Paterson Ewen
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Go LiveAlbum mini karya ONFDirilis07 Oktober 2019 (2019-10-07)Direkam2019Genre K-pop[1] Dance[2] Durasi16:39BahasaKoreaLabel WM Entertainment Stone Music Entertainment ProduserMonoTree[3]Kronologi ONF We Must Love(2019) Go Live(2019) Spin Off(2020) Singel dalam album Go Live WhyDirilis: 7 Oktober 2019 Video musikWhy di YouTube Go Live (ditulis sebagai GO LIVE) adalah album mini keempat dari grup vokal pria asal Korea Selatan ONF. Album ini dirilis pada tanggal...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat DeWalt (disambiguasi). Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: DeWalt – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Agustus 2012) DeWalt Industrial Tool CompanyJenisAnak perusahaanIndustriManufakturDidirikan1924; 1...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Cinta segitiga – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Artikel ini bukan mengenai Teori segitiga cinta, Ménage à trois, atau Cinta Segitiga. Bagian dari seri tentangCintaRed-outline heart i...
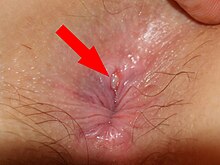
Not to be confused with intergluteal cleft. Medical conditionAnal fissureOther namesFissure in ano, rectal fissureAn anal fissureSpecialtyGastroenterology An anal fissure is a break or tear in the skin of the anal canal. Anal fissures may be noticed by bright red anal bleeding on toilet paper and undergarments, or sometimes in the toilet. If acute they are painful after defecation,[1] but with chronic fissures, pain intensity often reduces. Causes Most anal fissures are caused b...

City in Minnesota, United States City in Minnesota, United StatesInver Grove Heights, MinnesotaCityNickname: Inver GroveInteractive map outlining Inver Grove HeightsLocation of Inver Grove Heights, MinnesotaCoordinates: 44°50′15″N 93°3′6″W / 44.83750°N 93.05167°W / 44.83750; -93.05167CountryUnited StatesStateMinnesotaCountyDakotaEstablished1852IncorporatedMarch 9, 1965Government • TypeWeak Mayor–Council • MayorBrenda DietrichA...

Stasiun Tachikōji立小路駅Stasiun Tachikōji pada April 2009LokasiTomizawa, Mogami-machi, Mogami-gun, Yamagata-ken 999-6105JepangKoordinat38°44′31″N 140°32′34″E / 38.7420°N 140.5427°E / 38.7420; 140.5427Koordinat: 38°44′31″N 140°32′34″E / 38.7420°N 140.5427°E / 38.7420; 140.5427Operator JR EastJalur■ Jalur Rikuu TimurLetak62.8 kilometer dari KogotaJumlah peron1 peron sampingInformasi lainStatusTanpa stafSitus webSit...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (septembre 2012). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ?...

Political party in East and West Pakistan For other uses, see National Awami Party (disambiguation). National Awami Party National People's PartyUrdu nameنیشنل عوامی پارٹیBengali nameন্যাশনাল আওয়ামী পার্টিAbbreviationNAPLeaderAbdul Hamid Khan BhashaniFoundersAbdul Hamid Khan Bhashani and Yar Mohammad KhanFounded1957 (1957)Dacca, East Pakistan, PakistanDissolvedNovember 30, 1967 (1967-11-30)Merger ofAPPSindh Mah...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

British flautist Sutherland in 2007 Rowland Sutherland is a British flautist, who studied flute at the Guildhall School of Music and Drama with Kathryn Lukas, Philippa Davies and Peter Lloyd and participated in master classes given by the late Geoffrey Gilbert. He studied jazz with the late pianist Lionel Grigson in the mid-1980s.[1] Sutherland performs in new music ensembles, jazz groups, symphony orchestras, various non-Western groups, pop outfits and as a soloist. Many of Sutherlan...

Village in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland For the townland of Tobermore, see Tobermore (townland). Human settlement in Northern IrelandTobermoreIrish: An Tobar MórThe village centreTobermoreLocation within Northern IrelandPopulation578 (2001 Census)Irish grid referenceH8396• Belfast34 mi (55 km)DistrictMid-UlsterCountyCounty LondonderryCountryNorthern IrelandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townMAGHERAFELTPostcode districtBT45Dialling cod...

