Roanoke station (Virginia)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ada Cinta Di SMASutradaraPatrick EffendyProduserChand Parwez ServiaFiaz ServiaSkenarioHaqi AchmadPatrick EffendyCeritaSalman AristoPemeranIqbaal RamadhanCaitlin HaldermanTeuku RyzkiAgatha ChelseaAlvaro MaldiniGege ElisaCassandra LeePenata musikCJRAndhika TriyadiSinematograferDicky R. MalandPenyuntingAline JusriaPerusahaanproduksiStarvision PlusDistributorStarvision PlusTanggal rilis 6 Oktober 2016Negara IndonesiaBahasaBahasa IndonesiaPendapatankotorRp 11,9 miliar Ada Cinta Di SMA adalah...
Maria Farida IndratiMaria Farida Indrati Hakim Konstitusi Republik IndonesiaMasa jabatan19 Agustus 2008 – 13 Agustus 2018Ditunjuk olehPresiden SBY PendahuluDr. Harjono, S.H., M.C.L.PenggantiProf. Dr. Enny Nurbaningsih, S.H., M.Hum. Informasi pribadiLahir14 Juni 1949 (umur 74)Kota Surakarta, Jawa Tengah, IndonesiaSuami/istriC. Soeprapto HaesAnak3Alma materUniversitas IndonesiaPekerjaanAkademisiHakimPenelitiPenghargaan Bintang Jasa Utama NararyaSunting kotak info • L ...

List of first orbital launches by country Orbital launch projects and capabilities Confirmed orbital launch capable country Confirmed orbital launch capable intergovernmental organization (ESA) members Orbital launch project in development or planned Abandoned orbital launch project This is a timeline of first orbital launches by country. While a number of countries, incl. Canada, Australia, Germany, Brazil, Algeria, Kazakhstan, Turkey, Argentin...

Medali Kemenangan Perang Dunia I dengan lima penjepit medali. Penjepit medali atau Klip medali adalah penjepit logam tipis yang disematkan pada pita dekorasi militer, dekorasi sipil, atau medali lainnya. Biasanya menunjukkan penghargaan atas jasa-jasa selama kampanye atau operasi militer. Beberapa penjepit yang ada pada satu pita medali menunjukkan bahwa penerima telah memenuhi kriteria untuk menerima medali di beberapa teater pertempuran. Lihat pula Medali Piala Referensi Dorling, Henry Tapr...

Robust australopithecinesRentang fosil: Pleistosen Skull of Paranthropus boisei Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Mammalia Ordo: Primates Famili: Hominidae Subfamili: Homininae Tribus: Hominini Subtribus: Hominina Genus: ParanthropusBroom, 1938 Species †Paranthropus aethiopicus †Paranthropus boisei †Paranthropus robustus Robust australopithecines, anggota genus hominin Paranthropus yang telah punah, adalah hominin bipedal yang merupakan keturunan dari hominin...

Азартні ігриАзартні ігриза країнами та територіямиІнтер'єр казино Marina Bay Sands Сінгапур Австралія та Океанія Нова Зеландія Європа Австрія Албанія Бельгія Болгарія Велика Британія ( Гібралтар, Північна Ірландія, Уельс, Шотландія) Вірменія Естонія Данія Ірландія Іспанія...

Extracción en peines y zanja canal. Camino a través de Las Miédolas Se conoce como Miédolas, Miédulas o Médulas a los restos de explotaciones auríferas romanas en Las Omañas, en la provincia de León, España.[1] Las Miédulas, de menor extensión que las Médulas bercianas, pero no menos interesantes al presentar ejemplos de dos de los tres métodos principales utilizados para la extracción del oro en el noroeste peninsular. Uno de ellos era el sistema conocido como arado en ...

Arsinoitherium Periode Eosen Akhir – Oligosen Awal~36–27 jtyl PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N Cetakan A. zitteli, Natural History Museum, LondonTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasMammaliaOrdoEmbrithopodaFamiliArsinoitheriidaeGenusArsinoitherium Beadnell, 1902 Tipe taksonomiArsinoitherium zitteli,Beadnell 1902 Tata namaDinamakan berdasarkanArsinoe II dari Mesir dan Arsinoe I dari Mesir Spesies A. zitteli Beadnell 1902 A. andrewsi Lankester 1903 A. giganteus Sanders et al. 2004 l...

نظام ويندوز الفرعي للينكسمعلومات عامةنوع مكون في نظام تشغيل مايكروسوفت ويندوز النظام الفرعي البيئي نظام التشغيل ويندوز 10ويندوز 11 النموذج المصدري حقوق التأليف والنشر محفوظة المطورون مايكروسوفت المدونة الرسمية devblogs.microsoft.com… (الإنجليزية) موقع الويب learn.microsoft.com… (الإنجليز�...

Ice climbing loop knot This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Abalakov thread – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Abalakov thread Abseiling with an Abalakov thread The Abalakov thread, also known as a V-thread, A-thread, or 0-thread ...

