Pedra Furada
|
Read other articles:

Statua di Pieter Mauritz Retief al Monumento ai Voortrekker a Pretoria Pieter Mauritz Retief, Piet Retief (Wellington, 12 novembre 1780 – kwaMatiwane, 6 febbraio 1838), è stato un generale e politico sudafricano. Fu considerato uno dei maggiori leader della grande migrazione boera chiamata Grande Trek. Biografia Copia del trattato firmato da Rietief e Dingane in data 4 febbraio 1838 Pieter Mauritz Retief nacque il 12 novembre 1780 a Wagenmakersvallei, l'attuale Wellington, quinto dei dieci...

Balai kota Les Marêts. Les MarêtsNegaraPrancisArondisemenProvinsKantonVilliers-Saint-GeorgesAntarkomuneCommunauté de communes du ProvinoisPemerintahan • Wali kota (2008-2014) Gérard Cognyl • Populasi1135Kode INSEE/pos77275 / 2 Population sans doubles comptes: penghitungan tunggal penduduk di komune lain (e.g. mahasiswa dan personil militer). Les Marêts merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Seine-et-Marne di region Île-de-France di utara-tengah Prancis. Demog...

Chronologies Couverture du Petit Journal, représentant l'arrestation de Ravachol (1858-1892), 16 avril 1892.Données clés 1889 1890 1891 1892 1893 1894 1895Décennies :1860 1870 1880 1890 1900 1910 1920Siècles :XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Vert, République centrafricaine, Co...

Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Halaman bahasa acak Bahasa Maliseet-Passamaquoddy skicinuwatuwewakon Dituturkan diKanada, Amerika SerikatWilayahNew Brunswick, MaineEtnisSuku Maliseet serta Suku Passamaquoddy (2010)PenuturRincian data penutur Jumlah penutur beserta (jika ada) metode pengambilan, jenis, tanggal, dan tempat.[1] 590 (2011) Rumpun bahasaAlgik AlgonquiaAlgonquian TimurMa...

American college football season 2013 Stanford Cardinal footballPac-12 championPac-12 North Division co-championPac-12 Championship Game, W 38–14 vs. Arizona StateRose Bowl, L 20–24 vs. Michigan StateConferencePac-12 ConferenceDivisionNorth DivisionRankingCoachesNo. 10APNo. 11Record11–3 (7–2 Pac-12)Head coachDavid Shaw (3rd season)Offensive coordinatorMike Bloomgren (1st season)Offensive schemeMultipleDefensive coordinatorDerek Mason (3rd season)Base ...

BPJS KesehatanJenisBadan Hukum PublikIndustriKesehatanDidirikan1968 (sebagai BPDPK)KantorpusatJln. Let. Jend. Suprapto Cempaka Putih Jakarta Pusat, JakartaTokohkunciAli Ghufron Mukti (Direktur Utama)Abdul Kadir(Ketua Dewan Pengawas)PendapatanRp 3.64 triliun (2016)Laba bersihRp 763.88 miliar (2016)Total asetRp 12.49 triliun (2016)PemilikNegara Republik IndonesiaSitus webwww.bpjs-kesehatan.go.id Logo Askes sebelum menjadi BPJS Kesehatan Gedung kantor pusat PT Askes Indonesia. BPJS Kesehatan (Ba...

Mohammad Uswanas Bupati FakfakMasa jabatan17 Februari 2016 – 17 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurAbraham Octavianus AtururiEko Subowo (Pj.)Dominggus MandacanWakilAbraham SopaheluwakanPendahuluOktovianus Mayor (Pj.)PenggantiAli Baham Temongmere (Plh.)Untung TamsilMasa jabatan7 Desember 2010 – 7 Desember 2015PresidenSusilo Bambang YudhoyonoJoko WidodoGubernurTimbul Pudjianto (Plt.)Abraham Octavianus AtururiTanribali Lamo (Pjs.)Abraham Octavianus AtururiWakilDonatus ...
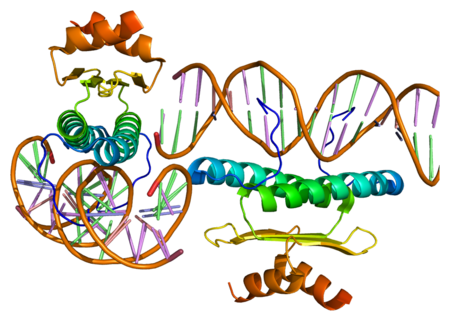
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens BORCS8-MEF2BAvailable structuresPDBHuman UniProt search: PDBe RCSB List of PDB id codes1N6J, 1TQEIdentifiersAliasesBORCS8-MEF2B, LOC729991-MEF2B, MEF2B, MEF2BNB-MEF2B, BORCS8-MEF2B readthrough, RSRFR2External IDsGeneCards: BORCS8-MEF2B Gene ontologyMolecular function DNA-binding transcription factor activity RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding DNA binding DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymer...

Romanian professional footballer Florea Dumitrache Dumitrache with Dinamo BucureștiPersonal informationFull name Florea DumitracheDate of birth (1948-05-22)22 May 1948Place of birth Bucharest, RomaniaDate of death 26 April 2007(2007-04-26) (aged 59)Place of death Bucharest, RomaniaHeight 1.74 m (5 ft 9 in)Position(s) StrikerYouth career1961–1963 Rapid București1963–1964 TUG București1964–1965 Dinamo BucureștiSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1965–1976 Dinamo B...

