Northern Combat Area Command
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
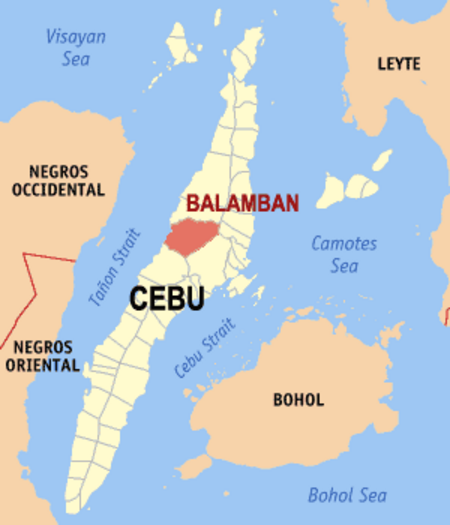
Balamban Munisipalitas di Filipina Tempat categoria:Articles mancats de coordenades Negara berdaulatFilipinaRegion di FilipinaVisayas TengahProvinsi di FilipinaCebu NegaraFilipina Pembagian administratifAbucayan (en) Aliwanay (en) Arpili (en) Baliwagan (pob.) (en) Bayong (en) Biasong (en) Buanoy (en) Cabagdalan (en) Cabasiangan (en) Cambuhawe (en) Cansomoroy (en) Cantibas (en) Cantuod (en) Duangan (en) Gaas (en) Ginatilan (en) Hingatmonan (en) Lamesa (en) Liki (en) Luca (en) Matun‑og (en) N...

Kalubu esut[1] Echymipera kalubu Status konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN7018 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasMammaliaOrdoPeramelemorphiaFamiliPeramelidaeGenusEchymiperaSpesiesEchymipera kalubu (J.B. Fischer, 1829) Tata namaProtonimPerameles kalubu Distribusi lbs Kalubu esut ( Echymipera kalubu ), atau kusu-tanah duri biasa, adalah sejenis kusu-tanah . Moncongnya panjang bahkan menurut standar bandicoot. Bagian atasnya berwarna coklat kemerahan kasar, berbintik-bintik berduri dan...

John A. Ryan Skating ArenaLocation1 Paramount PlWatertown, MA 02472OwnerCity of WatertownOperatorCity of WatertownCapacity1,250 (hockey)TenantsBentley Falcons men's ice hockey (1977-2018) East Coast Jumbos The John A. Ryan Skating Arena is a 1,000-seat hockey rink owned and operated by the city of Watertown, Massachusetts. It served as the home ice of the Bentley University Falcons men's ice hockey team from 1977 to 2018, until the team moved into its new on-campus home, the Bentley Arena, in...
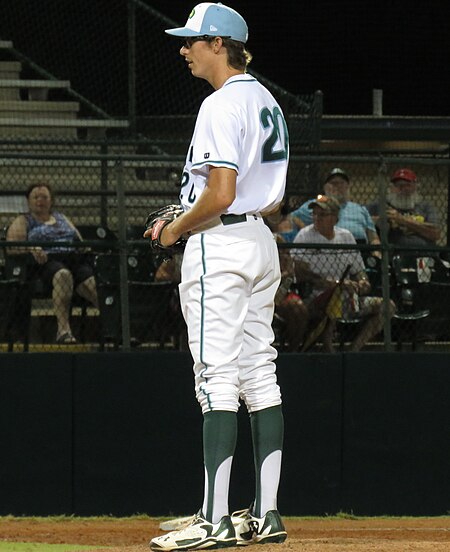

American baseball player (born 1993) Baseball player Jimmy HergetHerget with the Daytona Tortugas in 2016Los Angeles Angels – No. 46PitcherBorn: (1993-09-09) September 9, 1993 (age 30)Tampa, Florida, U.S.Bats: RightThrows: RightMLB debutJuly 7, 2019, for the Cincinnati RedsMLB statistics (through 2023 season)Win–loss record7–8Earned run average3.47Strikeouts126 Teams Cincinnati Reds (2019) Texas Rangers (2020–2021) Los Angeles Angels (2021–present) Jimmy Matthew ...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Fermat little theorem di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan pe...

U.S. TV series Getting OnGenreDark comedyMedical comedyCreated by Mark V. Olsen Will Scheffer Based onGetting On(BBC Four series)by Jo BrandJoanna ScanlanVicki PepperdineWritten byMark V. OlsenWill SchefferDirected byMiguel ArtetaHoward DeutchBecky MartinStarring Laurie Metcalf Alex Borstein Niecy Nash Mel Rodriguez Country of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons3No. of episodes18 (list of episodes)ProductionExecutive producers Geoff Atkinson Jane Tranter Jo Brand Joanna ...

Atypical antipsychotic Not to be confused with sulpyrine. SulpirideClinical dataTrade namesDogmatil, othersAHFS/Drugs.comInternational Drug NamesRoutes ofadministrationBy mouth (tablets, capsules, solution), intramuscular injectionATC codeN05AL01 (WHO) Legal statusLegal status BR: Class C1 (Other controlled substances)[1] UK: POM (Prescription only) In general: ℞ (Prescription only) Pharmacokinetic dataBioavailability25–40%[2][3]Protei...

