Southampton station (Pennsylvania)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Boeing E-4 Advanced Airborne Command Post, dengan nama proyek Nightwatch, adalah pesawat udara yang dioperasikan oleh Angkatan Udara Amerika Serikat (USAF). Untuk membuat seri E-4, empat Boeing 747-200 airframes secara khusus dimodifikasi untuk melayani sebagai pos komando survivable mobile untuk National Command Authority, yaitu Presiden Amerika Serikat, dengan Menteri Pertahanan, dan penerusnya . Keempat E-4s dioperasikan oleh 1st Airborne Command dan Control Squadron dari 55th Wing yang t...

Keuskupan BilbaoDioecesis FlaviobrigensisDiócesis de BilbaoKatedral BilbaoLokasiNegara SpanyolProvinsi gerejawiBurgosMetropolitBurgosStatistikLuas2.193 km2 (847 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2012)1.172.9001,146,400 (97.7%)InformasiRitusRitus LatinKatedralKatedral Santo Yakobus di BilbaoKepemimpinan kiniPausFransiskusUskupMario Iceta GavicagogeascoaUskup agungFrancisco Gil HellínPetaSitus webSitus Web Keuskupan Keuskupan Bilbao (Latin: Dioecesis F...

Archery at the Olympics Women's teamat the Games of the XXVII OlympiadThe Sydney International Archery Park, where the event took placeVenueSydney International Archery ParkDate16–21 SeptemberCompetitors36 from 12 nationsMedalists Kim Nam-SoonKim Soo-NyungYun Mi-Jin South Korea Nataliya BurdeynaOlena SadovnychaKateryna Serdyuk Ukraine Barbara MensingCornelia PfohlSandra Wagner-Sachse Germany← 19962004 → Archery at the2000 Summer OlympicsIndi...

Part of a series onBritish law Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom Year 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 1808 1809 1810 1811 1812 1813 1814 1815 1816 1817 1818 1819 1820 1821 1822 1823 1824 1825 1826 1827 1828 1829 1830 1831 1832 1833 1834 1835 1836 1837 1838 1839 1840 1841 1842 1843 1844 1845 1846 1847 1848 1849 1850 1851 1852 1853 1854 1855 1856 1857 1858 1859 1860 1861 1862 1863 1864 1865 1866 1867 1868 1869 1870 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877 1878 ...

Language from Austronesian language PohnpeicPonapeicGeographicdistributionMicronesiaLinguistic classificationAustronesianMalayo-PolynesianOceanicMicronesianMicronesian ProperNuclear MicronesianChuukic-PohnpeicPohnpeicGlottologpona1248Map of the Micronesian languages; Pohnpeic languages are shaded in pink, while the Chuukic languages are red. Pohnpeic, also rendered Ponapeic, is a subgroup of the Chuukic–Pohnpeic branch of Micronesian in the Austronesian language family.[1] The langu...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori argentini è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. René Enrique Seghini René Seghini al Bologna nel 1956 Nazionalità Argentina Altezza 162 cm Peso 62 kg Calcio Ruolo Attaccante Termine carriera 1960 Carriera Squadre di club1 1951 Boca Juniors26 (8)1952 Sarmiento (J)? (?)1953-1954 Platense25 (2)1954-1956 Independiente Medellín40 ...

Chemical compound DiclofensineClinical dataATC codeNoneLegal statusLegal status In general: legal Identifiers IUPAC name 4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-7-methoxy-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline CAS Number67165-56-4 YPubChem CID68871ChemSpider62103 NUNII09HKW863J6ChEMBLChEMBL287257 NChemical and physical dataFormulaC17H17Cl2NOMolar mass322.23 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES CN1CC(C2=C(C1)C=C(C=C2)OC)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)Cl)Cl InChI InChI=1S/C17H17Cl2NO/c1-2...

Scientific study of humans, human behavior, and societies This article is about the study of humans. For the study of human origins, see Anthropogeny. For other uses, see Anthropology (disambiguation). An anthropologist with indigenous American people Part of a series onAnthropology OutlineHistory Types Archaeological Biological Cultural Linguistic Social Archaeological Aerial Aviation Battlefield Biblical Bioarchaeological Environmental Ethnoarchaeological Experiential Feminist Forensic Mari...

GF Thormeyer secondo Carl Christian Vogel, 1813 Tomba di Thormeyer nel cimitero di Elias Gottlob Friedrich Thormeyer (Dresda, 23 ottobre 1775 – Dresda, 11 febbraio 1842) è stato un architetto tedesco del neoclassicismo. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Galleria d'immagini 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Era uno dei sette figli del calzolaio Gottlob Friedrich e di Christiane Regina. Studiò pittura presso l'Accademia d'arte di Dresda con Giovanni Battista Casanova, ma p...

