Potty parity in the United States
|
Read other articles:

Abdulrachman Setjowibowo Duta Besar Indonesia untuk FinlandiaMasa jabatan23 Juni 1979 – 24 Juni 1982PresidenSoeharto PendahuluMoekijatPenggantiSoerjadi KromomihardjoDirektur Jenderal AgrariaMasa jabatan29 Maret 1969 – 5 Agustus 1978PresidenSoeharto PendahuluSuyono SupartoBasuki Rachmat (penjabat)PenggantiDaryonoAnggota Dewan Perwakilan RakyatMasa jabatan25 Juni 1960 – 29 Maret 1969PresidenSoekarnoGrup parlemenABRI Informasi pribadiLahir(1916-09-21)21 September...

Eparki Agung Ivano-FrankivskArchieparchia StanislaopolitanaАрхиєпархія з Івано-ФранківськаGereja Katolik Yunani Ukraina Katedral KebangkitanLambang Eparki Agung Ivano-FrankivskLokasiNegara UkrainaStatistikLuas6.700 km2 (2.600 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2009)792272603,918 (76.2%)InformasiDenominasiGereja Katolik Yunani UkrainaGereja sui iurisGereja Katolik Yunani UkrainaRitusRitus BizantiumPendirian26 Maret 1885Katedra...
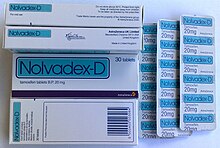
Drugs acting on the estrogen receptor Selective estrogen receptor modulatorDrug classTamoxifen, a nonsteroidal triphenylethylene antiestrogen and a widely used drug in the treatment of breast cancer.Class identifiersSynonymsSERM; Estrogen receptor agonist/antagonist; ERAAUseBreast cancer, infertility, osteoporosis, vaginal atrophy, dyspareunia, contraception, male hypogonadism, gynecomastia, breast pain, othersATC codeG03XCBiological targetEstrogen receptorLegal statusIn Wikidata Selective es...

Watchdog group advocating government reform For other uses, see Common Cause (disambiguation). Common CauseFounded1970; 54 years ago (1970)FounderJohn W. GardnerLocationWashington, D.C., U.S.Area served United StatesMethodAdvocacyWebsitecommoncause.org Common Cause is a watchdog group based in Washington, D.C., with chapters in 35 states. It was founded in 1970 by John W. Gardner, a Republican, who was the Secretary of Health, Education, and Welfare in the administration of ...

Domenico Tintoretto, Tancred Membaptis Clorinda, Museum of Fine Arts (Houston), 1585. Domenico Robusti, juga dikenal sebagai Domenico Tintoretto, (1560 – 17 Mei 1635) adalah seorang pelukis Italia asal Venesia. Ia dibesarkan di bawah bimbingan ayahnya, pelukis terkenal Jacopo Tintoretto. Referensi Edward Chaney and Timothy Wilks, The Jacobean Grand Tour: Early Stuart Travellers in Europe (I.B. Tauris: London, 2014) “Domenico Tintoretto.” Grove Art Online. “A Portrait by Domenico Tinto...

Indoor exhibition center in New Jersey, United States Asbury Park Convention HallAddress1300 Ocean AvenueLocationAsbury Park, New JerseyPublic transitNJ Transit at Asbury Park station North Jersey Coast Line NJT Bus: 832, 837 Asbury Park Convention HallU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesNew Jersey Register of Historic Places Show map of Monmouth County, New JerseyShow map of New JerseyShow map of the United StatesLocationOcean Avenue, Asbury Park, New JerseyCoordinates40°13...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Bicara Itu Ada Seninya – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke art...

Karen GillanGillan pada 2019Lahir28 November 1987 (umur 36)Inverness, Scotland, UKPendidikanItalia Conti Academy of Theatre ArtsPekerjaanAktris, artis suara, sutradara, model dan penulisTahun aktif2006–sekarangKaryaDaftar pertunjukanSuami/istriNick Kocher (m. 2022)Tanda tangan Karen Sheila Gillan (/ˈɡɪlən/; lahir 28 November 1987) adalah seorang aktris dan pembuat film Inggris. Dia mendapat pengakuan atas karyanya dalam film dan televisi Inggris...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Hamilton, BermudaKotaJalanan utama di Hamilton.Peta letak kota Hamilton di wilayah Bermuda.Koordinat: 32°17′35″N 64°46′55″W / 32.293°N 64.782°W / 32.293; -64.782Koordinat: 32°17′35″N 64°46′55″W / 32.293°N 64.782°W / 32.293; -64.782Negara Britania RayaWilayah Seberang Laut BermudaParokiPembrokeDidirikan1790Pemerintahan • WalikotaCharles R. Gosling[2]Luas • Total0,28 sq mi (70&...