松岡禎丞2022年松岡禎丞配音演员昵称つぐつぐ[1]国籍 日本出生 (1986-09-17) 1986年9月17日(37歲) 日本北海道十勝支廳帶廣市出道作品AKX20000(東之伊甸)代表作品藤島鳴海(神的記事本)桐人/桐谷和人(刀劍神域)草薙護堂(Campione 弒神者!)神田空太(櫻花莊的寵物女孩)空(NO GAME NO LIFE 遊戲人生)愛徒勇氣(漫畫家與助手)安藝倫也(不起眼女主角培育�...

Fox River Butter company building in Chicago Cream receiving at the Fox River Butter Co, World War I The Chicago Butter and Egg Board, founded in 1898, was a spin-off entity of the Chicago Produce Exchange. In the year 1919, it was re-organized as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Roots of the Chicago Butter and Egg Board are traceable to the 19th century.[1] Initially, the Chicago Butter and Egg Board traded only two types of contracts, butter and eggs. Over several decades, it ...
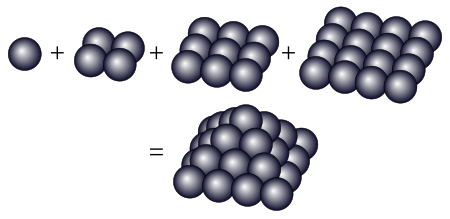
1 + 4 + 9 + 16 = 30 は四角錐数 四角錐数(しかくすいすう、square pyramidal number)は球を右図のように1段目に1個、2段目に4個、3段目に9個、…というように正四角錐の形に積んだとき、そこに含まれる球の総数にあたる自然数である。つまり1から順に平方数をいくつか加えた数のことである。 四角錐数を小さい順に列記すると 1, 5, 14, 30, 55, 91, 140, 204, 285, 385, 506, 650, 819, 1015, 124...

1950 studio album by Jo StaffordAutumn in New YorkStudio album by Jo StaffordReleased1950 [10 LP] [8 track version] 1955 [12 LP] [12 track version]RecordedOctober–December 1947 Some Enchanted Evening recorded March 1949 Almost Like Being in Love recorded March 1947 Sometimes I'm Happy recorded November 1945GenreTraditional popLength33:15 [1955 version]LabelCapitolDRGJo Stafford chronology American Folk Songs(1950) Autumn in New York(1950) Songs for Sunday Evening(1950) Professional ...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Hennessy dan Hennessey. Jas Hennessy & Co.Didirikan1765; 258 tahun lalu (1765)PendiriRichard HennessyKantorpusatCognac, PrancisWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaTokohkunciLaurent Boillot, Chairman & CEO; Boris de Vroomen, Direktur InternasionalProdukKonyakPendapatan €954,2 juta (2012)PemilikChris HennessyIndukLVMH (66%)Diageo (34%)Situs webHennessy.com Jas Hennessy & Co., atau biasa disebut sebagai Hennessy (pengucapan bahasa Prancis: [ɛnsi]), ada...

大坂直美大坂なおみ2020年的大坂國家/地區 日本居住地 美国加利福尼亞州比佛利山出生 (1997-10-16) 1997年10月16日(26歲) 日本大阪市中央區身高1.80米(5英尺11英寸)教練維姆·費塞特(英语:Wim Fissette)(2020–2022;2024–)轉職業年2013持拍右手持拍(雙手反拍)職業獎金$21,683,713美元[1]單打成績職業戰績280–160(63.64%)冠軍頭銜7最高排名1(2019年1月28日)現...

Canadian computer scientist and Professor of Industrial Engineering Mark Stephen Fox (born 1952) is a Canadian computer scientist, Professor of Industrial Engineering and Distinguished Professor of Urban Systems Engineering at the University of Toronto, known for the development of Constraint Directed Scheduling in the 1980s[1][2] and the TOVE Project to develop an ontological framework for enterprise modeling and enterprise integration in the 1990s.[3][4] Biog...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne s'appuie pas, ou pas assez, sur des sources secondaires ou tertiaires (septembre 2019). Pour améliorer la vérifiabilité de l'article ainsi que son intérêt encyclopédique, il est nécessaire, quand des sources primaires sont citées, de les associer à des analyses faites par des sources secondaires. MetLife BuildingLe MetLife Building.HistoireArchitectes The Architects Collaborative, Pietro B...

ロビン・ギブRobin Gibb 2008年アラブ首長国連邦ドバイにて基本情報出生名 Robin Hugh Gibb生誕 (1949-12-22) 1949年12月22日 マン島、ダグラス出身地 Rised in: イングランド、マンチェスターMoved to: オーストラリア、ブリスベン死没 (2012-05-20) 2012年5月20日(62歳没) イングランド、ロンドンジャンル ディスコ、ポップ、ロック、ソフトロック職業 シンガーソングライター担当楽器 ボ�...

Part of a series on theAnthropology of kinship Basic concepts Family Lineage Affinity Consanguinity Marriage Incest taboo Endogamy Exogamy Moiety Monogamy Polygyny Polygamy Concubinage Polyandry Bride price Bride service Dowry Parallel / cross cousins Cousin marriage Levirate Sororate Posthumous marriage Joking relationship Clan Cohabitation Fictive / Milk / Nurture kinship Descent Cognatic / Bilateral Matrilateral Lineal Collateral House society Avunculat...
この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 独自研究が含まれているおそれがあります。(2023年10月) あまり重要でない事項が過剰に含まれているおそれがあり、整理が求められています。(2023年10月) この項目では、ポピュラー音楽の名称について説明しています。イギリスのバンドについては「ニュー・ミュージック (バ...