Miguel Martínez Datos personalesNombre completo Miguel Ángel MartínezApodo(s) NegroNacimiento Buenos Aires (Argentina)19 de enero de 1984 (40 años)Nacionalidad(es) ArgentinaMexicanaAltura 1.85 mCarrera deportivaDeporte FútbolClub profesionalDebut deportivo 2006(Belgrano de Córdoba)Posición Defensa central[editar datos en Wikidata] Miguel Ángel Martínez (Buenos Aires, Argentina, 19 de enero de 1984) es un exfutbolista argentino nacionalizado mexicano. Jugaba como d...
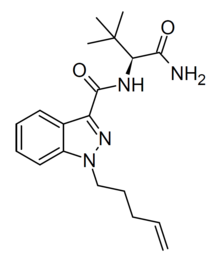
Chemical compound ADB-4en-PINACALegal statusLegal status CA: Schedule II DE: NpSG (Industrial and scientific use only) UK: Class B US: Schedule I Identifiers IUPAC name N-[(2S)-1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]-1-(pent-4-en-1-yl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide CAS Number2659308-44-6 YPubChem CID162705324ChemSpider103835283UNII76QQ7SDU32CompTox Dashboard (EPA)DTXSID601038864 Chemical and physical dataFormulaC19H26N4O2Molar mass342.443 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Inte...

American college football rivalry For the all sports rivalry, see Lone Star Showdown. Lone Star Showdown Texas Longhorns Texas A&M Aggies SportFootballFirst meetingOctober 19, 1894Texas 38, Texas A&M 0Latest meetingNovember 24, 2011Texas 27, Texas A&M 25Next meetingNovember 30, 2024StatisticsMeetings total118All-time seriesTexas leads, 76–37–5[1]Largest victoryTexas, 48–0 (1898)Longest win streakTexas, 10 (1957–1966)Current win streakTexas, 1 (2011–present) 300km...

Edgar Wright al Comic-Con del 2017 Edgar Howard Wright (Poole, 18 aprile 1974) è un regista, sceneggiatore e produttore cinematografico britannico. È noto per aver diretto e collaborato alla sceneggiatura della Trilogia del Cornetto insieme a Simon Pegg. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Filmografia 2.1 Regista 2.1.1 Cinema 2.1.2 Televisione 2.1.3 Cortometraggi 2.1.4 Documentari 2.1.5 Videoclip 2.2 Sceneggiatore 2.3 Produttore 2.4 Attore 3 Riconoscimenti 4 Note 5 Altri progetti 6 Collegamenti esterni Bi...

Area of south-east London, England For another place, see West Wickham, Cambridgeshire. Not to be confused with West Wycombe or West Wykeham. Human settlement in EnglandWest WickhamWest Wickham High StreetWest WickhamLocation within Greater LondonPopulation14,884 (ward, 2011)[1]OS grid referenceTQ379660• Charing Cross10.3 mi (16.6 km) NWLondon boroughBromleyCeremonial countyGreater LondonRegionLondonCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnite...

Cecil Crawford O'GormanBorn1874IrelandDied1943(1943-00-00) (aged 68–69)MexicoNationalityIrish Cecil Crawford O'Gorman (1874 – 1943) was an Irish mining engineer, chemist and painter. Life Cecil Crawford O'Gorman was born in Ireland in 1874. He was the son of John O'Gorman, and the grandson of Charles O'Gorman, the first British consul to Mexico in 1823. O'Gorman studied engineering in Dublin.[1][2][3] O'Gorman moved to Mexico to work for a British mining ...

مهدي النراقي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1716نراق الوفاة 1795النجف مواطنة إيران الديانة الإسلام، الشيعة الحياة العملية التلامذة المشهورون محمد بن عبد الله الرمضان المهنة رياضياتي، وموظف ديني [لغات أخرى]، ومتصوف اللغات العربية سبب الشهرة جامع السع...

Movement in Lutheranism Altarpiece in the Uppsala Cathedral of the Church of Sweden Part of a series onLutheranism Background Christianity Start of the Reformation Reformation Protestantism Doctrine and theology Bible Old Testament New Testament Creeds Apostles' Creed Nicene Creed Athanasian Creed Book of Concord Augsburg Confession Apology of the Augsburg Confession Luther's Small / Large Catechism Smalcald Articles Treatise on the Power and Primacy of the Pope Formula of Concord Di...

German general (1891–1959) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Kurt DittmarBorn(1891-01-05)5 January 1891Magdeburg , Province of Saxony, Kingdom of Prussia, German EmpireDied26 April 1959(1959-04-26) (aged 68)Stadtoldendorf, Lower Saxony, West Germa...

Village in Russia Village in Pskov Oblast, RussiaIzborsk ИзборскVillageIzborsk Fortress Coat of armsIzborskShow map of Pskov OblastIzborskShow map of RussiaCoordinates: 57°42′37.10″N 27°51′33.40″E / 57.7103056°N 27.8592778°E / 57.7103056; 27.8592778CountryRussiaRegionPskov OblastDistrictPechorsky DistrictTime zoneUTC+3:00 Izborsk (Russian: Избо́рск; Estonian: Irboska; Seto: Irbosk, Irbuska) is a rural locality (village) in Pechorsky District ...




