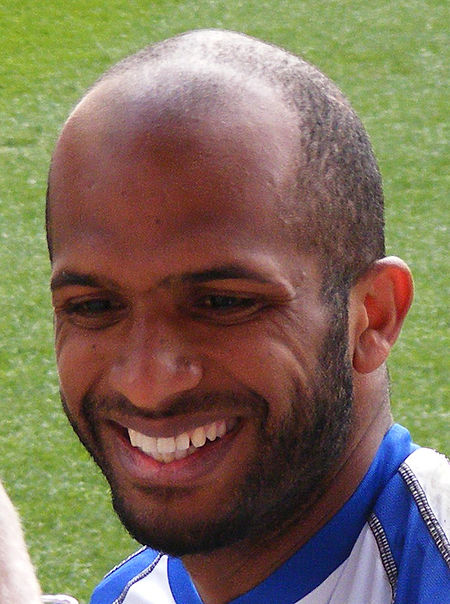

Ali Al-Habsi Al Habsi bermain untuk Wigan pada 2011.Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Ali Abdullah Harib Al-HabsiTanggal lahir 30 Desember 1981 (umur 42)Tempat lahir Muscat, OmanTinggi 1,94 m (6 ft 4+1⁄2 in)[1]Posisi bermain KiperInformasi klubKlub saat ini Wigan AthleticNomor 26Karier junior1997–1998 Al-NasrKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)1998–2002 Al-Midhaibi 56 (0)2002–2003 Al-Nasr 27 (0)2003–2006 Lyn Oslo 62 (0)2006–2010 Bolton Wanderers 10 (0)...

James HeilmanJames Heilman di Wikimania 2015 Anggota Dewan Pengawas Yayasan WikimediaMasa jabatan15 Juli 2015 – 28 Desember 2015Masa jabatan10 Agustus 2017 – petahana Informasi pribadiLahir1979/1980 (umur 43–44) Saskatchewan, KanadaPendidikanUniversity of British ColumbiaProfesiDokter James Heilman memperkenalkan diri recorded August 2017 Sunting kotak info • L • B James M. Heilman (lahir, 1979 atau 1980) adalah seorang dokter darurat Kanada,...

Bupati Raja AmpatLambang Kabupaten Raja AmpatPetahanaAbdul Faris Umlatisejak 17 Februari 2016Masa jabatan5 tahunDibentuk2003Pejabat pertamaMarcus WanmaSitus webrajaampatkab.go.id Berikut ini adalah Daftar Bupati Raja Ampat dari masa ke masa. No Bupati Mulai Menjabat Selesai Menjabat Prd. Ket. Wakil Bupati ౼ Marcus Wanma 12 April 2003 16 November 2005 ౼ [Ket. 1] lowong 1 16 November 2005 16 November 2010 1(2005) [Ket. 2] Inda Arfan 16 November 2010 16 November 2015 2(2...

Jimmy ButlerButler dengan Miami Heat pada tahun 2020No. 22 – Miami HeatPosisiSmall forwardLigaNBAInformasi pribadiLahir14 September 1989 (umur 34)Houston, Texas, U.S.Tinggi6 ft 7 in (2,01 m)Berat230 pon (104 kg)Informasi karierSekolah menengah atasSMA Tomball (Tomball, Texas)Perguruan tinggi Tyler JC (2007–2008) Marquette (2008–2011) Draf NBA2011 / Babak: 1 / Urutan pemilihan: ke-30 secara keseluruhanDipilih oleh Chicago BullsKarier bermain2011–se...

Cargo airline of the United States For the Yellowcard album, see Southern Air (album). Not to be confused with China Southern Airlines, Southern Airways, Southern Airways Express, or Southern Airways Ltd. Southern Air IATA ICAO Callsign 9S SOO SOUTHERN AIR Founded1947; 77 years ago (1947) (as Southern Air Transport)March 5, 1999; 25 years ago (1999-03-05) (as Southern Air)Commenced operationsNovember 1999; 24 years ago (1999-11)Ceased...

Group of stars on the celestial sphere This article is about the star grouping. For other uses, see Constellation (disambiguation). Four views of the constellation Orion: Top: Baroque drawing of Orion from Johannes Hevelius' star atlas Firmamentum Sobiescianum, showing the stars as they would appear to an observer looking down upon the imaginary celestial sphere from the outside (left); and illustration from the medieval Persian astronomical text Book of Fixed Stars (right) Bottom: Contem...

Eduard Heinrich Henoch BiografiKelahiran16 Juni 1820 Berlin Kematian26 Agustus 1910 (90 tahun)Dresden Data pribadiPendidikanUniversitas Humboldt Berlin KegiatanPekerjaandokter, dosen, pediatrician Bekerja diUniversitas Humboldt Berlin Charité Eduard Heinrich Henoch (16 Juni 1820 – 26 Agustus 1910) adalah seorang dokter Jerman. Ia mengajar di Universitas Berlin (1868–1894). Henoch berdarah Yahudi dan merupakan keponakan dari Moritz Heinrich Romberg.[1] Re...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...
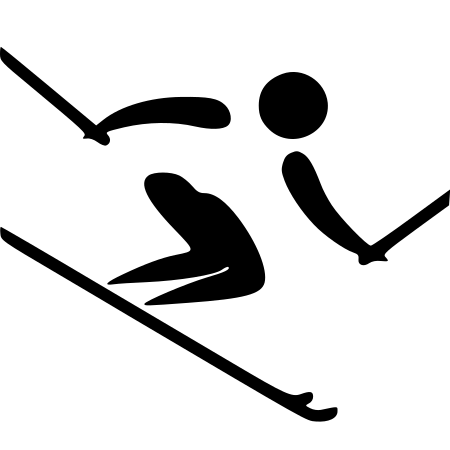