Martian meteorite discovered in India Shergotty meteorite 50 milligram fragment of the Shergotty meteoriteTypeAchondriteClassMartian meteoriteGroupShergottiteParent bodyMarsCountryIndiaRegionSherghati, Gaya district, BiharFall date1865-08-25TKW5-kilogram (11 lb)Alternative namesSherghati meteorite Related media on Wikimedia CommonsThe Shergotty meteorite (Named after Sherghati) is the first example of the shergottite Martian meteorite family. It was a 5-kilogram (11 lb) meteori...

Balai kota Morley Morley adalah kota pasar dan kampung sipil dalam distrik metropolitan Kota Leeds, di West Yorkshire, Inggris. Wilayah ini terletak sekitar 5 mil (8 km) di barat-daya pusat kota Leeds. Bersamaan dengan Drighlington, Gildersome, Churwell, Tingley dan East/West Ardsley, kabupaten ini memiliki populasi 47.579 menurut sensus tahun 2001.[1] Bagian kampung sipil memiliki populasi 27.738. Kabupaten ini dibangun di atas tujuh bukit, sebagaimana Roma: Bukit Scatcherd, Buk...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 2010–11 Polish Cup – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2012) Football tournament season 2010–11 Polish CupTournament detailsCountry PolandTeams83Defending championsJagiellonia BiałystokFinal positionsChampionsLegia WarsawR...

Dialect of Mandarin Chinese Jiao–Liao MandarinRegionShandong and LiaodongNative speakers35 million (2019)[citation needed]Language familySino-Tibetan SiniticChineseMandarinJiao–Liao MandarinLanguage codesISO 639-3–ISO 639-6jliuLinguist Listcmn-jiaGlottologNonehuab1238 Central Plain GuanhuaLinguasphere79-AAA-bd[image reference needed] Jiaoliao or Jiao–Liao Mandarin (simplified Chinese: 胶辽官话; traditional Chinese: 膠遼官話; pinyi...

1983 single by Irene Cara Flashdance...What a FeelingSide-A label of US 7-inch vinyl releaseSingle by Irene Carafrom the album What a Feelin' and Flashdance: Original Soundtrack from the Motion Picture B-sideLove Theme from Flashdance (instrumental)Found ItReleasedMarch 1983RecordedEarly 1983Genre Pop[1] dance-pop[2] disco[3] Length3:55LabelCasablancaNetworkComposer(s)Giorgio MoroderLyricist(s)Keith ForseyIrene CaraProducer(s)Giorgio MoroderIrene Cara singles chronolog...

Eiga Pretty Cure All Stars - Minna de utau♪ Kiseki no mahō!Tutte le Pretty Cure fino alla 13ª serie (versione CGI)Titolo originale映画 プリキュアオールスターズ みんなで歌う♪奇跡の魔法! Lingua originalegiapponese Paese di produzioneGiappone Anno2016 Durata70 min Rapporto1,78:1 Genereanimazione, fantastico, musicale RegiaYutaka Tsuchida SoggettoIzumi Tōdō SceneggiaturaIsao Murayama Casa di produzioneToei Animation MusicheHiroshi Takaki Art directorYosh...

Невадский испытательный полигонангл. Nevada Test Site Солдаты на ядерном полигоне в Неваде в 6 милях от эпицентра взрыва 21-килотонного снаряда «Dog» операции Buster-Jangle в ноябре 1951 г. Расположение полигона Расположение в 105 км от Лас-Вегаса, США Принадлежность США Тип Ядерный и�...

You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Japanese article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Consider ad...

US modern Western crime drama television series LongmireTitle cardGenreCrime dramaNeo-WesternBased onWalt Longmire Mysteries book seriesby Craig JohnsonDeveloped by John Coveny Hunt Baldwin Starring Robert Taylor Katee Sackhoff Lou Diamond Phillips Adam Bartley Cassidy Freeman Bailey Chase Country of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons6No. of episodes63 (list of episodes)ProductionExecutive producers John Coveny Hunt Baldwin Christopher Chulack Greer Shephard Michael M. ...
