South Carolina Canal and Railroad Company
| |||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

For the town in Vermont, see Canaan, Vermont. Town in New Hampshire, United StatesCanaan, New HampshireTownChurch Street in 1907 SealMotto(s): Land of Milk and HoneyLocation in Grafton County, New HampshireCoordinates: 43°38′48″N 72°00′37″W / 43.64667°N 72.01028°W / 43.64667; -72.01028CountryUnited StatesStateNew HampshireCountyGraftonIncorporated1761VillagesCanaanCanaan CenterCanaan StreetWest CanaanGovernment • Select Board...

Artikel ini tentang tahun 1953. 1953MileniumMilenium ke-2AbadAbad ke-19Abad ke-20 Abad ke-21Dasawarsa 1930-an1940-an1950-an1960-an1970-anTahun1950195119521953195419551956 1953 (MCMLIII) merupakan tahun biasa yang diawali hari Kamis dalam kalender Gregorian, tahun ke-1953 dalam sebutan Masehi (CE) dan Anno Domini (AD), tahun ke-953 pada Milenium ke-2, tahun ke-53 pada Abad ke-20, dan tahun ke- 4 pada dekade 1950-an. Denominasi 1953 untuk tahun ini telah digunakan sejak periode Abad Perten...

Edward BalliolEngravir abad ke-18 Edward BalliolPengklaim Tahta SkotlandiaBerkuasaSeptember 1332 sampai 1336Informasi pribadiKelahiranc. 1283Kematians. 1367Wheatley, DoncasterWangsaWangsa BalliolAyahJohn BalliolIbuIsabella de WarenneAgamaKatolik Roma Edward Balliol (c. 1283 – 1367) adalah seorang pengklaim tahta Skotlandia (1314–1356). Dengan bantuan Inggris, ia memerintah sebagian negara tersebut selama tiga periode antara 1332 dan 1336. Kehidupan Segel Edward Balliol, Raja Skotlan...

2007 single by Keyshia Cole featuring Missy Elliott and Lil' KimLet It GoSingle by Keyshia Cole featuring Missy Elliott and Lil' Kimfrom the album Just Like You ReleasedJune 19, 2007Length 3:58 (album version/radio edit) 5:15 (single version) Label Imani Geffen Songwriter(s) Keyshia Cole Kimberly Jones Melissa Elliott Jack Knight Cainon Lamb James Mtume Producer(s)Missy ElliottKeyshia Cole singles chronology Dreamin'(2007) Let It Go(2007) Shoulda Let You Go(2007) Lil' Kim singles chro...

Schröcken Lambang kebesaranKoordinat: Coordinates: Missing longitude{{#coordinates:}}: lintang salahNegaraAustriaNegara bagianVorarlbergDistrikBregenzPemerintahan • WalikotaHerbert SchwarzmannLuas • Total23,43 km2 (905 sq mi)Ketinggian1.269 m (4,163 ft)Populasi (1 Januari 2014)[1] • TotalTemplat:Metadata population AT−8Zona waktuUTC+1 (WET) • Musim panas (DST)UTC+2 (WMPET)Kode pos6888Kode area telepon0551...
Voce principale: Fußball-Club Bayern München. Fußball-Club Bayern MünchenStagione 1992-1993Sport calcio Squadra Bayern Monaco Allenatore Erich Ribbeck All. in seconda Klaus Augenthaler Presidente Fritz Scherer Bundesliga2º posto Coppa di GermaniaSecondo turno Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Helmer (34)Totale: Helmer (36) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Labbadia (11)Totale: Labbadia (14) StadioStadio Olimpico Maggior numero di spettatori64 000 (5 partite) Minor numero di spettatori13...

Dux limites TripolitaniL'Africa romana con la provincia della Tripolitania nella cartina in alto, sulla destra. Descrizione generaleAttivafine IV secolo - V secolo NazioneImpero romano Tipocomandante di un tratto di limes africano Voci su unità militari presenti su Wikipedia Il Dux limites Tripolitani era il comandante di truppe di limitanei della diocesi d'Africa,[1] provincia di Tripolitania, e facenti parte dell'armata imperiale del Numerus intra Africam. Suo diretto superiore era...

Island in San Francisco Bay Angel IslandAerial photograph of Angel Island.Angel IslandShow map of San Francisco Bay AreaAngel IslandShow map of CaliforniaAngel IslandShow map of the United StatesGeographyLocationSan Francisco BayCoordinates37°52′N 122°26′W / 37.86°N 122.43°W / 37.86; -122.43Area1.2 sq mi (3.1 km2)Highest elevation788.76 ft (240.414 m)Highest pointMount Caroline LivermoreAdministrationUnited StatesStateCaliforn...

Jembatan Pelantikan di Sevoke Sevoke (juga Sevok atau Sivok) (bahasa Nepali: सेवोक) (Bengali: সেভক) adalah sebuah kota di dekat Siliguri, distrik Darjeeling, negara bagian Bengal Barat, India di perbatasan dengan negara bagian Sikkim. Kota tersebut merupakan sebuah bagian dari Dooars. Beberapa kamp angkatan darat dan Pasukan Keamanan Perbatasan terletak di wilayah tersebut. Suaka Margasatwa Mahananda terletak di wilayah tersebut. Jalan Raya Nasional NH31 melewati kota te...

