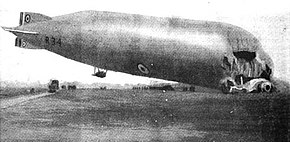
R33-class airship
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Johnny CashJohnny Cash nel 1968 Nazionalità Stati Uniti GenereCountryAmericanaGospelBluesOutlaw countryFolkRhythm and bluesTalking blues Periodo di attività musicale1955 – 2003 Strumentovoce, chitarra EtichettaSun, Columbia, Mercury, American, House of Cash, Legacy Recordings Album pubblicati192 Studio67 Live16 Colonne sonore4 Raccolte105 Sito ufficiale Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Johnny Cash (nato J. R. Cash[1]; Kingsland, 26 febbraio 1932 �...

2012 fighting game for the Nintendo 3DS 2012 video gameTekken 3D: Prime EditionNorth American box artDeveloper(s)ArikaNamco Bandai GamesPublisher(s)Namco Bandai Games[a]Producer(s)Katsuhiro HaradaComposer(s)Ayako SasoYousuke YasuiKazuhiro KobayashiTakahiro EguchiSeriesTekkenPlatform(s)Nintendo 3DSReleaseNA: February 14, 2012JP: February 16, 2012[1]EU: February 17, 2012AU: February 23, 2012Genre(s)Fighting Tekken 3D: Prime Edition[b] is a 2012 fighting video game develo...

William Holman HuntSelf-portrait, 1867, Galleria degli Uffizi, FlorenceLahir(1827-04-02)2 April 1827Cheapside, LondonMeninggal7 September 1910(1910-09-07) (umur 83)Kensington, LondonKebangsaanInggrisPekerjaanPelukisTanda tangan William Holman Hunt OM (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) adalah seorang pelukis Inggris, dan salah satu pendiri Persaudaraan Pra-Raphael. Galeri Ilustrasi puisi My Beautiful Lady karya Thomas Woolner (1850) A Converted British Family Sheltering a Christian Miss...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

British theosophist (1849–1919) Part of a series onTheosophy Founders Helena Blavatsky William Quan Judge Henry Steel Olcott Theosophists Annie Besant Isabel Cooper-Oakley Robert Crosbie Abner Doubleday Geoffrey Hodson Raghavan N. Iyer Wassily Kandinsky Archibald Keightley C. W. Leadbeater G. R. S. Mead Arthur E. Powell James Morgan Pryse Subba Row William Scott-Elliot Alfred Percy Sinnett Rudolf Steiner Brian Stonehouse Katherine Tingley Ernest Wood Concepts Root races Seven rays Theosophi...

Comics character Glorious GodfreyGlorious Godfrey as depicted in The Forever People #7 (March 1972). Art by Jack Kirby.Publication informationPublisherDC ComicsFirst appearanceThe Forever People #3 (June 1971)Created byJack Kirby (writer-artist)In-story informationAlter egoGlorious Gordon GodfreySpeciesNew GodPlace of originApokolipsTeam affiliationsDarkseid's EliteGalaxy CommunicationsNotable aliasesG. Gordon Godfrey, Reverend G. Godfrey Goode, GodfreyAbilities Immortality Superhuman physica...

2020 miniseries by Ethan Hawke The Good Lord BirdOfficial posterGenre Historical drama Dark comedy[1][2] Created by Ethan Hawke Mark Richard Based onThe Good Lord Birdby James McBrideStarring Ethan Hawke Hubert Point-Du Jour Beau Knapp Nick Eversman Ellar Coltrane Jack Alcott Mo Brings Plenty Daveed Diggs Joshua Caleb Johnson Opening themeCome on Children, Let's Sing by Mahalia Jackson[3]Country of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of episodes7ProductionEx...

Questa voce sull'argomento veicoli spaziali è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Soyuz 7K-TNavetta Soyuz 7K-TDati generaliOperatoreAgenzia Spaziale Sovietica Nazione Unione Sovietica Principale costruttoreKorolev Tipo di missioniTrasporto di due cosmonauti in orbita e rientro OrbitaLow earth orbit Durata della missione2 giorni in autonomia Equipaggio2 OperativitàStatusFuori servizio Primo lancioCosmos 496 (26 giugno 1972) Ultimo lanci...

هذه المقالة عن المجموعة العرقية الأتراك وليس عن من يحملون جنسية الجمهورية التركية أتراكTürkler (بالتركية) التعداد الكليالتعداد 70~83 مليون نسمةمناطق الوجود المميزةالبلد القائمة ... تركياألمانياسورياالعراقبلغارياالولايات المتحدةفرنساالمملكة المتحدةهولنداالنمساأسترالي�...

United States tariff to resolve the Nullification Crisis Senator Henry Clay Senator John C. Calhoun The Tariff of 1833 (also known as the Compromise Tariff of 1833, ch. 55, 4 Stat. 629), enacted on March 2, 1833, was proposed by Henry Clay and John C. Calhoun as a resolution to the Nullification Crisis. Enacted under Andrew Jackson's presidency, it was adopted to gradually reduce the rates following Southerners' objections to the protectionism found in the Tariff of 1832 and the 182...