Liga Komunitas Stand Up Kompas TVLiga Komunitas Stand UpPembuatTeezar SjamsuddinPresenterUus (2014) Hifdzi Khoir (2014, 2022) Rigen (2022)JuriErnest Prakasa (2014) Babe Cabita (2014) Pandji Pragiwaksono (2014) Arief Didu (2014) Mo Sidik (2014) Kartika Putri (2014) Chika Jessica (2014) Hesti Purwadinata (2014) Indro Warkop (2014) Raditya Dika (2022) Adjis Doa Ibu (2022) Livy Renata (2022)Negara asalIndonesiaProduksiProduser eksekutifArgalaras Kusumahananda (2014) Fina Merliane Vidya (2022)Dur...
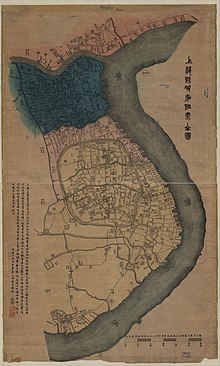
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. كان الامتياز الأمريكي أو التسوية الأمريكية جيبًا أجنبيًا (امتياز) في شانغهاي داخل إمبراطورية تشينغ، وقد كانت موجودة منذ حوالي العام 1848 حتى توحيدها مع المنطقة البريطانية بال�...

The Way We Live Now (TV serial) redirects here. For the 1969 series based on the same novel, see The Way We Live Now (1969 TV serial). British TV series or programme The Way We Live NowU.S. DVD coverBased onThe Way We Live Now by Anthony TrollopeWritten byAndrew Davies (adaptation)Directed byDavid YatesStarringDavid SuchetMatthew MacfadyenShirley HendersonCillian MurphyComposerNicholas HooperCountry of originUnited KingdomOriginal languageEnglishNo. of series1No. of episodes4ProductionExecuti...

Sharp PC-1251Sharp PC-1251ManufacturerSharp CorporationGenerationFirstRelease date1982 (1982)Memory4 Kbit RAM modulesDisplay24 digit dot matrix LCDInputFull QWERTY-style keyboardPower2 built-in batteriesSuccessorSharp PC-5000RelatedSharp PC-1211Sharp PC-1500 The Sharp PC-1251 was a small pocket computer that was also marketed as the Tandy Pocket Computer. It was created by Sharp Corporation in 1982.[1] Technical specifications PC-1251, with its printer and microcassette reco...

Wilderness survival skills This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bushcraft – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) A hatchet, a knife, and sometimes a saw are staple tools for bushcraft. A billhook (a common tool in Europe) with a sa...

2000 Maine Democratic presidential primary ← 1996 March 7, 2000 (2000-03-07) 2004 → ← ID (caucus)MD →33 delegates to the Democratic National Convention (23 pledged, 10 unpledged)The number of pledged delegates received is determined by the popular vote Candidate Al Gore Bill Bradley Home state Tennessee New Jersey Delegate count 13 10 Popular vote 34,725 26,520 Percentage 54.02% 41.26% Primary results by countyG...

VeteranSutradaraRyoo Seung-wanProduserKang Hye-jung Kim Jung-minDitulis olehRyoo Seung-wanPemeranHwang Jung-min Yoo Ah-inPenata musikBang Jun-seokSinematograferChoi Young-hwanPenyuntingKim Sang-bum Kim Jae-bumDistributorCJ EntertainmentTanggal rilis 5 Agustus 2015 (2015-08-05) (Korea Selatan) 1 Oktober 2015 (2015-10-01) (Hong Kong)Durasi123 menitNegaraKorea SelatanBahasaKoreaAnggaranUS$5,1 jutaPendapatankotorUS$92 juta Veteran (Hangul: 베테랑; RR: Bete...

French politician This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Bertrand Pancher – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) You can h...

Historical territory in South Germany and North Switzerland For other uses, see Baden (disambiguation). Grand Duchy of Baden with the Margraviate (red) and gains after 1803 Hohenbaden Castle on the Battert above Baden-Baden Monument to Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Baden in front of Karlsruhe Palace Baden (/ˈbɑːdən/; German: [ˈbaːdən]) is a historical territory in South Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleon...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of governors of Kandahar – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This is a list of the governors of the province of Kandahar, Afghanistan. Governor Period Extra Note Muhammad 'Amin Khan ?-18...

Křesomysl Biografi Data pribadiAgamaPaganisme Slavia KeluargaKeluargaWangsa Přemyslid AnakNeklan AyahVnislav Křesomysl merupakan pangeran kelima dari ketujuh pangeran mitos Bohemia antara (juga mitos) pendiri Dinasti Přemyslid Přemysl, Pembajak Tanah dan pangeran sejarah pertama Bořivoj. Nama-nama pangeran yang pertama kali dicatat di dalam riwayat Cosmas dan kemudian ditransmisikan kedalam buku-buku yang paling bersejarah pada abad ke-19 termasuk František Palacký Sejarah Bangsa Ceko...

