Quebec Conference, 1864
|
Read other articles:

Town in Virginia, United StatesGrottoes, VirginiaTownU.S. Route 340 thru Grottoes SealLocation of Grottoes within the Rockingham CountyGrottoes, VirginiaLocation in VirginiaShow map of VirginiaGrottoes, VirginiaGrottoes, Virginia (the United States)Show map of the United StatesCoordinates: 38°16′3″N 78°49′30″W / 38.26750°N 78.82500°W / 38.26750; -78.82500CountryUnited StatesStateVirginiaCountiesRockingham, AugustaArea[1] • Total2.07 ...

Voce principale: Unione Sportiva Salernitana 1919. Unione Sportiva SalernitanaStagione 1945Sport calcio Squadra Salernitana Allenatore Antonio Valese e Vittorio Mosele (1ª-13ª) poi Ferenc Hirzer (13ª-18ª) Presidente Felice Del Galdo Campionato Campano 19452º posto StadioCampo di Piazza d'Armi 1944 1945-1946 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Salernitana nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1945. Indice 1 Stagione 1.1 P...

Prefecture and commune in Brittany, FranceSaint-Brieuc Sant-Berioec (Gallo) Sant-Brieg (Breton)Prefecture and communeSaint-Brieuc Cathedral FlagCoat of armsLocation of Saint-Brieuc Saint-BrieucShow map of FranceSaint-BrieucShow map of BrittanyCoordinates: 48°30′49″N 2°45′55″W / 48.5136°N 2.7653°W / 48.5136; -2.7653CountryFranceRegionBrittanyDepartmentCôtes-d'ArmorArrondissementSaint-BrieucCantonSaint-Brieuc-1 and 2IntercommunalitySaint-Brieuc ArmorGo...

Questa voce sull'argomento cestisti statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Nolan Smith Smith in azione con la maglia di Duke Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 188 cm Peso 84 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo Vice-allenatore (ex playmaker) Squadra Louisville Cardinals Termine carriera 2016 - giocatore CarrieraGiovanili ?-2007Oak Hill Academy2007-2011 Duke Blue Devils143 (1.911...
Todd HaberkornHaberkorn pada tahun 2015LahirTodd Michael Haberkorn16 Agustus 1982 (umur 41)Arlington, Texas, Amerika SerikatTempat tinggalLos Angeles, California, Amerika Serikat[1][2]Nama lainTodd StoneAlmamaterSouthern Methodist University (BFA)PekerjaanPengisi suara, ADR voice directorTahun aktif1994 - sekarangAgenThe Horne AgencyVOX Inc.Anak1[1][3]Situs webwww.thehabertat.com Todd Michael Haberkorn (lahir 16 Agustus 1982 di Arlington, Texas,...

1958 California lieutenant gubernatorial election ← 1954 November 4, 1958 1962 → Nominee Glenn M. Anderson Harold J. Powers Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 2,626,626 2,536,396 Percentage 50.87% 49.13% Lieutenant Governor before election Harold J. Powers Republican Elected Lieutenant Governor Glenn M. Anderson Democratic Elections in California Federal government U.S. President 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 190...

Village near Longford town, Ireland This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Excessive replication of content from other sources. Excessive links of loosely related sources. Please help improve this article if you can. (April 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Village in Leinster, IrelandMoydow Maigh DumhaVillageMoydow (Castlerea) CastleMoydowLocation in IrelandCoordinates: 53°39′50″N 7°47′17″W / ...

Part of the remains of the barracks of the Whelk Point Fort The Whelk Point Fort was a colonial fort erected on the southeast part of Tortola in the British Virgin Islands. The fort fell into disrepair and ruin, and relatively little of the original structure remains. In 1992 a house was built over the original foundations of the fort, but the remains of the barracks can still be seen on the land behind the house. The ruins are on private property and are not generally accessible to the publ...
本表是動態列表,或許永遠不會完結。歡迎您參考可靠來源來查漏補缺。 潛伏於中華民國國軍中的中共間諜列表收錄根據公開資料來源,曾潛伏於中華民國國軍、被中國共產黨聲稱或承認,或者遭中華民國政府調查審判,為中華人民共和國和中國人民解放軍進行間諜行為的人物。以下列表以現今可查知時間為準,正確的間諜活動或洩漏機密時間可能早於或晚於以下所歸�...

