Primary hyperparathyroidism
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2008 filmThe Anarchist's WifeFilm posterDirected byMarie NoellePeter SehrWritten byMarie NoelleRay LorigaProduced byMarie NoelleNorbert LlarasPhillippe PlanellsPeter SehrJordi RediuStarringJuan Diego BottoMaría ValverdeIvana BaqueroMusic byZacarías M. de la RivaRelease dates June 2008 (2008-06) (Munich) 25 October 2008 (2008-10-25) (Seminci) 23 January 2009 (2009-01-23) (Spain) LanguagesSpanishFrench The Anarchist's Wife (Spanish: La mujer...

Zhang Zhidong張之洞Zhang mengenakan jubah resmi Informasi pribadiLahir(1837-09-04)4 September 1837Prefektur Xingyi, Guizhou, Dinasti QingMeninggal5 Oktober 1909(1909-10-05) (umur 72)Beijing, Dinasti QingAnakZhang YanqingZhang RenliPekerjaanPejabatSunting kotak info • L • B Zhang Zhidong Hanzi tradisional: 張之洞 Hanzi sederhana: 张之洞 Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Zhāng Zhīdòng - Wade-Giles: Chang1 Chih1-tung4 Zhang Zhidong (Hanzi: 張之洞) (4 Sept...

Not to be confused with Hartford Public Library. United States historic placeHartford LibraryU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesU.S. Historic districtContributing property Library building (c. 1897)Show map of VermontShow map of the United StatesLocation1587 Maple St.,Hartford, VermontCoordinates43°39′41″N 72°20′35″W / 43.66139°N 72.34306°W / 43.66139; -72.34306Built1893 (1893)ArchitectLyman WhippleArchitectural style Queen Anne Coloni...

Mémoire retrouvée (Recovered Memory), une sculpture de Nicola Hicks sur le thème de la mémoire retrouvée[1]. Un faux souvenir est un phénomène psychologique qui se produit lorsqu'une personne se remémore un événement qui n'a pas eu lieu. Histoire du concept Les observations ou les hypothèses sur l'existence de faux souvenirs remontent aux débuts de la psychanalyse et de la psychologie clinique ; on les retrouve dans les écrits de Sigmund Freud et Pierre Janet. Dans les anné...
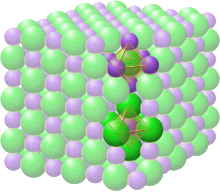
هذه المقالة عن ملح الطعام من الناحية الكيميائية. لملح الطعام كطعام، طالع ملح الطعام. لملح الطعام من الناحية الجيولوجية، طالع الهاليت. لالأملاح بشكل عام، طالع ملح (كيمياء). كلوريد الصوديوم كلوريد الصوديوم كلوريد الصوديوم الاسم النظامي (IUPAC) كلوريد صوديوم أسماء أخرى * م...

Downtown Miami skyline from Bayfront Park, February 2020 Brickell skyline from the south, December 2020 Miami skyline from William Powell Bridge in February 2018 Downtown viewed from the north in 2011 Downtown and Brickell skyline from the west in 2012 List of tallest buildings in Miami The city of Miami, Florida has the third-tallest skyline in the United States (after New York City and Chicago) with 439 high-rises, over 100 of which stand taller than 400 feet (120 m)[1] and 70...

Unemployment among people with an academic degree This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (October 2020) Graduate unemployment, or educated unemployment, is unemployment among people with an academic degree. Aggravating factors for unemployment are the rapidly increasing quantity of international graduates competing for an inadequate number...

2007 WD5Discovery[1]Discovered byMount Lemmon SurveyAndrea Boattini(unofficial credits)Discovery date20 November 2007DesignationsMinor planet categoryNEO · Apollo[1][2]Mars-crosserOrbital characteristics[2]Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5)Uncertainty parameter 5[2] · 0[1]Aphelion3.9289 AU (587.76 Gm)Perihelion0.991120 AU (148.2694 Gm)Semi-major axis2.4600 AU (368.01 Gm)...

Subject in Christian art Lamentation by Giotto, 1305 The Lamentation of Christ[1] is a very common subject in Christian art from the High Middle Ages to the Baroque.[2] After Jesus was crucified, his body was removed from the cross and his friends mourned over his body. This event has been depicted by many different artists. Lamentation works are very often included in cycles of the Life of Christ, and also form the subject of many individual works. One specific type of Lament...

German World War II submarine U-505, a typical Type IXC boat History Nazi Germany NameU-501 Ordered25 September 1939 BuilderDeutsche Werft, Hamburg Yard number291 Laid down12 February 1940 Launched25 January 1941 Commissioned30 April 1941 FateSunk on 10 September 1941 General characteristics Class and typeType IXC submarine Displacement 1,120 t (1,100 long tons) surfaced 1,232 t (1,213 long tons) submerged Length 76.76 m (251 ft 10 in) o/a 58.75 m (192 ft 9&...

