Queen's Own Highlanders (Seaforth and Camerons)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

España10.º puesto Titular Alternativo Datos generales Asociación RFEF Confederación UEFA Seudónimo La roja Ranking FIFA 10.º lugar (junio de 2018) Participación 15.ª Mejor resultado Campeón (2010) Entrenador Fernando Hierro Estadísticas Partidos 4 Goles anotados 7 (1.75 por partido) Goles recibidos 6 (1.5 por partido) Goleador Diego Costa (3 goles) Cronología Anterior Brasil 2014 Siguiente Catar 2022 La selección de fútbol de España fue una de las 32 selecciones que participaro...

No debe confundirse con Estación sencilla Santa Isabel la estación del sistema TransMilenio de Bogotá. Santa Isabel Estación Santa IsabelUbicaciónCoordenadas 33°26′49″S 70°37′50″O / -33.447075, -70.63045Dirección Av. General Bustamante con Avenida Santa IsabelComuna ProvidenciaDatos de la estaciónInauguración 5 de abril de 1997Servicios N.º de andenes 2N.º de vías 2Operador Metro de SantiagoServicios detalladosClasificación Posición SubterráneaColor ...

Ediakara~635 – 538.8 ± 0.2 Ma Had'n Arkean Proterozoikum Pha. Peta dunia pada Ediakara Akhir.EtimologiNama resmiFormalNama ratifikasi1990Informasi penggunaanBenda angkasaBumiPenggunaan regionalGlobal (ICS)Skala waktuICS Time ScaleRentang waktuSatuan kronologisPeriodeSatuan stratigrafikSistemJangka waktu resmiFormalAmbang batas jangka waktu Bawah Karbonat tutup yang berbeda di seluruh dunia. Permulaan dari pola khas perubahan sekuler dalam isotop karbon. Versi GSSPBagian Enorama Creek, Flin...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Diah Kumorowati Marsidi (lahir dan meninggal di Jakarta, 20 April 1957 – 6 Mei 2021) merupakan jurnalis senior Kompas. Ia dikenal sebagai seorang wartawan poliglot yang menguasai beberapa bahasa asing, yaitu bahasa Prancis, Inggris, Italia, Spanyol, ...

Indian actor (died 2023) Chandra MohanChandra Mohan in 2015BornMallampalli Chandrasekhara Rao(1946-05-23)23 May 1946[disputed – discuss]Pamidimukkala, Madras Province, British IndiaDied11 November 2023(2023-11-11) (aged 80)Hyderabad, Telangana, IndiaOccupationActorYears active1966–2023 Chandra Mohan (born Mallampalli Chandrasekhara Rao;[1] 23 May 1946[disputed – discuss] – 11 November 2023) was an Indian actor known for his works pre...

MoonLagu oleh Koda Kumi dengan Fergiedari album TrickSisi-BLady Go!, Once AgainDirilis11 Juni 2008 (Jepang) FormatSingel CDUnduhan digitalDirekam2008GenreJ-pophip hopR&BLabelRhythm ZoneKronologi singel Anytime(2008) Moon Taboo(2008) Labels or Love(2008) That Ain't Cool(2008) Just Stand Up!(2008) Moon (ditulis sebagai MOON) adalah singel keempat puluh yang dirilis oleh penyanyi-penulis lagu Jepang Koda Kumi. Seperti singel musim panas masa lampaunya Freaky dan 4 Hot Wave, Moon terdiri dari...

Questa voce sull'argomento sollevatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Genny Pagliaro Nazionalità Italia Altezza 145 cm Peso 48 kg Sollevamento pesi Categoria fino a 48 kg Società Esercito Palmarès Mondiali Argento Parigi 2011 -48 kg Argento Juniores 2004 -44 kg Europei Oro Palermo 2006 -48 kg Bronzo Wladyslawowo 2006 -48 kg Oro Juniores 2005 -48 kg Oro Cadetti 2005 -44 kg Oro Juniores 2004 -44 kg Or...

Orbiter in NASA's Space Shuttle program; operational from 1981 until the 2003 disaster ColumbiaColumbia landing at Kennedy on March 18, 1994, at the conclusion of STS-62TypeSpaceplaneClassSpace Shuttle orbiterEponymColumbia Rediviva[1]Apollo CSM Columbia[2]Serial no.OV-102OwnerNASAManufacturerRockwell InternationalSpecificationsDry mass81,600 kilograms (179,900 lb)RocketSpace ShuttleHistoryFirst flightApril 12–14, 1981STS-1Last flightJanuary 16 – February 1, 2003...

Sporting event delegationHungary at theParalympicsIPC codeHUNNPCHungarian Paralympic CommitteeWebsitewww.hparalimpia.huMedalsRanked 38th Gold 38 Silver 55 Bronze 65 Total 158 Summer appearances19721976198019841988199219962000200420082012201620202024Winter appearances200220062010201420182022 Hungary made its Paralympic Games début at the 1972 Summer Paralympics in Heidelberg, with a delegation of four athletes in track and field. Following another appearance in 1976 the country was then absen...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: IEC 60929 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this mess...

