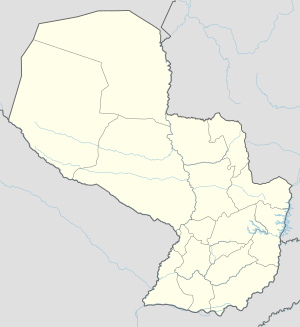
Second Battle of Nanawa
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Xu / HsuPronunciationXǔ (Mandarin)Khó (Hokkien)Heoi2 (Cantonese)Kóu (Teochew)Hứa (Vietnamese)Language(s)ChineseOriginLanguage(s)ChineseMeaningto allowOther namesVariant form(s)Xu, Hsu (Mandarin)Hui, Hoi, Hua (Cantonese)Shue, Shea (Taiwanese)Kho, Khor, Khaw, Ko (Hokkien)Koh, Khoh, Kho (Teochew)Hii, Hee, Hoo (Fuzhou)Koo (Hakka)Hy (Vietnamese)Co, Ngo (Filipino)Kosasih, Kusno, Sunarko etc. (Indonesian)Derivative(s)Heo (Korean) XuTraditional Chinese許Simplified Chinese许TranscriptionsS...

Perampokan 300 juta yen (三億円事件code: ja is deprecated , San Oku En Jiken) adalah sebuah pencurian tunggal terbesar dalam sejarah Jepang pada masa itu. Peristiwa tersebut terjadi pada pagi 10 Desember 1968, di Tokyo, Jepang. Setengah abad kemudian, kasus tersebut masih belum terpecahkan. Perampokan Penjara Fuchū Pada pagi 10 Desember 1968, empat karyawan cabang Kokubunji dari Nihon Shintaku Ginko (bank) membawa 294.307.500 yen (sekitar US$817,520 pada tingkat nilai tukar 1968) memaka...

Place in New Hampshire, United StatesGoshen, New HampshireTown HallLocation in Sullivan County and the state of New HampshireCoordinates: 43°18′04″N 72°08′52″W / 43.30111°N 72.14778°W / 43.30111; -72.14778CountryUnited StatesStateNew HampshireCountySullivanIncorporated1791VillagesGoshenGoshen Four CornersGovernment • Board of SelectmenDianne Craig, ChairDerek TremblayAlicea BurseyArea[1] • Total22.53 sq mi (58.36&#...

2005 video gameFIFA 06: Road to FIFA World CupCover art featuring RonaldinhoDeveloper(s)EA CanadaPublisher(s)EA SportsSeriesFIFAFIFA World CupPlatform(s)Xbox 360ReleaseNA: 22 November 2005EU: 2 December 2005JP: 10 December 2005KOR: 25 February 2006[1][better source needed]Genre(s)SportsMode(s)Single player, multiplayer, multiplayer online FIFA 06: Road to FIFA World Cup is a video game developed by EA Sports and DICE for the Xbox 360. The game is an officially licen...

Al-Shaghour (en arabe : الشاغور, Chaghour sous le mandat français) est une municipalité et un quartier situé dans la vieille ville de Damas, en Syrie, au sud et à l’est de la Vieille Ville, et à l’est d’al-Midan. Al-Shaghour est l’un des plus anciens quartiers connus dans la ville[1]. Le quartier traditionnel est divisé entre la partie située à l’intérieur de l’ancienne enceinte de la ville, connue comme Shaghour al-Juwani, et la plus grande partie situ�...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Malaysian legal history – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series on the History of Malaysia Prehistoric Malaysia Paleolithic Lenggong Valley c. 2.000.0000 BCE Mansuli...

National boundary between England and Wales For the area loosely based around the border, see Welsh Marches. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: England–Wales border – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) England–Wales borderFfin...

Building complex designed by Antoni Gaudí Güell PavilionsPavellons GüellGeneral informationArchitectural styleModernismeLocationBarcelona, SpainDesign and constructionArchitect(s)Antoni Gaudí Spanish Cultural HeritageTypeNon-movableCriteriaMonumentDesignated24 July 1969Reference no.RI-51-0003822 The gatehouse. The so-called Pavellons Güell, or Güell Pavilions, is a complex of buildings in the neighborhood of Pedralbes, Barcelona, by the Catalan Modernist architect Antoni Gaudí, bu...

For other uses, see Tasek Gelugor (disambiguation). Suburb of Seberang Perai in Penang, MalaysiaTasek GelugorSuburb of Seberang PeraiOther transcription(s) • Mandarin打昔汝莪 • HokkienTá-sek-lú-gô (Tâi-lô) • Tamilதாசேக் குளுகோர்Tācēk Kuḷukōr (Transliteration)Location within Seberang Perai in PenangTasek GelugorCoordinates: 5°29′0″N 100°30′0″E / 5.48333°N 100....

Explanation for the rates of electron transfer reactions In theoretical chemistry, Marcus theory is a theory originally developed by Rudolph A. Marcus, starting in 1956, to explain the rates of electron transfer reactions – the rate at which an electron can move or jump from one chemical species (called the electron donor) to another (called the electron acceptor).[1] It was originally formulated to address outer sphere electron transfer reactions, in which the two chemical spec...

