SPHERES
|
Read other articles:
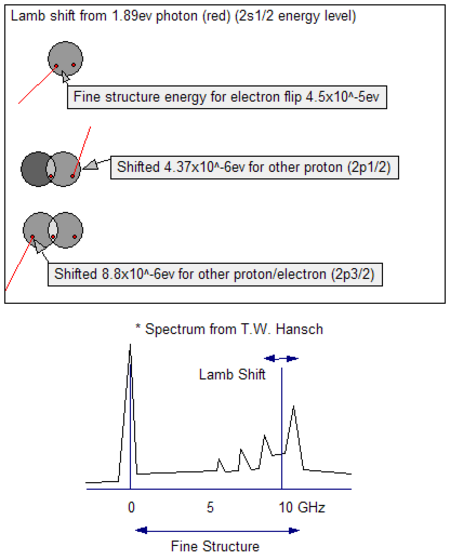
Pergeseran Lamb pada hidrogen Pergeseran Lamb adalah peristiwa pergeseran suatu tingkat energi karena interaksi spin–orbit.[1] Para fisikawan dapat memberikan penjelasan mengenai pergeseran Lamb melalui teori elektrodinamika kuantum.[2] Referensi ^ Siregar, Rustam E. Mekanika Kuantum Molekul: Struktur Elektronik Atom dan Molekul. UNPAD Press. hlm. 53. ISBN 978-602-9238-62-4. Parameter |url-status= yang tidak diketahui akan diabaikan (bantuan) ^ Merches, ...

Chandler RobbinsLahir(1918-07-17)17 Juli 1918Belmont, Massachusetts, Amerika SerikatMeninggal20 Maret 2017(2017-03-20) (umur 98)Laurel, Maryland, Amerika SerikatKebangsaan AmerikaAlmamaterUniversitas Harvard, Universitas George WashingtonDikenal atasSurvey perkembangbiakan burungKarier ilmiahBidangOrnitologiInstitusiPatuxent Wildlife Research Center Chandler Seymour Robbins (17 Juli 1918 – 20 Maret 2017) adalah seorang ornitolog Amerika Serikat. Ia lahir di Belmont,...

How to Buy a FriendPoster promosiHangul계약우정 GenreSekolahBeranjak dewasaDramaRomansaBerdasarkanContract Friendshipoleh Kwon LaadDitulis olehKim Joo-manSutradaraYoo Young-eunPemeranLee Shin-youngShin Seung-hoKim So-hyeNegara asalKorea SelatanBahasa asliKoreaJmlh. episode8ProduksiProduser eksekutifMoon Joon-ha Kim Yong-jinSohn Jae-sungPengaturan kameraSingle-cameraRumah produksiMega MonsterDistributorKBSRilis asliJaringanKBS2Format audioDolby DigitalRilis6 April (2020-04-06) �...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: List of talukas of Maharashtra – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2021) The Table below list all the talukas (tahsils/tehsils) of all the thirty-six districts in the Indian state of Maharashtra, along with district-subdivision a...

This article is about the rugby union club in Boston, Massachusetts. For various association football (soccer) clubs in Massachusetts and England, see Boston F.C. Rugby teamBostonFull nameBoston Rugby Football ClubUnionUSA RugbyFounded1960; 64 years ago (1960)Ground(s)Union Point Sports Complex, Weymouth, MassachusettsPresidentJoseph DolanCoach(es)Brennan Moore, Ben GlauserLeague(s)NERFU Team kit Official websitewww.brfc.org Boston Rugby Football Club (also known as BRFC) is...

Dalam artikel ini, nama keluarganya adalah Loke (陆).Yang Berhormat TuanAnthony Loke Siew FookAP陆兆福 Menteri PerhubunganPetahanaMulai menjabat 3 Desember 2022Penguasa monarkiAbdullahPerdana MenteriAnwar IbrahimPendahuluWee Ka SiongPenggantiPetahanaDaerah pemilihanSerembanMasa jabatan21 Mei 2018 – 24 Februari 2020Penguasa monarkiMuhammad V (2018-2019) Abdullah (2019-2020)WakilKamarudin JaffarPendahuluLiow Tiong LaiPenggantiWee Ka SiongDaerah pemilihanSerembanSekretaris Je...

Football League Cup 1996-1997The Coca-Cola Cup 1996-1997 Competizione Football League Cup Sport Calcio Edizione 37º Organizzatore Football League Date dal 20 agosto 1996al 16 aprile 1997 Luogo Inghilterra Galles Partecipanti 92 Formula Eliminazione diretta Risultati Vincitore Leicester City(2º titolo) Secondo Middlesbrough Semi-finalisti Stockport County Wimbledon FC Statistiche Miglior marcatore Fabrizio Ravanelli (9) Cronologia della competi...

