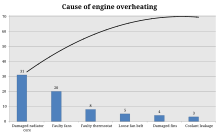
Pareto principle
|
Read other articles:

Bayam gajah Amaranthus tricolor TaksonomiDivisiTracheophytaSubdivisiSpermatophytesKladAngiospermaeKladmesangiospermsKladeudicotsKladcore eudicotsOrdoCaryophyllalesFamiliAmaranthaceaeSubfamiliAmaranthoideaeGenusAmaranthusSpesiesAmaranthus tricolor Linnaeus, 1753 lbs Amaranthus tricolor, yang dikenal sebagai bayam gajah, [1] adalah spesies tumbuhan berbunga dalam genus Amaranthus, bagian dari famili Amaranthaceae . Tanaman ini sering dibudidayakan untuk keperluan hias dan kuliner. Ini d...

نظام بلوري ثلاثي في علم المعادن (بالإنجليزية: trigonal crystal system أو rhombohedral lattice system) هو أحد السبعة أنظمة التبلور مثل النظام البلوري المكعب والنظام البلوري السداسي.[1] تتبلور بعض الأملاح والمعادن في النظام الثلاثي، مثل ملح الدولوميت والكوارتز، البزموت والأنتيمون والكوروند وغ...

Untuk tempat lain yang bernama sama, lihat Labuhan Haji. Labuhan HajiKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiNusa Tenggara BaratKabupatenLombok TimurPemerintahan • Camat-Populasi • Total51,603 jiwa jiwaKode Kemendagri52.03.17 Kode BPS5203071 Luas49,57 km²Desa/kelurahan-3 Labuhan Haji adalah sebuah kecamatan di kabupaten Lombok Timur, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Indonesia. Sejarah Pemandangan laut di Labuhan Haji pada tahun 1925 Berdasarkan sejarah daerah ini dinamakan Labuhan ...

Space news website & media organisation NASASpaceflightScreenshot Screenshot of the NASASpaceflight.com website from May 2023Type of siteYouTube channel, Online newspaper, & internet forumAvailable inEnglishFounder(s)Chris BerginURLwww.nasaspaceflight.comCommercialYesRegistrationOptionalLaunchedMarch 16, 2005; 19 years ago (2005-03-16)Current statusOnline NASASpaceFlightYouTube informationChannel NASASpaceFlight Years active2019–presentGenres Livest...

Sloane StephensStephens at the 2017 Wimbledon ChampionshipsKebangsaan Amerika SerikatTempat tinggalFort Lauderdale, Florida, Amerika Serikat[1]Lahir20 Maret 1993 (umur 31)[2]Plantation, Florida, Amerika SerikatTinggi170 m (557 ft 9 in)Memulai pro2009[3]Tipe pemainTangan kanan (two-handed backhand)PelatihKamau Murray (2015–18, 2019–)Total hadiahUS$15,466,260Situs web resmisloanestephens.comTunggalRekor (M–K)296–206 (58.96%)Gelar6Peringka...
Bernkastel-Wittlich rural district of Rhineland-Palatinate (en) Tempat Negara berdaulatJermanNegara bagian di JermanRheinland-Pfalz NegaraJerman Ibu kotaWittlich PendudukTotal110.833 (2014 )GeografiLuas wilayah1.168 km² [convert: unit tak dikenal]Ketinggian337 m Berbatasan denganRhein-Hunsrück Birkenfeld Trier-Saarburg Bitburg-Prüm Daun (distrik) Cochem-Zell Organisasi politikAnggota dariLandkreistag Rheinland-Pfalz (en) Informasi tambahanZona waktuUTC+1 UTC+2 Kode NUTSDEB22 Lai...
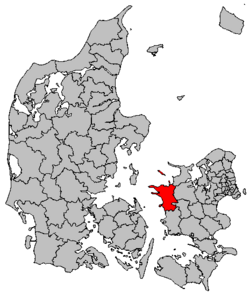
Municipality in Zealand, DenmarkKalundborg Municipality Kalundborg Kommune (Danish)Municipality Coat of armsCoordinates: 55°40′50″N 11°05′53″E / 55.68064°N 11.09797°E / 55.68064; 11.09797CountryDenmarkRegionZealandEstablished1 January 2007SeatKalundborgGovernment • MayorMartin Damm (V)Area • Total604 km2 (233 sq mi)Population (1. January 2023)[1] • Total48,602 • Density80/km2 (...

Gambar 2 dimensi dari Hati Dahalia, lambo Buton dari Jinato. Ia dibangun pada tahun 1990, menggunakan lambung lambo Buton dan sistem layar lambo Sulawesi Barat (layar nade). Gambar ini adalah jiplakan dari foto yang diambil oleh Nick Burningham, yang bertemu dengan perahu ini pada tahun 1990.Istilah lambo atau lamba merujuk kepada dua jenis perahu tradisional dari Indonesia. Lambo Buton Sebuah lambo dengan 2 tiang dan 1 tiang, 1907–1915. Lambo adalah versi Indonesia dari perahu dagang kecil...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Walter Mantovani Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Attaccante Termine carriera 1949 Carriera Squadre di club1 1937-1938 SIME Popoli? (?)1938-1939 Carpi18 (4)1939-1944 Mantova97 (67)1945-1946 Suzzara? (?)1946-1949 Reggiana56 (20) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segna...