Bowling style Part of a series onBowling techniques Fast bowling Seam Swing Spin bowling Finger off spin left-arm orthodox Wrist leg spin left-arm unorthodox Fast bowler deliveries Bouncer Inswinger Knuckle ball Leg cutter Off cutter Outswinger Reverse swing Slower ball Yorker Spin bowler deliveries Arm ball Carrom ball Doosra Flipper Googly Leg break Off break Slider Teesra Topspinner vte In cricket, roundarm bowling is a bowling style that was introduced in the first quarter of the 19th cen...

American baseball pitcher (born 1977) Baseball player Heath BellBell with the San Diego PadresPitcherBorn: (1977-09-29) September 29, 1977 (age 46)Oceanside, California, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutAugust 24, 2004, for the New York MetsLast MLB appearanceMay 3, 2014, for the Tampa Bay RaysMLB statisticsWin–loss record38–32Earned run average3.49Strikeouts637Saves168 Teams New York Mets (2004–2006) San Diego Padres (2007–2011) Miami Marlins (...

American radio station For other uses, see WFTL (disambiguation). WFTLWest Palm Beach, FloridaBroadcast areaSouth FloridaFrequency850 kHzBranding850 WFTLProgrammingFormatTalk radioAffiliations ABC News Radio Fox News Radio Compass Media Networks Westwood One Florida State Seminoles WPTV-TV OwnershipOwnerHubbard Broadcasting(WPB FCC License Sub, LLC)Sister stationsWRMF, WEAT, WIRK, WMBX, WMENHistoryFirst air dateFebruary 14, 1948; 76 years ago (1948-02-14)Former call signsWE...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Comté de Knox. Cet article est une ébauche concernant le Kentucky. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Comté de KnoxKnox County Palais de justice du comté de Knox à Barbourville Administration Pays États-Unis État Kentucky Chef-lieu Barbourville Fondation 1800 Démographie Population 31 883 hab. (2010) Densité 32 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonné...

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒�...

Danny AielloAiello di Kota New York, Desember 2011LahirDaniel Louis Aiello Jr.(1933-06-20)20 Juni 1933Manhattan, New York, Amerika SerikatMeninggal12 Desember 2019(2019-12-12) (umur 86)New Jersey, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanAktorTahun aktif1973–2019Suami/istriSandy Cohen (m. 1955)Anak4, termasuk DannySitus webdannyaiello.com Daniel Louis Aiello Jr. (/aɪˈɛloʊ/; 20 Juni 1933 – 12 Desember 2019)[1] adalah seorang aktor asal Ame...

American writer Jim RutenbergRutenberg in 2016BornUnited StatesOccupationJournalistSpouseOndine Karady Jim Rutenberg is a writer at large for The New York Times and The New York Times Magazine. He has written over 2,300 articles for The New York Times.[1] Career After finishing college in 1991, Rutenberg began working for the New York Daily News as a gossip stringer. He eventually worked his way up to becoming a general assignment reporter. In 1996, he was hired on staff and became a ...

American sports podcast PodcastWhat's Wright? with Nick WrightPresentationHosted byNick WrightDamonza ByrdGenreSportsFormatAudio · VideoLanguageEnglishUpdates3× weekly (M, Th, F)Length28–60 minutesProductionProductionBlue Duck MediaVideo formatYouTube · Apple PodcastsAudio formatPodcast (via streaming or downloadable MP3)PublicationOriginal releaseMarch 15, 2022RelatedWebsitewww.foxsports.com/shows/whats-wright-with-nick-wright What's Wright? with Nick Wright (sometimes capitalized What'...
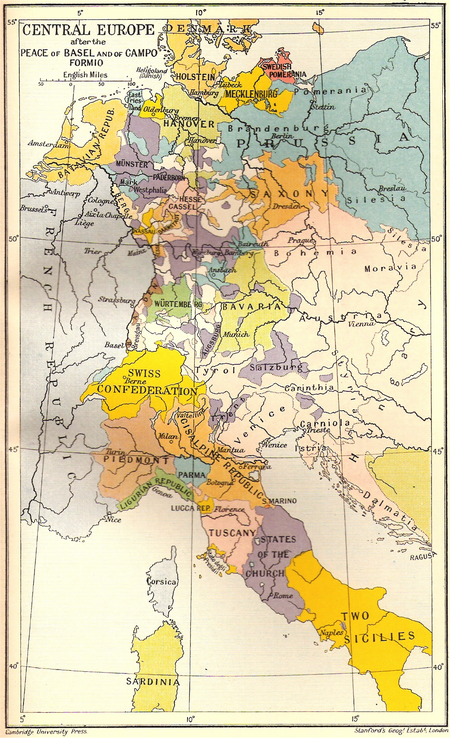
1797 treaty during the War of the First Coalition This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (October 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Treaty of Campo FormioTreaty of Campo Formio between the French Republic and AustriaTraité de Campo-Formio entre la République française et l'AutricheLast page of the public part of the treatySigned17&#...

Character in the DC Universe For other uses, see Harley Quinn (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Harlequin (DC Comics). Comics character Harley QuinnThe classic and modern iterations of Harley Quinn.Art by Terry and Rachel Dodson.Publication informationPublisherDC ComicsFirst appearanceBatman: The Animated SeriesJoker's Favor (September 11, 1992)First comic appearanceThe Batman Adventures #12 (September 1993, non-canon)Batman: Harley Quinn #1 (October 1999, canon)Created byPaul Dini (w...