Alfabeto QuechuaTipo AlfabetoIdiomas QuechuaÉpoca 1975Antecesores Jeroglíficos egipciosProtosinaíticoFenicioGriegoEtruscoAlfabeto LatinoAlfabeto Quechua [editar datos en Wikidata] Los alfabetos quechuas (en quechua sureño : achaha o achahala; en quichua norteño: llika)[1] son adaptaciones del alfabeto latino empleadas para escribir las lenguas quechuas que según la lengua y la convención utilizan diferente cantidad de letras. En Perú y Bolivia se emplea una ortog...

Australian association football player Bailey Wright Wright with Preston North End in 2016Personal informationFull name Bailey Colin Wright[1]Date of birth (1992-07-28) 28 July 1992 (age 31)[2]Place of birth Melbourne, AustraliaHeight 1.84 m (6 ft 0 in)[3]Position(s) Centre-backTeam informationCurrent team Lion City SailorsNumber 26Youth career1998–2004 Langwarrin2005 Mornington2006 Dandenong Thunder2007–2008 VIS2009–2010 Preston North EndSeni...

This article is about the racial insult. For the Australian TV series, see Go Back to Where You Came From. Racial insult The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (April 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series onDiscrimination Forms Institutional Structural Statistical Taste-based Attributes Age Caste Class ...
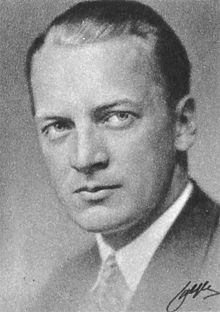
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Alf Sjöberg – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message)Swedish film director Alf SjöbergBornSven Erik Alf Sjöberg(1903-06-21)21 June 1903Stockholm, SwedenDied17 April 1980(1980-04-17) (aged 76)St...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. AT. Символы со сходным начертанием: ⓐ · Эт коммерческое @ Изображение ◄ < = > ? @ A B C D ► Характеристики Название commercial at Юникод U+0040 HTML-код @ или @ UTF-16 0x40 URL-код %40 Одна из теорий эволюции начертани...

Financial district of Tokyo, Japan Buildings surrounding the moat (2022) Marunouchi at night (2019) Marunouchi in flames following the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake The Marunouchi north exit of Tokyo Station Marunouchi (丸の内) is a commercial district located in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. Situated between Tokyo Station and the Imperial Palace, the name, meaning inside the circle, derives from its location within the palace's outer moat. It is also Tokyo's financial district and the country's t...

Sembilan blok model bisnis, Osterwalder, Pigneur & al. 2010 Business Model Canvas (BMC) ialah suatu kerangka kerja yang membahas model bisnis dengan disajikan dalam bentuk visual berupa kanvas lukisan, agar dapat dimengerti dan dipahami dengan mudah. Model ini digunakan untuk menjelaskan, memvisualisasikan, menilai, dan mengubah suatu model bisnis, agar mampu menghasilkan kinerja yang lebih optimal.[1] BMC dapat digunakan untuk semua lini bisnis tanpa terbatas sektor usahanya. BMC...

Christian scholar, ascetic, and theologian (c. 185 – c. 253) This article is about the third-century Christian scholar. For the pagan philosopher with the same name, see Origen the Pagan. For other uses, see Origen (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Orogen. OrigenRepresentation of Origen writing, from a manuscript of In numeros homilia XXVII, c. 1160Bornc. 185 ADAlexandria, Province of Egypt, Roman EmpireDiedc. 253 AD (aged c. 69)Probably Tyre, Phoenice, Roman EmpireAlma materCa...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أكتوبر 2019) IC 4886 الكوكبة المقراب[1] رمز الفهرس IC 4886 (كتالوج مفهرس)ESO 232-18 (فهرس المرصد الأوروبي الجنوبي)ESO-LV 232-0180 (فهرس المرصد الأوروبي الجنوبي و The surface photometry catalogue of ...

جائزة غولدن غلوب لأفضل فيلم - موسيقي أو كوميديمعلومات عامةالبلد قالب:بيانات بلد دولي مقدمة من رابطة هوليوود للصحافة الأجنبية المكان الولايات المتحدة أول جائزة 1951 موقع الويب goldenglobes.com تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات جائزة الغولدن غلوب لأفضل فيلم - موسيقي أو كوميدي هي ...

Church in Capernaum, IsraelSt. Peter's Churchכנסיית בית פטרוסLocationCapernaumCountry IsraelDenominationRoman Catholic ChurchArchitectureArchitect(s)Ildo Avetta Internal view St. Peter's Church[1] (Hebrew: כנסיית בית פטרוס), also called the Pilgrimage Church of St. Peter in Capernaum, is a modern Catholic pilgrimage church found in the archaeological site of Capernaum,[2][3] northern Israel. The church is part of the Franciscan monaster...
