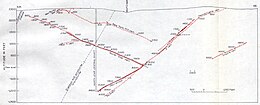
North Star Mine and Powerhouse
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Lakshadwip Peta India dengan letak Lakshadwip ditandai. Ibu kota - Koordinat Kavaratti - 10°34′N 72°37′E / 10.57°N 72.62°E / 10.57; 72.62 Kota terbesar Kavaratti Populasi (2011) - Kepadatan 64.473 (Ke-7) - 2.015/km² Area - Distrik 32 km² (Ke-7) - 1 Zona waktu UTC +5:30 Pembentukan - Administrator 1 November, 1956 - Shri Rajendra Kumar Bahasa resmi Malayalam &a...

The following is a list of current National Lacrosse League (NLL) team rosters. Each National Lacrosse League team may carry twenty-three players on their active roster.[1] In addition, teams may keep two players on their practice team. Also, teams may place players on a number of restricted lists, such as injured reserve, unable to play, hold out, and protected. For each game, teams are allowed to dress a total of eighteen players. This must include two goaltenders and sixteen runne...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la littérature. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. RomancierPortrait du romancier Sir Walter Scott, auteur de romans historiques.PrésentationForme féminine RomancièreSecteur littératureCompétencesCompétences requises Écriture littéraireCodesROME (France) E1102 - Écriture d'ouvrages, de livresmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Un romancie...

Эта статья описывает ситуацию применительно лишь к одному региону, возможно, нарушая при этом правило о взвешенности изложения. Вы можете помочь Википедии, добавив информацию для других стран и регионов. Встреча на 85-й годовщине Питтсбургской ассоциации глухих Протесту...

Cyclisme aux Jeux olympiques d'été de 2004 Généralités Sport Sport cycliste Éditions 25e Lieu(x) Athènes Participants 464 Disciplines Route, Piste, VTT Épreuves 18 Navigation Sydney 2000 Pékin 2008 modifier Aux Jeux olympiques de 2004, trois disciplines de cyclisme sont au programme : le cyclisme sur piste, le cyclisme sur route et le vélo tout terrain. Au total, sur le 464 cyclistes qui participent, on retrouve 334 hommes et 130 femmes, représentant 61 pays différents. ...

Public transport This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Rhein-Neckar-Verkehr – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Logo of Rhein-Neckar-Verkehr Rhein-Neckar-Verkehr GmbH (RNV, Rhine-Neckar Transport Ltd) is a company operati...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) جان ميلو معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالفرنسية: Jean Émile Van Gindertael) الميلاد سنة 1906 [1][2][3] الوفاة سنة 1993 (86–87 سنة)[4][5][1][2]&...

ロバート・デ・ニーロRobert De Niro 2011年のデ・ニーロ生年月日 (1943-08-17) 1943年8月17日(80歳)出生地 アメリカ合衆国・ニューヨーク州ニューヨーク市身長 177 cm職業 俳優、映画監督、映画プロデューサージャンル 映画、テレビドラマ活動期間 1963年 -配偶者 ダイアン・アボット(1976年 - 1988年)グレイス・ハイタワー(1997年 - )主な作品 『ミーン・ストリート』(1973年)...

Guangzhou International Women's Open 2011 Sport Tennis Data 17 - 24 settembre Edizione 8ª Superficie Cemento Campioni Singolare Chanelle Scheepers Doppio Hsieh Su-wei / Zheng Saisai 2010 2012 Il Guangzhou International Women's Open 2011 (chiamato anche WANLIMA Guangzhou International Women's Open per ragioni di sponsor) è stato un torneo di tennis giocato sul cemento all'aperto. È stata l'8ª edizione del torneo che fa parte della categoria International nell'ambito del WTA Tour 2011. Il ...
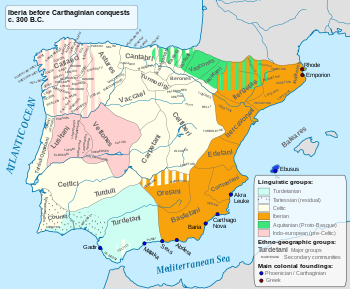
The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC. The Cerretani or Ceretani were ancient pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula who occupied what became the modern-day Cerdanya, in the valley Segre and part of Aragon. Their neighbours from the east were Ausetani and from the south Ilergetes. Their capital was Julia libyca, modern Llívia.[1] They are noted in Greek and Roman geographical treatises.[2] References ^ Spain, Encyclopaedia Britannica (5 ed.), 1815, p. 492 ^...

