Race and ethnicity in the NBA
|
Read other articles:

Sebotol Radithor di Museum Sains & Sejarah Nuklir Nasional di New Mexico, Amerika Serikat Radithor adalah obat paten yang merupakan contoh terkenal dari perdukunan radioaktif dan khususnya penerapan prinsip hormesis radiasi yang terlalu luas dan pseudosaintifik. Radithor terdiri dari tiga air suling yang mengandung minimal 1 mikrocurie (37 kBq) untuk setiap isotop radium 226Ra dan 228Ra. Masa kejayaan Radithor dan obat mujarab radioaktif lainnya berakhir pada tahun 1932, dengan kematian d...

Yus YunusLahir(1962-09-19)19 September 1962Sumenep, Jawa Timur, IndonesiaMeninggal25 Februari 2022(2022-02-25) (umur 59)PekerjaanpenyanyiPartai politikPartai Amanat Nasional (2019—2022)Karier musikGenredangdutInstrumenvokalTahun aktif1978-2022 Yus Yunus (19 September 1962 – 25 Februari 2022) adalah seorang penyanyi dangdut berkebangsaan Indonesia. Yus dikenal dengan beberapa lagu dangdut yang menggunakan bahasa Madura. Awal karier Yus Yunus berangkat dari keluarga peda...

1985 American boxing film directed by Sylvester Stallone Rocky IVTheatrical release posterDirected bySylvester StalloneWritten bySylvester StalloneBased onCharactersby Sylvester StalloneProduced by Irwin Winkler Robert Chartoff Starring Sylvester Stallone Talia Shire Burt Young Carl Weathers Brigitte Nielsen Dolph Lundgren CinematographyBill ButlerEdited by Don Zimmerman John W. Wheeler Music byVince DiColaProductioncompanies United Artists Chartoff-Winkler Productions Distributed by MGM/UA E...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento attori italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Il Mago Forest nel 2022 Mago Forest o Mr. Forest, pseudonimo di Michele Foresta (Nicosia, 22 febbraio 1961), è un comico, showman e conduttore televisivo italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Vita privata 3 Film...

Kosei AmanoLahirHironari Yokozawa09 April 1978 (umur 46)Prefektur AichiKebangsaanJepangPekerjaanAktor Kosei Amano (天野 浩成code: ja is deprecated , Amano Kōsei), terlahir sebagai Hironari Yokozawa (横澤 浩成code: ja is deprecated , Yokozawa Hironari) (lahir 9 April 1978) adalah seorang aktor asal Jepang. Dia dikenal dengan peran-perannya dalam serial tokusatsu dan drama: sebagai Sakuya Tachibana / Kamen Rider Garren dalam Kamen Rider Blade. Dia juga sering memainkan peran-pera...

American film producer Terrence MassonTerrence Masson opening address as Conference Chair of ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 in Los Angeles, CABorn (1966-09-20) September 20, 1966 (age 57)NationalityAmericanEducationMFAAlma materUniversity of Massachusetts Lowell, William Paterson UniversityOccupation(s)Interactive media visionary, producer & educator, Founder and CEO of Building Conversation[1]Years active1985 to present Terrence Masson is a computer graphics educator, producer,...

Indian civil engineer from Ladakh (born 1935) Chewang NorphelNorphel in 2009Born1935OccupationEngineerEngineering careerDisciplineCivil engineeringEmployer(s)Jammu and Kashmir rural development departmentSignificant designWater catchment; artificial glacierAwardsPadma Shri(2015) Chewang Norphel [needs IPA] (born 1935) is an Indian civil engineer from Ladakh, who has built 15 artificial glaciers.[1] He has earned the title of Ice Man.[2] Early life and career Comin...

Faculty of the University of Mumbai This article about higher education may require cleanup. Please review editing advice and help improve this article. (April 2017) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jamnalal Bajaj Institute of Management StudiesMottosetting new standards in the business of...

Para pemain kostum di Yukicon 2014, sebuah konvensi penggemar di Finlandia Tiga pemain kostum di Comic Con di Long Beach 2014, mewakili tokoh dalam Star Trek, pahlawan super Wonder Woman (semesta komik DC) dan penjahat super Loki (semesta komik Marvel) Bermain kostum dari tokoh dalam Final Fantasy XIII Main kostum atau lakon kostum (bahasa Inggris: cosplay; gabungan dari costume play), adalah aktivitas dan pertunjukan seni di mana para peserta yang disebut cosplayer (pemain kostum) mengenakan...
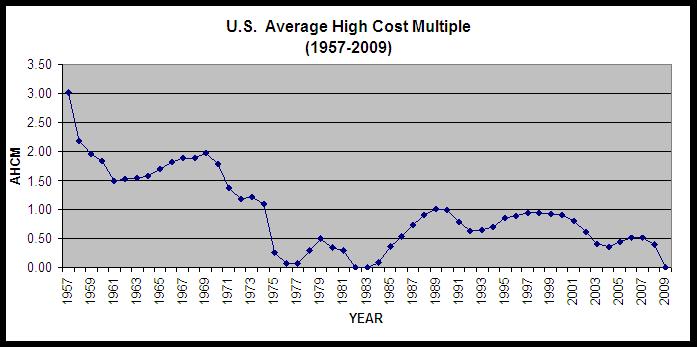
In unemployment insurance (UI) in the United States, the average high-cost multiple (AHCM) is a commonly used actuarial measure of Unemployment Trust Fund adequacy. Technically, AHCM is defined as reserve ratio (i.e., the balance of UI trust fund expressed as % of total wages paid in covered employment) divided by average cost rate of three high-cost years in the state's recent history (typically 20 years or a period covering three recessions, whichever is longer). In this definition, c...