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2017年8月)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 密西西比州 美國联邦州State of Mississippi 州旗州徽綽號:木蘭之州地图中高亮部分为密西西比州坐标:30°13'N�...

迪奥斯达多·马卡帕加尔Diosdado Pangan Macapagal第9任菲律賓總統任期1961年12月30日—1965年12月30日前任卡洛斯·P·加西亚继任费迪南德·马科斯第6任菲律賓副總統任期1957年12月30日—1961年12月30日前任卡洛斯·P·加西亚继任伊曼纽尔·佩莱斯 个人资料出生(1910-09-28)1910年9月28日 美屬菲律賓馬尼拉逝世1997年4月21日(1997歲—04—21)(86歲) 菲律賓馬卡迪墓地 菲律賓馬卡迪達義市英...

British TV game show This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Gameshow Marathon British game show – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Gameshow MarathonPresented byAnt & DecVernon KayBen ShephardJameliaNarrated byPeter Dickso...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Banda. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (mars 2018). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : ...

Overview of the use and culture of cannabis in Florida, U.S. Part of a series onCannabis ArtsCulture 420 (chan) Books Magu (deity) Names Religion Judaism Latter-day Saints Sikhism Smoke-in Spiritual use Sports Stoner film Stoner rock Terms Chemistry Cannabinoid receptors Cannabinoid receptor type 1 Cannabinoid receptor type 2 Cannabinoids 2-AG 2-AGE, Noladin ether AEA CBC CBL CBD CBDV CBG CBN CBV NADA THC THCV Virodhamine Synthetic cannabinoids AM-2201 CP-55940 Dimethylheptylpyran HU-210 HU-3...

Waria (lakuran dari kata wanita dan pria) atau wadam (lakuran dari kata hawa dan adam) atau jantina (lakuran dari kata jantan dan betina) adalah laki-laki yang lebih suka berperan dan berperilaku sebagai perempuan dalam kehidupan sehari-harinya. Secara fisik, mereka adalah laki-laki (memiliki alat kelamin layaknya laki-laki), tetapi mereka mengekspresikan identitas gendernya sebagai perempuan. Keberadaan waria telah tercatat sejak lama dalam sejarah dan memiliki posisi yang berbeda-beda dalam...

Class of medications AnticonvulsantDrug classClass identifiersSynonymsAntiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugsUseEpilepsyATC codeN03Biological targetBrainLegal statusIn Wikidata Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures.[1] Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder[2][3] and b...

Transrapid Eslogan Volar a altitud cero[1]Tipo de producto tren de levitación magnéticaProducido por Siemens AGthyssenkrupp[editar datos en Wikidata] El Transrapid es un tren de tecnología alemana que se desplaza mediante levitación magnética. El tren circula sobre una viga situada sobre pilares a varios metros de altura sobre el suelo. La vía está constituida por un caballete de hormigón que incorpora un sistema de levitación magnética que eleva el tren a 15 m...

Swiss politician This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jean-Pascal Delamuraz Jean-Pascal Delamuraz (1 April 1936, in Vevey – 4 October 1998 in Lausanne) was a Swiss politician and member of the Swiss Federal Council (1983–1998). He obtained a degree in political science in 1960 from ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Apocalisse (disambigua). Il termine apocalisse deriva dal greco apokálypsis (ἀποκάλυψις), composto da apó (ἀπό, da, usato come prefissoide anche in apostrofo, apogeo, apostasia) e kalýptō (καλύπτω, nascondo, come in Calipso), significa un gettar via ciò che copre, un togliere il velo, letteralmente scoperta o disvelamento, rivelazione.[1] Il concetto sembrerebbe essersi originato presso gli ebrei ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Universo (disambigua). L'universo e le sue componenti L'universo è comunemente definito come il complesso che racchiude tutto lo spazio e ciò che contiene,[1][2][3][4] cioè la materia e l'energia, che comprendono pianeti, stelle, galassie, e il contenuto dello spazio intergalattico.[5][6] L'osservazione scientifica dell'universo, la cui parte osservabile ha un diametro di circa...

The 1962–63 Volleyball Women's European Cup was the third edition of the official competition for European women's volleyball national champions. It was contested by eleven teams, with West Germany making its debut, and the quarterfinals and semifinals were reinstated instead of the previous edition's group stage. WVC Dynamo Moscow defeated AZS Warsaw to win its second title.[1] Preliminary round Team #1 Agg. Team #2 1st 2nd Montpellier UC 6–0 CDUL Lisboa 3–0 3–0 Dynamo Berlin...

Dalam artikel ini, nama keluarganya adalah Phạm. Phạm Nhật VượngVượng pada 2019Lahir5 Agustus 1968 (umur 56)Hanoi, VietnamKebangsaanVietnamWarga negaraVietnamAlmamaterUniversitas Pertambangan dan Geologi Hanoi[1]Moscow Geological Prospecting Institute[2]PekerjaanPengembang propertiOrganisasiVingroupDikenal atasMiliuner Vietnam pertama, orang Vietnam terkaya, pendiri dan ketua VingroupKekayaan bersihUS$9 miliar[3]Suami/istriPhạm Thu HươngAnak3T...