US presidential campaign Pony Up for Vermin SupremeCampaign2020 United States presidential election (Libertarian primaries)CandidateVermin SupremePerennial candidate and performance artistSpike CohenPodcasterAffiliationLibertarian PartyStatusInactiveAnnouncedMay 18, 2019SuspendedMay 23, 2020Key peopleDesarae Lindsey (campaign manager)Richard Manzo (chief strategist)ReceiptsUS$59,068.35[1] (May 13, 2020)SloganThis is the way.In on the joke.Pony up America.Websiteverminsupreme2020....

Country in South Asia from 1948 to 1972 Ceylon[1]1948–1972 Top: Flag (1948–1951) Bottom: Flag (1951–1972) Coat of arms Anthem: Sri Lanka Matha (1951–1972) God Save the King (1948–1951) Capitaland largest cityColombo6°56′04″N 79°50′34″E / 6.93444°N 79.84278°E / 6.93444; 79.84278Common languagesSinhalaTamilEnglishReligion Buddhism (official)HinduismChristianityIslamDemonym(s)CeyloneseGovernmentUnitary parliamentary constitutional m...

一中同表,是台灣处理海峡两岸关系问题的一种主張,認為中华人民共和国與中華民國皆是“整個中國”的一部份,二者因為兩岸現狀,在各自领域有完整的管辖权,互不隶属,同时主張,二者合作便可以搁置对“整个中國”的主权的争议,共同承認雙方皆是中國的一部份,在此基礎上走向終極統一。最早是在2004年由台灣大學政治学教授張亞中所提出,希望兩岸由一中各表�...

South-Indian Literature by language This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may contain excessive or irrelevant examples. Please help improve the article by adding descriptive text and removing less pertinent examples. (July 2020) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this art...

Football stadium in London, England Selhurst ParkSelhurst Park aerial view (2023)Full nameSelhurst ParkLocationSelhurst, London, SE25EnglandCoordinates51°23′54″N 0°5′8″W / 51.39833°N 0.08556°W / 51.39833; -0.08556Public transit Norwood Junction Selhurst Thornton HeathOwnerCrystal PalaceCapacity25,486[1]Field size101 by 68 metres (110.5 yd × 74.4 yd)[1]SurfaceGrassMasterScoreboardJumboTronConstructionBroke ground1922 / 1923Bui...

Two ComediansArtiste Edward HopperDate 1965Dimensions (H × L) 73,7 × 101,6 cmLocalisation époux Sinatra puis collection privée modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Two Comedians (Deux comédiens[1], parfois Deux Personnages comiques[2] en français) est une peinture à l'huile sur toile réalisée par l'artiste américain Edward Hopper en 1965 et conservée dans une collection privée depuis une vente par Sotheby's/Christie's à New York, le 16 novembre ...

Not to be confused with Royal Naval Barracks, Chatham. Royal Marine Barracks, Chatham Chatham, Kent WRNS officers and ratings drilling at the Royal Marine Barracks, ChathamRoyal Marine Barracks, ChathamLocation within KentCoordinates51°23′17″N 0°31′28″E / 51.388°N 0.5245°E / 51.388; 0.5245TypeRoyal Marines BaseSite historyBuilt1779Built forAdmiraltyIn use1779-1950Garrison informationOccupantsChatham Division, Royal Marines The Royal Marine Barrack...

Suburb of Dublin, Ireland Suburb in County Dublin, Leinster, IrelandClonskeagh Cluain SceachSuburbClonskeaghLocation in IrelandCoordinates: 53°18′30″N 6°14′25″W / 53.308333°N 6.240278°W / 53.308333; -6.240278CountryIrelandProvinceLeinsterCountyCounty DublinLocal government areasDublin, Dún Laoghaire–RathdownPopulation (2011) • Urban11,273[1]Eircode (Routing Key)D14Area code01 (+3531) Clonskeagh Green Clonskeagh or Clonskea (/klɒ...