非洲联盟成员国非洲联盟非洲大陆非洲聯盟成員國,而成員國包括暫停會籍國家。 非洲聯盟是一个由55個非洲國家組成的政治、經濟和軍事發展聯盟[1]。 组织前身是1963年成立的非洲統一組織,當時所有成員均可以加入於2002年6月9日在改組而成的非洲聯盟,2017年起所有非洲的聯合國成員國亦是非洲聯盟成員國。 因為摩洛哥在西撒哈拉與阿拉伯撒哈拉民主共和國有領土�...

1964–1967 Arab nationalist military organisation in the Federation of South Arabia Front for the Liberation of Occupied South YemenStencil cut from metal sheet with Arabic inscription and F.L.O.S.Y. initials, Imperial War Museum; the Arabic text reads jabhat al-taḥrīr, Liberation FrontActive1964 – November 7, 1967Country Federation of South Arabia Protectorate of South ArabiaAllegiance South YemenTypeGuerrillaRoleGuerrilla warfareGarrison/HQMountains and deserts of YemenEquipm...

A Primera C do Campeonato Argentino de Futebol de 2022, também conhecida oficialmente como Campeonato de Primera División C 2022 ou simplesmente como Primera C 2022, foi a 37.ª temporada da Primera C equivalente à quarta divisão do futebol argentino para os clubes diretamente afiliados à Associação do Futebol Argentino (a 90.ª temporada como Primera C e a 116ª edição da quarta divisão para clubes afiliados). A liga foi organizada pela própria Associação do Futebol Argentino (A...

Vous lisez un « article de qualité » labellisé en 2011. Bentley 6½ Litre Une Bentley 6½ Litre Tourer de 1928. Marque Bentley Motors Années de production 1926 - 1930 Production 545 exemplaire(s) Classe Sportive de luxe Usine(s) d’assemblage Crewe, Royaume-Uni Moteur et transmission Énergie Essence Moteur(s) 6 cylindres en ligne Position du moteur Longitudinale avant Cylindrée 6 597 cm3 Puissance maximale De 147 à 200 ch (soit 108 à 147 kW) Trans...

الاتحاد الاسكتلندي لكرة القدم الرياضة كرة القدم أسس عام 1873 (منذ 151 سنة) المقر إدنبرة، اسكتلندا، المملكة المتحدة الانتسابات الفيفا : 1910 الاتحاد الأوروبي : 1954 رمز الفيفا ENG الموقع الرسمي www.scotishfa.co.uk تعديل مصدري - تعديل شعار الاتحاد حتى 30 نوفمبر 2012 تأسس الاتحاد الإس...

American talk show host Joe PagsBornJoseph John Pagliarulo (1966-08-01) August 1, 1966 (age 58)Amityville, New York, U.S.Occupation(s)Television and radio talk show hostYears active1989–present Radio show The Joe Pags ShowGenreTalk radioRunning timeWeekdays: 3 hours (ET) (6:00 pm – 9:00 pm)Country of originUnited StatesLanguage(s)EnglishHome stationWOAI, San AntonioSyndicatesCompass Media NetworksHosted byJoe PagsOriginal releasepresentWebsitewww.joepags.com Joseph John Pagl...

ADH secreting nucleus of the hypothalamus. Supraoptic nucleusHuman supraoptic nucleus (SON, dorsolateral and ventromedial components) in this coronal section is indicated by the shaded areas. Dots represent vasopressin (AVP) neurons (also seen in the paraventricular nucleus, PVN). The medial surface is the 3rd ventricle (3V), with more lateral to the left.DetailsIdentifiersLatinnucleus supraopticusMeSHD013495NeuroNames385NeuroLex IDbirnlex_1411TA98A14.1.08.912TA25721FMA62317Anatomical terms o...

جبن السفطمعلومات عامةالمنشأ تركيا بلد المطبخ مطبخ تركي تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات جبن السفط أو السلة (بالتركية: sepet peyniri) هو نوع من الجبن مصدره مناطق البحر الأبيض المتوسط. كما يوحي اسمها تُكوَّن الجبنة سلة أو سفط ما يترك بصمة منسوجة على سطحها. الجبن الطازج ليس مال�...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Frosinone Calcio. Frosinone CalcioStagione 1998-1999 Sport calcio Squadra Frosinone Allenatore Claudio Di Pucchio Presidente Giacomo Carbone Serie C216º posto nel girone C. Retrocesso in Serie D. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: D'Antimi (34) Miglior marcatoreCampio...

Natural region in Germany Wendland and Altmark (‹See Tfd›German: Wendland und Altmark), named after the German regions of Wendland and Altmark, is the name of a natural regional major landscape unit group in Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt, North Germany. In the Handbook of Natural Region Divisions of Germany it is given serial number 86,[1] the Bundesamt für Naturschutz gives the same region the serial number D29. Location The eastern part of the North German Plain showing Wendla...