NGC 4499 الكوكبة قنطورس[1] رمز الفهرس NGC 4499 (الفهرس العام الجديد)MCG-07-26-008 (فهرس المجرات الموروفولوجي)PGC 41537 (فهرس المجرات الرئيسية)ESO 322-22 (European Southern Observatory Catalog)2MASX J12320494-3958568 (Two Micron All-Sky Survey, Extended source catalogue)ESO-LV 322-0220 (The surface photometry catalogue of the ESO-Uppsala galaxies)6dFGS gJ123204.9-395857 (6dF Galaxy Survey)SGC 122924...

Liberal political party in the Philippines Liberal Party Partido LiberalAbbreviationLPPresidentEdcel LagmanChairpersonFrancis PangilinanSecretary-GeneralTeddy BaguilatSpokespersonLeila de LimaFoundersManuel RoxasElpidio QuirinoJosé AvelinoFoundedJanuary 19, 1946; 78 years ago (1946-01-19)Split fromNacionalistaHeadquartersAGS Building, EDSA, Guadalupe Viejo, Makati City, Metro ManilaThink tankCenter for Liberalism and Democracy[1]Youth wingLiberal YouthIdeologyL...

Legality of sexual relationships between family members This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Legality of incest – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Family law Family Marriage and other unions and status Types of marriages Cohabi...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Berkas:FireShot-lite-version.pngPengaya/ add ons software FireShot (tanda lingkaran) di Mozilla Firefox. FireShot adalah sebuah perangkat lunak add-on yang berguna untuk mengambil screenshot sebuah website secara keseluruhan atau penuh tanpa menggunaka...

1953 Hindi film by Raja Nawathe For the 2001 Maldivian film starring Mohamed Shavin and Sheela Najeeb, see Aaah (film). For the 2014 Tamil film starring Ambuli Gokulnath and Bobby Simha, see Aaaah (film). AahTheatrical posterDirected byRaja NawatheWritten byInder Raj AnandScreenplay byInder Raj AnandStory byInder Raj AnandProduced byRaj KapoorStarringRaj KapoorNargisPranCinematographyJaywant PathareEdited byG. G. MayekarMusic byShankar JaikishanProductioncompanyR. K. FilmsDistributed byR. K. ...

Ethnic group Black BrazilianBrasileiros PretosTotal population20,656,45810.2% of the Brazilian population(2022 Census)[1]Regions with significant populationsBrazilLanguagesPortugueseReligionPredominantly Christianity (majority Roman Catholic)Related ethnic groupsBrazilian People, Black People, African American, Afro Chilean, Afro Argentine, Afro-Cuban, Afro-Ecuadorian, Afro-Latin American, Afro-Mexican, Afro-Peruvian, Afro-Trinidadian, Black Canadian, African Australian, Afro-Jamaica...

В статье не хватает ссылок на источники (см. рекомендации по поиску). Информация должна быть проверяема, иначе она может быть удалена. Вы можете отредактировать статью, добавив ссылки на авторитетные источники в виде сносок. (22 октября 2022) Эта статья или раздел нуждается в ...

Bulgarian footballer Georgi Radev Personal informationFull name Georgi Plamenov RadevDate of birth (1994-09-15) 15 September 1994 (age 29)Place of birth Dobrich, BulgariaHeight 1.87 m (6 ft 1+1⁄2 in)[1]Position(s) Centre-backTeam informationCurrent team AksakovoYouth career2002–2009 Dobrudzha Dobrich2009–2013 Cherno MoreSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2012–2013 Cherno More 0 (0)2013 Dobrudzha 2 (0)2014 Lyubimets 2007 13 (0)2014–2016 Sozopol 32 (1)2...

Algerian footballer Rafik Saïfi Personal informationDate of birth (1975-02-07) 7 February 1975 (age 49)Place of birth Algiers, AlgeriaHeight 1.78 m (5 ft 10 in)Position(s) Forward, attacking midfielderSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1993–1994 CM Bordj El Kiffan 18 (31)1994–1995 IRB Sougueur 18 (27)1995–1996 IB Khémis El Khechna 18 (19)1996–1999 MC Alger 29 (20)1999–2004 Troyes 110 (19)2004–2005 Istres 35 (4)2005–2006 Ajaccio 26 (2)2006–2009 Lorient 95 ...

Ethnic culture of Hmong people Students performing a traditional dance at a high school on the outskirts of Vientiane, Laos. Many Hmong families are moving into lowland villages, and are becoming more integrated into Lao life but still retain a strong sense of their own culture and heritage. This performance was in appreciation of Big Brother Mouse, a literacy project that had visited the school that day with books and interactive educational activities. The Hmong people are an ethnic group c...