Pratap Singh of Jammu and Kashmir
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pengepakan kapas di Dédougou Koordinat: 12°28′N 3°28′W / 12.467°N 3.467°W / 12.467; -3.467 Dédougou adalah sebuah kota yang terletak di Burkina Faso bagian barat. Merupakan ibu kota Provinsi Mouhoun dan Region Boucle du Mouhoun. Suku utama di kota ini adalah Marka dan Bwa. Penduduk Dédougou mencapai 37.793 jiwa pada tahun 2006; 18.778 adalah pria dan 19.015 adalah wanita.[1] Ini adalah kota terbesar ke-9 di Burkina Faso.[1] Kota kembar Dowaai...
Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (mars 2014). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Comm...
Voce principale: Karlsruher Sport-Club Mühlburg-Phönix. Karlsruher Sport-Club Mühlburg-PhönixStagione 2008-2009Sport calcio Squadra Karlsruhe Allenatore Edmund Becker All. in seconda Ralf Becker Bundesliga17º posto Coppa di GermaniaOttavi di finale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Freis (34)Totale: Freis (37) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Freis (9)Totale: Freis (10) StadioWildparkstadion Maggior numero di spettatori30 600 vs Hertha Berlino (23 maggio 2009) Minor numero di spettator...

Government in existence 1921–1992 This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (April 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. Yo...

Indonesian replica ship Samudra Raksa viewed from the front History NameSamudra Raksa, Samudraraksa, Lallai Beke Ellau Launched2003 General characteristics TypeReplica ship Length19 metres (62.34 ft) Beam4.25 metres (13.94 ft) Draft1.5 metres (4.92 ft) PropulsionSails, paddles, and 2 × Dongjiong 22k outboard motor (22 PS (21.70 hp) each)[1][2] Sail planTanja sail. 3 sails on 2 vertical masts and 1 bowsprit. Speed9 knots (16.67 km/h)[3] No...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Christian Brothers College High School – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Private school in Town and Country , Missouri, United StatesChristian Brothers College High SchoolAddress1850 De La Sal...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Belarusian poet You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Belarusian. (February 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do not translate text that appe...

Order of bytes in a computer word Big-endian and Little-endian redirect here. For the conflicting ideologies in Gulliver's Travels, see Lilliput and Blefuscu § History and politics. For the specific use of endianness in date formats, see Calendar date. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Endianness – news · ...

Запрос «Котайк» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Котайкская областьԿոտայքի մարզ Герб 40°25′ с. ш. 44°45′ в. д.HGЯO Страна Армения Адм. центр Раздан Глава Романос Петросян История и география Дата образования 1995 Площадь 2 100 Население Населен�...

County in Oklahoma, United States County in OklahomaOsage CountyCountyOsage County CourthouseLocation within the U.S. state of OklahomaOklahoma's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 36°38′N 96°24′W / 36.63°N 96.4°W / 36.63; -96.4Country United StatesState OklahomaFounded1907Named forOsage NationSeatPawhuskaLargest cityHominyArea • Total2,304 sq mi (5,970 km2) • Land2,246 sq mi (5,820 km2) •...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une actrice mexicaine. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les conventions filmographiques. Elizabeth ÁlvarezBiographieNaissance 30 août 1977 (46 ans)Ciudad Juárez, État de Chihuahua, MexiqueNom de naissance Elizabeth Álvarez RonquilloNationalité MexicaineFormation Centro de Educación ArtísticaUniversité autonome du Chihuahua (en)Activités ActricePériode d'activité Depuis 2000Conjoint Jorge ...

Women marching in Joburg Pride parade in 2006 There have been pride parades in South Africa celebrating LGBT pride since 1990. South African pride parades were historically used for political advocacy protesting against legal discrimination against LGBT people, and for the celebration of equality before the law after the apartheid era.[1][2] They are increasingly used for political advocacy against LGBT hate crimes, such as the so-called corrective rape of lesbians in townshi...

Furniture in the ancient world From left to right: Image from the Standard of Ur, Ancient Egyptian chair, Dilmunite seal, ancient Greek bed, ancient Roman couch, ancient Indian chair, ancient Chinese bronze sculpture, mushiro mat, and Aztec Pottery. Ancient furniture was made from many different materials, including reeds, wood, stone, metals, straws, and ivory. It could also be decorated in many different ways. Sometimes furniture would be covered with upholstery, upholstery being padding, s...

State of North Dakota Staat van de Verenigde Staten (Details) Coördinaten 47°30'NB, 100°30'WL Algemeen Oppervlakte 183.272 km² (2,4% water) Inwoners 683.932 (3,83 inw./km²) Hoofdstad Bismarck Politiek Gouverneur Doug Burgum (R)(sinds 2016) Overig Tijdzone −6 / −7 Toegetreden 2 november 1889 Bijnaam Peace Garden State Website nd.gov Detailkaart Portaal Verenigde Staten North Dakota (Nederlands: Noord-Dakota) is een van de staten van de Verenigde Staten. De standaard...
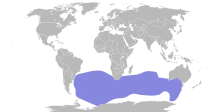
Seabird in the family Diomedeidae Sooty albatross Conservation status Endangered (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Procellariiformes Family: Diomedeidae Genus: Phoebetria Species: P. fusca Binomial name Phoebetria fusca(Hilsenberg, 1822)[2] Immature Stuffed specimen at the Natural History Museum, Vienna Sooty albatross on Crozet Island Sooty albatross on Amsterdam Island The sooty albatros...

Extinct genus of reptiles NakonanectesTemporal range: Campanian, 73 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ Life restoration Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Superorder: †Sauropterygia Order: †Plesiosauria Family: †Elasmosauridae Genus: †NakonanectesSerratos et al., 2017 Type species Nakonanectes bradtiSerratos et al., 2017 Nakonanectes bradti is an elasmosaurid plesiosaur of the late Cretaceous found in 2010 the st...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «Ciudad de Belice» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 12 de junio de 2010. Para otros usos de este término, véase Belice (desambiguación). Ciudad de Belice Ciudad más poblada de Belice De izquierda a derecha desde arriba: la Catedral de San Juan, la Casa de Gobierno, el Monumento a la Bandera de CARICOM, el Instituto Bliss...

Civilizations of South America's Andes Mountains This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Andean civilizations – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Part of a series onHuman history ↑ Prehistory (Stone Age) (Pleistocene e...
この項目では、政治家で実業家の野田俊作について説明しています。同名の精神科医・心理学者については「野田俊作 (精神科医・心理学者)」をご覧ください。 この記事には参考文献や外部リンクの一覧が含まれていますが、脚注による参照が不十分であるため、情報源が依然不明確です。 適切な位置に脚注を追加して、記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(2019年1...