Narrow body jet airliner Boeing 727 A stretched 727-200 of Iberia Role Narrow-body jet airlinerType of aircraft National origin United States Manufacturer Boeing Commercial Airplanes First flight February 9, 1963[1] Introduction February 1, 1964, with Eastern Air Lines Status In cargo and executive service[a] Primary users Líneas Aéreas SuramericanasTotal Linhas Aereas Produced 1962–1984 Number built 1,832[3] The Boeing 727 is an American narrow-body airliner ...

5 Detik dan Rasa Rindu Sampul bukuPenyuntingFuad JauharudinPengarangPrilly LatuconsinaNegaraIndonesiaBahasaIndonesiaGenrePuisiromantismePenerbitThe PanasDalam PublishingTanggal terbitFebruari 2017Jenis mediaBukuHalaman156 halamanISBNISBN 978-602-61007-0-2 5 Detik dan Rasa Rindu adalah buku kumpulan puisi oleh aktris Indonesia, Prilly Latuconsina. 5 Detik dan Rasa Rindu merupakan buku debut kepenulisan Prilly yang diterbitkan pada bulan Februari 2017 melalui The PanasDalam Publishing...

Arms of Liechtenstein The music of Liechtenstein has produced an internationally renowned composer in Josef Rheinberger (1839–1901), who was mentor to Engelbert Humperdinck and a friend of Franz Liszt. The national anthem of Liechtenstein is Oben am jungen Rhein, which was written in 1850 by Jakob Josef Jauch to the tune of God Save the King, the national anthem of the United Kingdom. One of the most notable singers from Liechtenstein is Al Walser. Other notable acts that have had success ...

Dutch darts player For the American baseball player, see Danny Jansen. Darts playerDanny JansenJansen in 2022Personal informationFull nameDanny JansenNicknameThe Mullet[1]Born (2002-05-15) 15 May 2002 (age 21)[2]Holten, NetherlandsHome townHolten, NetherlandsDarts informationPlaying darts since2018Darts26g Bull'sLateralityRight-handedWalk-on musicWelcome to the Jungle by Guns N' RosesOrganisation (see split in darts)PDC2022– (Tour Card: 2022-2023)Cur...

For Tromsø's former airport, see Tromsø Airport, Skattøra. Airport in Tromsøya, TromsøTromsø AirportTromsø lufthavnIATA: TOSICAO: ENTCSummaryAirport typePublicOwner/OperatorAvinorServesTromsø, NorwayLocationLangnes, Tromsøya, TromsøFocus city for Lufttransport Widerøe Elevation AMSL10 m / 32 ftCoordinates69°40′53″N 018°55′04″E / 69.68139°N 18.91778°E / 69.68139; 18.91778Websiteavinor.noMapTOSRunways Direction Length Surface m ft 18...

On the Flip Side is an hour long television musical with music by Burt Bacharach, lyrics by Hal David, and a book by Robert Emmett.[1] The story concerns rock 'n' roll star Carlos O'Conner, whose career is on the skids after early success at age 20. He tries to make a comeback, but his style is out of date. He prays for a miracle, and gets one, when Angie and the Celestials, four angels, join his act.[2] On the Flip Side was made for the anthology series ABC Stage 67, and it w...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Sekolah Tinggi Analis Bakti Asih adalah perguruan tinggi yang sejak tahun 200 telah menyelenggarakan pendidikan keanalisan. Penyelenggaraan dimulai dengan berdirinya Akademi Analis Kesehatan Bakti Asih pada tahun 1999. Salah satu bentuk kepercayaan pem...

Национальное аэрокосмическое агентство Азербайджана Штаб-квартира Баку, ул. С. Ахундова, AZ 1115 Локация Азербайджан Тип организации Космическое агентство Руководители Директор: Натиг Джавадов Первый заместитель генерального директора Тофик Сулейманов Основание Осн�...

Distrik adalah wilayah administratif tingkat satu di Uganda. No.peta Nama Ibu kota Kode Region Populasi(sensus 2014) 1 Abim Abim UG-314 Utara 107,966 2 Adjumani Adjumani UG-301 Utara 225,251 3 Amolatar Amolatar UG-315 Utara 147,166 4 Amuria Amuria UG-216 Timur 270,928 5 Apac Apac UG-302 Utara 368,626 6 Arua Arua UG-303 Utara 782,077 7 Budaka Budaka UG-217 Timur 207,597 8 Bugiri Bugiri UG-201 Timur 382,913 9 Bukwa Bukwa UG-220 Timur 89,356 10 Buliisa Buliisa UG-416 Barat 113,161 11 Bundibugyo ...

Gunung SoputanTitik tertinggiKetinggian1.784 m (5.853 ft)Koordinat1°06′37″S 124°43′55″E / 1.11032°S 124.73197°E / -1.11032; 124.73197Koordinat: 1°06′37″S 124°43′55″E / 1.11032°S 124.73197°E / -1.11032; 124.73197 GeografiLetakSulawesi Utara, IndonesiaGeologiJenis gunungStratovolcanoLetusan terakhir5 Oktober 2018 Gunung Soputan adalah gunung berapi yang terletak di provinsi Sulawesi Utara, Indonesia. Gunung ...

Pemilihan umum federal Jerman Barat 19531949195706 September 1953 (1953-09-06)[1]Seluruh 509 kursi dalam Bundestag255 kursi untuk meraih status mayoritasKehadiran pemilih86.0% (suara layak)[2]Kandidat Partai pertama Partai kedua Partai ketiga Ketua Konrad Adenauer Erich Ollenhauer Franz Blücher Partai CDU/CSU SPD FDP Kursi sebelumnya 144 140 57 Kursi yang dimenangkan 249 162 53 Perubahan kursi 105 22 4 Suara Populer 12,443,981 7,94...