Releasing Fish from hatchery Stocking fish in a river in California Fish stocking is the practice of releasing fish that are artificially raised in a hatchery into a natural body of water (river, lake, or ocean), to supplement existing wild populations or to create a new population where previously none exists. Stocking may be done for the benefit of commercial, recreational or tribal heritage fishing, but may also be done for ecological conservation to restore or increase the population of t...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

1993 (1993) NAIA Division II men's basketball tournamentTeams20Finals siteMontgomery Fieldhouse Nampa, IdahoChampionsWillamette Bearcats (1st title, 1st title game)Runner-upNorthern State Wolves (1st title game)SemifinalistsNorthwest Nazarene CrusadersWilliam Jewell CardinalsCharles StevensonHustle AwardBart Stepp (Albertson)Chuck Taylor MVPMike Ward (Willamette)Top scorerEric Kline (Northern State)(109 points) NAIA Division II men's tournaments «1992 1994» The ...

Dessin du XVIIe siècle montrant un Juif allemand prêtant un « serment juif », à moitié dévêtu, sur une peau de truie ensanglantée. Le serment more judaico ou serment juif est une forme spéciale de serment, accompagnée par un certain protocole, que les Juifs étaient obligés de respecter dans les cours de justice européennes jusqu'au début du XXe siècle, et qui était souvent humiliante, voire dangereuse. More judaico signifie en latin « d'après/par l...
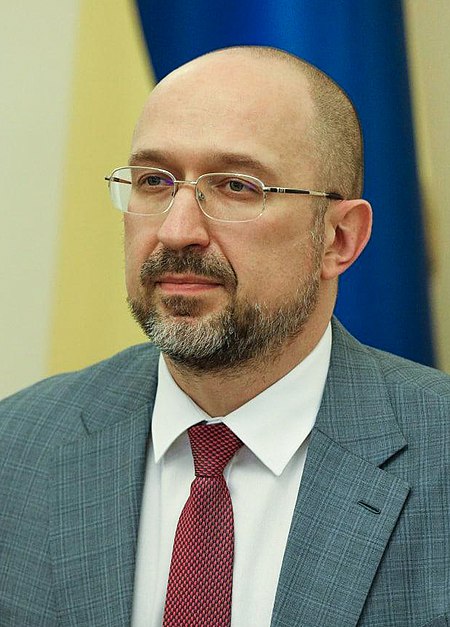

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

Village in Val Ferret in the Swiss canton of Valais La Fouly La Fouly is a village in Val Ferret in the Swiss canton of Valais. At an altitude of 1,600 metres, it is part of the municipality of Orsières (900 m). It sits at the foot of Mont Dolent (3,823 m) and the Tour Noir (3,836m) in the Mont Blanc massif. La Fouly is a starting point for many hikes into the surrounding mountains and is also a small ski resort. It is also often used as a stopping place for the Tour du Mont Blanc, and is a ...

اضغط هنا للاطلاع على كيفية قراءة التصنيف باندد لوتش حالة الحفظ أنواع غير مهددة أو خطر انقراض ضعيف جدا [1] المرتبة التصنيفية نوع التصنيف العلمي فوق النطاق حيويات مملكة عليا حقيقيات النوى مملكة حيوان عويلم ثنائيات التناظر مملكة فرعية ثانويات الفم ...

Scream 3SutradaraWes CravenProduserCathy KonradMarianne MaddalenaKevin WilliamsonDitulis olehEhren KrugerPemeranNeve CampbellDavid ArquetteCourteney Cox Arquette Parker PoseyPatrick DempseyJenny McCarthyDeon RichmondPenata musikMarco BeltramiDistributor Dimension FilmsTanggal rilis4 Februari 2000Durasi117 menitNegara Amerika SerikatBahasaInggrisAnggaranAS$40,000,000PendapatankotorAS$161,834,276 Scream 3 adalah film jagal Amerika tahun 2000 yang disutradarai oleh Wes Craven dan ditulis o...

Federal motorway in Germany You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do not translate text that appears unreliabl...

Tir aux Jeux olympiques d'été de 1936 Généralités Sport Tir sportif Éditions 8e Lieu(x) Berlin, Allemagne Nations 29 Participants 140 Épreuves 3 Navigation Los Angeles 1932 Londres 1948 modifier Trois épreuves de tir sportif sont disputées à l'occasion des Jeux olympiques d'été de 1936. À domicile, les tireurs allemands terminent à la première place du classement des médailles. Tableau des médailles Tableau des médailles Rang Nation Or Argent Bronze Total 1 Reich ...

مجموعة الجيوش إي الدولة ألمانيا النازية الإنشاء 1943 الانحلال 1945 الاشتباكات الحرب العالمية الثانية تعديل مصدري - تعديل مجموعة الجيوش إي مجموعة من الجيش الألماني نشطت خلال الحرب العالمية الثانية. تم إنشاء مجموعة الجيش إي في 1 يناير 1943 من الجيش الثاني عشر....