1995 Pink Floyd concert video directed by David Mallet Pulse2006 DVD coverDirected byDavid MalletProduced byDavid GilmourJames GuthrieSteve O'RourkeLana TophamStarringPink FloydCinematographyDavid MalletEdited byDave GardenerMusic byPink FloydDistributed byPMISony Music Video (SMV) EnterprisesRelease dates6 June 1995 (VHS)10-11 July 2006 (DVD)Running time145 minutesLanguageEnglish Pulse (stylised as P•U•L•S•E) is a concert video by Pink Floyd of their 20 October 1994 concert at Earls ...

French footballer and manager Gérard Gili Gili as Umm Salal managerPersonal informationDate of birth (1952-08-07) 7 August 1952 (age 71)Place of birth Marseille, FranceHeight 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)[1]Position(s) GoalkeeperYouth career1967–1971 CA GombertoisSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1971–1973 Marseille 1973–1976 Bastia 1976–1978 Rouen 1978–1979 Olympique Alès 1979–1980 Rouen 1980–1981 Bastia 1981–1983 Marseille Managerial career1988–1990 Ma...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Jena. Cet article est une ébauche concernant les États-Unis. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Pétition à Los Angeles pour les six de Jena, en octobre 2007. Les « six de Jena » (Jena Six) est le nom donné à un groupe de six adolescents noirs accusés dans un premier temps de tentative de meurtre pour avoir frappé un étudiant blanc à la Jena Hig...

ХуторАрпачин 47°13′ с. ш. 40°10′ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия Субъект Федерации Ростовская область Муниципальный район Багаевский Сельское поселение Манычское История и география Основан 1757 Высота центра 6 м Часовой пояс UTC+3:00 Население Население 1469 человек (2010)...

Державний комітет телебачення і радіомовлення України (Держкомтелерадіо) Приміщення комітетуЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 2003Керівне відомство Кабінет Міністрів УкраїниРічний бюджет 1 964 898 500 ₴[1]Голова Олег НаливайкоПідвідомчі ор...

American college football season 2015 Michigan Wolverines footballCitrus Bowl championCitrus Bowl, W 41–7 vs. FloridaConferenceBig Ten ConferenceDivisionEast DivisionRankingCoachesNo. 11APNo. 12Record10–3 (6–2 Big Ten)Head coachJim Harbaugh (1st season)Offensive coordinatorTim Drevno (1st season)Offensive schemePro-styleDefensive coordinatorD. J. Durkin (1st year), Greg Mattison (bowl game)Base defense4–3MVPJehu ChessonCaptains Joe Bolden (Senior yea...
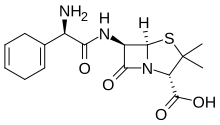
Chemical compound EpicillinClinical dataATC codeJ01CA07 (WHO) Identifiers IUPAC name (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-Amino-2-(1-cyclohexa-1,4-dienyl)acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid CAS Number26774-90-3 YPubChem CID71392ChemSpider64486 NUNII3LU1L73C8YCompTox Dashboard (EPA)DTXSID60181288 ECHA InfoCard100.043.623 Chemical and physical dataFormulaC16H21N3O4SMolar mass351.42 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive image SMILES O=C(...

Art museum in Place Yves Klein - Nice cedex FRANCEMusée d'art moderne et d'art contemporainLocation within NiceEstablished21 June 1990 (1990-06-21)LocationPlace Yves Klein - 06364 Nice cedex 4 FRANCECoordinates43°42′05″N 7°16′43″E / 43.7014°N 7.2785°E / 43.7014; 7.2785TypeArt museumVisitors135714 per year (2012)Websitewww.mamac-nice.orgThe MAMAC is closed as of Jan 2024 for four years of renovations. [1] The Musée d'art moderne et d...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Евтушенко. Вадим Евтушенко Общая информация Полное имя Вадим Анатольевич Евтушенко Родился 1 января 1958(1958-01-01)[1][2] (66 лет)Пятихатки, Днепропетровская область, Украинская ССР, СССР Гражданство СССР Украина...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: 2019 in Russia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2019) This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. (September 2022) List of events ← 2018 2017 2016 2019 in Russia → 2020 2021 2022 Decades: 1990s 2000s ...