هينديكورت ليه رانسارت شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالفرنسية: Hendecourt-lès-Ransart) الإحداثيات 50°12′19″N 2°43′55″E / 50.205277777778°N 2.7319444444444°E / 50.205277777778; 2.7319444444444 [1] [2] تقسيم إداري البلد فرنسا[3] التقسيم الأعلى باد كاليه خصائص جغرافية المساحة ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando l'omonimo singolo di Alex Britti, vedi Immaturi (singolo). ImmaturiUna scena del filmLingua originaleitaliano Paese di produzioneItalia Anno2011 Durata108 min Rapporto2,35:1 Generecommedia RegiaPaolo Genovese SoggettoPaolo Genovese SceneggiaturaPaolo Genovese ProduttoreMarco Belardi Casa di produzioneMedusa Film, Lotus Production in collaborazione con Libero e Technicolor Distribuzione in italianoMedusa Film FotografiaFabrizio Lucci MontaggioPatrizio Maro...

Metro-North Railroad station in New York TuxedoTuxedo station building, built in 1885 and renovated in the early 2010sGeneral informationLocation240 Route 17Tuxedo Park, New YorkCoordinates41°11′38″N 74°11′05″W / 41.1940°N 74.1848°W / 41.1940; -74.1848Owned byMetro-North RailroadLine(s)NS Southern Tier LinePlatforms1 side platformTracks1Connections Short Line Bus: 17M/MDConstructionStructure typeAt-gradeParking245 spaces[1]AccessibleNo[1]Oth...

Township in Burlington County, New Jersey, US Township in New Jersey, United StatesWillingboro Township, New JerseyTownship SealMotto: A Naturally Better Place to BeLocation of Willingboro Township in Burlington County highlighted in red (right). Inset map: Location of Burlington County in New Jersey highlighted in red (left).Census Bureau map of Willingboro Township, New JerseyWillingboro TownshipLocation in Burlington CountyShow map of Burlington County, New JerseyWillingboro TownshipL...

Questa voce sugli argomenti allenatori di calcio svizzeri e calciatori svizzeri è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Frank SéchehayeNazionalità Svizzera Calcio RuoloAllenatore (ex portiere) CarrieraSquadre di club1 1923-1929 Étoile Carouge? (?)1929-1931 Club Français? (?)1931-1934 Servette? (?)1934-1936 Losanna? (?) Nazionale 1927-1935 Svizzera37 (-?) Carrie...

Đừng nhầm lẫn với VTV7 hoặc Kênh Truyền hình Quốc hội Việt Nam. HTV7Quốc giaViệt NamKhu vựcphát sóngKhắp lãnh thổ Việt Nam và các nước Đông Nam ÁChương trìnhNgôn ngữTiếng ViệtĐịnh dạng hình1080i HDTVSở hữuChủ sở hữuĐài Truyền hình Thành phố Hồ Chí MinhKênh liên quanHTV1, HTV2 - Vie Channel, HTV3, HTV Key, HTV7, HTV9, HTV Thể ThaoLịch sửLên sóng1 tháng 1 năm 1984; ...

О древнем городе см. Дукля (древний город). У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Дукля. ГородДукляDukla Дворцово-парковый комплекс Флаг Герб 49°34′ с. ш. 21°41′ в. д.HGЯO Страна Польша Воеводство Подкарпатское воеводство Повят Кросненский повят Пре...

Papa Zefirino15º papa della Chiesa cattolicaElezione199 Fine pontificato20 dicembre 217 Predecessorepapa Vittore I Successorepapa Callisto I NascitaRoma, ? MorteRoma, 20 dicembre 217 SepolturaCatacombe di San Callisto Manuale San Zefirino Papa NascitaRoma, ? MorteRoma, 20 dicembre 217 Venerato daChiesa cattolica Santuario principaleCatacombe di San Callisto Ricorrenza20 dicembre Patrono diCaldari Manuale Zefirino, conosciuto anche come Zefferino o Geferino o Severi...

Ruler of the Zulu Kingdom from 1840 to 1872 For other people named Mpande, see Mpande (name). Mpande kaSenzangakhonaKing of Zulu KingdomAn 1849 portrait of King Mpande by George French AngasReign1840–1872Coronation1840PredecessorDinganeSuccessorCetshwayoBornc. 1798Died18 October 1872 (aged 73-74)ZululandBurialNodwengu28°17′54″S 31°25′34″E / 28.29833°S 31.42611°E / -28.29833; 31.42611 (Nodwengu)Spouseseveral wives (including Ngqumbazi, Monase, Noma...

この項目では、兵庫県丹波市について説明しています。 その他の「丹波市」については「丹波市 (曖昧さ回避)」をご覧ください。 ポケットモンスターシリーズに登場する「タンバシティ」については「ジョウト地方」をご覧ください。 「丹波篠山市」あるいは「京丹波町」とは異なります。 たんばし 丹波市 円通寺の紅葉 丹波市旗2004年11月1日制定 丹波市章 国 日...