Australian rules footballer Australian rules footballer Andrew Boston Boston in August 2018Personal informationFull name Andrew BostonDate of birth (1994-03-23) 23 March 1994 (age 30)Place of birth Gold Coast, Queensland, AustraliaOriginal team(s) Broadbeach (NEAFL)Draft No. 55, 2013 Rookie Draft, Gold CoastHeight 180 cm (5 ft 11 in)Weight 79 kg (174 lb)Position(s) Small forward, MidfielderPlaying career1Years Club Games (Goals)2013–2015 Gold Coast 16 (10)...

Theological reflection on the environment This article is about the field of ecotheology. For the journal Ecotheology (1996–2006), see Journal for the Study of Religion, Nature and Culture. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this article. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ecotheology – news · newspapers · books · scholar ...

This article is about the 1980 Bulgarian film. For the 1953 West German film, see Lady's Choice (film). 1980 Bulgarian filmДами Канят(Ladies' Choice)the original cinema poster (left)[1] and the new DVD cover (right)Directed byIvan AndonovWritten byGeorgi MishevStarringStefan DanailovGeorgi RusevNikola TodevNevena KokanovaTsvetana ManevaMariana DimitrovaDoroteya TonchevaYordanka KuzmanovaNadya TodorovaMariya StatulovaMusic byGeorgi GenkovProductioncompaniesBulgarian Cinematogr...

Miguel Letelier Espínola Diputado de la República de Chilepor La Victoria y Melipilla 1912-1915 Diputado de la República de Chilepor Rancagua, Cachapoal y Maipo 1915-1918 Ministro (S) de Estado de Chilepor Agricultura, Industrias y Colonización 27 de marzo-17 de mayo de 1923 Información personalNacimiento 15 de mayo de 1883Santiago, ChileFallecimiento 18 de noviembre de 1965 (82 años)Santiago, ChileNacionalidad ChilenaFamiliaPadres José Letelier SierraEdelmira Espínola MardonesC�...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يوليو 2019) فريدي سالازار معلومات شخصية الميلاد 11 أبريل 1949 (75 سنة) كاراكاس مواطنة فنزويلا الحياة العملية المهنة مُبارز بالسيف الرياضة مبارزة السلاح تعد�...

Battle of MulegéPart of Mexican–American WarAmerican forces after capturing the hill at Mulege.Date2 October 1847LocationMulegé, Baja California SurResult Mexican victoryBelligerents United States MexicoCommanders and leaders Thomas O. Selfridge Tunis Craven Manuel Pineda MuñozStrength 17 marines 54 seaman Dale[1]: 153 100 militia[1]: 33 Casualties and losses 2 wounded[1]: 32 none[1]: 33 vt...

A country's liabilities owed to nonresidents by residents A country's gross external debt (or foreign debt) is the liabilities that are owed to nonresidents by residents.[1]: 5 The debtors can be governments, corporations or citizens.[1]: 41–43 External debt may be denominated in domestic or foreign currency.[1]: 71–72 It includes amounts owed to private commercial banks, foreign governments, or international fina...

Reinhard ScheerReinhard ScheerLahir(1863-09-30)30 September 1863Obernkirchen, Pemilihan Hesse, Konfederasi JermanMeninggal26 November 1928(1928-11-26) (umur 65)Marktredwitz, Republik WeimarPengabdian German EmpireDinas/cabang Kaiserliche MarineLama dinas1879–1918PangkatLaksamanaKomandanSMS GazelleSMS ElsassPertempuran Skuadron IIPertempuran Skuadron IIIArmada Laut TinggiKepala staf Armada Laut TinggiPerang/pertempuranPerang Dunia I Perang Jutland Carl Friedrich...

Luxembourg aux Jeux olympiques d'été de 1900 Code CIO LUX Lieu Paris Participation 1re Athlètes 1 MédaillesRang : 14ème Or1 Arg.0 Bron.0 Total1 Luxembourg aux Jeux olympiques d'été Luxembourg aux Jeux olympiques de 1912 modifier Un athlète luxembourgeois participe aux Jeux olympiques de 1900 à Paris en France du 14 mai au 28 octobre 1900[1]. Tableau des médailles Ce bilan correspond au tableau de médailles intitulé Tableau des médailles de sports-reference.com qui se ...

Piala Thomas dan Uber 2022Logo Piala Thomas dan Uber 2022Informasi turnamenEdisiThomas: ke-32Uber: ke-29LevelInternasionalJadwalpenyelenggaraan8–15 Mei 2022TempatpenyelenggaraanArena Impact Bangkok, ThailandNegaraThomas: 16Uber: 16Hasil turnamenThomas IndiaUber Korea Selatan ← Aarhus 2020 Chengdu 2024 → Piala Thomas dan Uber 2022 (nama resminya TotalEnergies BWF Thomas & Uber Cup Finals 2022 untuk alasan sponsor) adalah sebuah penyelenggaraan bersama turnamen bulu tangkis ...