1991 album by R.E.M. Out of TimeCover to the standard release of Out of TimeStudio album by R.E.M.ReleasedMarch 12, 1991 (1991-03-12)[1]RecordedMid-1990StudioBearsville (Woodstock, New York)John Keane Studios (Athens, Georgia) (recording)Soundscape (Atlanta, Georgia) (strings)Paisley Park (Chanhassen, Minnesota) (mixing)GenreAlternative rock[2]folk rock[3]Length44:08LabelWarner Bros.ProducerScott LittR.E.M.R.E.M. chronology Green(1988) Out of Time(19...
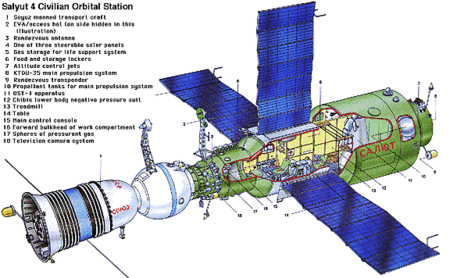
Soviet space station programme For the aircraft engine manufacturer, see Salyut Machine-Building Association. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Salyut programme – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Salyut programmeСа�...

Restaurant chain established in the United States This article is about the restaurant chain. For other uses, see Dennys (disambiguation). This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (July 2023) Denny's CorporationLogo since April 2, 2019Corporate headquarters in downtown Spartanburg, South Carolina, in July 2012Trade nameDenny'sFormerlyDanny's...

Plug In BabySingel oleh Musedari album Origin of SymmetryDirilis5 Maret 2001Format7, CD, DVDDirekam2001 di Studio Ridge FarmGenreRock alternatif, new progDurasi3:39LabelMushroom RecordsPenciptaMatthew BellamyProduserDavid Bottrill, Muse Plug In Baby adalah lagu dari grup musik asal Inggris beraliran rock alternatif, Muse yang masuk dalam album kedua mereka Origin of Symmetry. Lagu ini dirilis sebagai singel pada tanggal 5 Maret 2001 dan menjadi single tertinggi dari band yang pada saat itu me...
Arrondissement de Montbrison Situation de l'arrondissement de Montbrison dans le département Loire. Administration Pays France Région Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Département et collectivité territoriale Loire Chef-lieu Montbrison Code arrondissement 421 Démographie Population 185 892 hab. (2021) Densité 96 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 45° 36′ 14″ nord, 4° 03′ 47″ est Superficie 1 943,2 km2 Subdivisions Communes 135 modifie...

هذه المقالة عن المجموعة العرقية الأتراك وليس عن من يحملون جنسية الجمهورية التركية أتراكTürkler (بالتركية) التعداد الكليالتعداد 70~83 مليون نسمةمناطق الوجود المميزةالبلد القائمة ... تركياألمانياسورياالعراقبلغارياالولايات المتحدةفرنساالمملكة المتحدةهولنداالنمساأسترالي�...

坐标:43°11′38″N 71°34′21″W / 43.1938516°N 71.5723953°W / 43.1938516; -71.5723953 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2017年5月21日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:新罕布什尔州 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会马来西亚代表團马来西亚国旗IOC編碼MASNOC马来西亚奥林匹克理事会網站olympic.org.my(英文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員30參賽項目10个大项旗手开幕式:李梓嘉和吳柳螢(羽毛球)[1][2]閉幕式:潘德莉拉(跳水)[3]獎牌榜排名第74 金牌 銀牌 銅�...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Charles Ferren Hopkins Sr. (16 Mei 1842 – 14 Februari 1934) adalah prajurit Perang Saudara Union terakhir yang bertahan hidup di New Jersey dan penerima Medal of Honor. Ia menjabat sebagai Walikota Boonton, New Jersey.[1] Biografi Ia lahir pada 16 Mei 1842, di Hope Township, New Jersey dari pasangan Nathan Hopkins (1811–1889) dan Ann Wilson dan ia memiliki seorang saudara, John Robertson Hopkins (1844–1885). Ia menjabat sebagai Walikota Boonton, New Jersey. Ia memi...

Government of Moldova Recean CabinetCabinet of MoldovaIncumbentPrime minister Dorin ReceanDate formed16 February 2023 (2023-02-16) (1 year, 181 days)People and organisationsPresidentMaia SanduHead of governmentDorin ReceanDeputy head of governmentMihai PopșoiDumitru AlaibaVladimir BoleaCristina GherasimovOleg SerebrianNo. of ministers14Ministers removed8Total no. of members18Member partiesPASStatus in legislatureMajority government 62 / 101 (61%) Opposition par...

Questa voce sull'argomento fotografia è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard La stampa all'albume (o all'albumina) è un tipo di stampa fotografica introdotta nel 1850 da Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard. La carta all'albumina sostituì le precedenti carte salate e divenne in breve tempo il più diffuso positivo fotografico prodotto commercialmente. Indice 1 Cara...