Josef Walcher Josef Walcher a Val-d'Isère nel 1977 Nazionalità Austria Altezza 178 cm Peso 77 kg Sci alpino Specialità Discesa libera Squadra WSV Schladming Termine carriera 1982 Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Mondiali 1 0 0 Vedi maggiori dettagli Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Josef Walcher detto Sepp (Schladming, 8 dicembre 1954 – Schladming, 22 gennaio 1984) è stato uno sciatore alpino austriaco, campione del mondo nella discesa libera a Garmisch-P...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article has an unclear citation style. The references used may be made clearer with a different or consistent style of citation and footnoting. (March 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unso...
Terrorist attack on a popular nightclub in Israel 2011 Tel Aviv nightclub attackclass=notpageimage| The attack siteLocationTel Aviv, IsraelCoordinates32°03′14″N 34°45′59″E / 32.05389°N 34.76639°E / 32.05389; 34.76639Date29 August 2011 (2011-08-29) 1:40 (GMT+2)[1]Attack typeVehicle attack, stabbing spreeDeaths0Injured4 Israeli civilians4 Israeli police officers[2]AssailantMuhammad Sa'afan[3] The 2011 Tel Aviv nightclub ...

Montenegro-related events during 2024 ← 2023 2022 2021 2024 in Montenegro → 2025 2026 2027 Decades: 2000s 2010s 2020s See also: Other events of 2024 Timeline of Montenegrin history Events in the year 2024 in Montenegro. Incumbents President: Jakov Milatović Prime Minister: Milojko Spajić Events 5 March – An appeals court overturns a decision to extradite South Korean cryptocurrency mogul Do Kwon, who was arrested in Montenegro in March 2023, to the United States on fraud charg...

Édouard ClaparèdeLahir24 Maret 1873JenewaMeninggal29 September 1940 (1940-09-30) (aged 67)JenewaTempat tinggalJenewaKebangsaanSwissAlmamaterUniversitas JenewaDikenal atasGenevan SchoolKarier ilmiahBidangNeurologyInstitusiInstitut Rousseau, Biro Internasional Pendidikan Édouard Claparède (lahir 24 Maret 1873 di Jenewa, Swiss — meninggal 29 September 1940 di Jenewa pada umur 67 tahun) adalah seorang psikolog Swiss yang melakukan penelitian di bidang psikologi anak, psikologi pe...

Cet article relate le parcours de l’équipe d'Uruguay de football lors de la Coupe du monde de football 2018 organisée en Russie du 14 juin au 15 juillet 2018. Équipe d'Uruguay de football à la Coupe du monde 2018 Fédération AUF Classement 5e Organisateur(s) Russie Participation 13e Meilleure performance 1930, 1950 Sélectionneur Óscar Tabárez Capitaine Diego Godín Meilleur buteur Edinson Cavani (3) Maillots Domicile Extérieur Équipe d'Uruguay de football à la Coupe du monde Coup...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Ordre de la Couronne. Ordre de la Couronne de Saxe(de) Hausorden der Rautenkrone Médaille de l'ordre de la Couronne de Saxe Décernée par Royaume de Saxe( Empire allemand) Type Ordre dynastique Statut N'est plus décerné Chiffres Date de création Dresde, 1807 Dernière attribution Dresde, 1918 Importance Ordre militaire de Saint-Henri Ruban de l'ordre de la Couronne de Saxe. modifier Revers de la médaille Plaque et croix de l'ordre de la Couronne ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Court-circuit (homonymie). Un bypass gastrique (également orthographié by-pass gastrique), ou court-circuit gastrique, est une opération chirurgicale consistant à réduire le volume de l'estomac et à modifier le circuit alimentaire. Il s'agit d'un type de chirurgie bariatrique destinée à traiter certains cas d'obésité importante. Historique Les premières interventions datent de la fin des années 1960[1]. Statistique En 2014, 40 % des chirurgi...

شارون هورجان معلومات شخصية الميلاد 13 يوليو 1970 (54 سنة) حي هكني في لندن مواطنة جمهورية أيرلندا عدد الأولاد 2 الحياة العملية المهنة ممثلة، ومنتجة تلفزيونية اللغات الإنجليزية المواقع IMDB صفحتها على IMDB تعديل مصدري - تعديل شارون هورجان (بالإنجلي�...

Stefano RusconiRusconi con la maglia della Benetton TrevisoNazionalità Italia Altezza208 cm Peso125 kg Pallacanestro RuoloAllenatore (ex centro) Termine carriera2010 - giocatore2012 - allenatore CarrieraSquadre di club 1985-1991 Pall. Varese179 (1.416)1991-1995 Pall. Treviso159 (2.260)1995-1996 Phoenix Suns7 (8)1996-1998 Pall. Treviso32 (148)1998-1999 Saski Baskonia1999-2002 Olimpia Milano98 (1.054)2002-2003 Pall. Reggiana36 (579)2003-2004 Juvecas...

Family Not to be confused with McMahon family. Duc de Magenta redirects here. For the racehorse, see Duke of Magenta (horse). Coat of arms of MacMahon family, Dukes of Magenta Statue of Patrice de MacMahon in Magenta, Italy The MacMahon family[1] originated in Ireland and later established itself in France, where it gained prominence.[2] In the context of French nobility, the head of the family holds the titles of Duc de Magenta and Marquis de MacMahon. History John MacMahon (...



