North Carolina Sullivan Acts
|
Read other articles:

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Silvia Kurniady mempunyai Background Sekolah di William Blue Hotel Management School, Sydney di tahun 1996 - 2002. Kemudian Dia kembali ke Indones...

Men's basketball at the 2022 Asian GamesVenuesHangzhou Olympic Sports Centre GymnasiumZhejiang University Zijingang GymnasiumDates26 September – 6 October 2023Nations16Medalists Philippines Jordan China← 20182026 → Main article: Basketball at the 2022 Asian Games The men's 5-on-5 basketball tournament at the 2022 Asian Games was held in Hangzhou, China from 26 September to 6 October 2023.[1] Squads Bahrain Chi...

Air 1 radio station in Hiawatha–Cedar Rapids, Iowa KXGMHiawatha, IowaBroadcast areaCedar Rapids, IowaFrequency89.1 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingAir1ProgrammingFormatChristian worshipSubchannelsHD2: K-LoveHD3: Radio Nueva VidaAffiliationsAir1OwnershipOwnerEducational Media FoundationHistoryFirst air dateJuly 2002Former call signsKWOF-FM (2002–2008)KXGM-FM (2008–2015)Call sign meaningGod'x Extreme Grace and MercyTechnical information[1]Licensing authorityFCCFacility ID85165ClassC3ERP3,60...

Biografi ini memerlukan lebih banyak catatan kaki untuk pemastian. Bantulah untuk menambahkan referensi atau sumber tepercaya. Materi kontroversial atau trivial yang sumbernya tidak memadai atau tidak bisa dipercaya harus segera dihapus, khususnya jika berpotensi memfitnah.Cari sumber: Desy Genoveva – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Desy GenovevaDesy pada tahun 2019La...

Dog vaccination against rabies Vaccination of dogs is the practice of animal vaccination applied to dogs. Programs in this field have contributed both to the health of dogs and to the public health. In countries where routine rabies vaccination of dogs is practiced, for example, rabies in humans is reduced to a very rare event. Currently, there are geographically defined core vaccines and individually chosen non-core vaccine recommendations for dogs. A number of controversies surrounding adve...

Lina HeydrichDi Praha, sehari sebelum serangan yang menyebabkan kematiannya, Reinhard Heydrich dan istrinya Lina menghadiri konser musik Richard Bruno Heydrich di Waldstein Palace, 26 Mei 1942.LahirLina Mathilde von Osten(1911-06-14)14 Juni 1911Fehmarn, Schleswig-Holstein, Kekaisaran JermanMeninggal14 Agustus 1985(1985-08-14) (umur 74)Fehmarn, Schleswig-Holstein, Jerman BaratKebangsaanJermanNama lainLina ManninenSuami/istri Reinhard Heydrich (m. 1931;...

Девіз UNIX у формі номерного знака Генеалогічне дерево Unix-систем UNIX® (Ю́нікс) — це сімейство багатозадачних комп'ютерних операційних систем, що підтримують одночасне використання багатьма користувачами. Воно походить від оригінального «AT&T Unix», розробленого впродов�...

Bagian dari seriGereja Katolik menurut negara Afrika Afrika Selatan Afrika Tengah Aljazair Angola Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Chad Eritrea Eswatini Etiopia Gabon Gambia Ghana Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guinea Khatulistiwa Jibuti Kamerun Kenya Komoro Lesotho Liberia Libya Madagaskar Malawi Mali Maroko Mauritania Mauritius Mesir Mozambik Namibia Niger Nigeria Pantai Gading Republik Demokratik Kongo Republik Kongo Rwanda Sao Tome dan Principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra Leone Somalia Somaliland ...

Television series This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Take the High Road – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Take the High RoadOpening titlesGenreSoap operaCreated byDon HoughtonCountry of originUnited KingdomOriginal languageEngli...
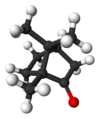
Camphre Structure du camphre Identification Nom UICPA 1,7,7-triméthylbicyclo[2,2,1]heptan-2-one Synonymes 2-bornanone2-camphanone No CAS 76-22-2 (±) No ECHA 100.000.860 No CE 200-945-0 FEMA 4513 Apparence cristaux incolores ou blancs, d'odeur caractéristique[1]. Propriétés chimiques Formule C10H16O [Isomères] Masse molaire[2] 152,233 4 ± 0,009 4 g/mol C 78,9 %, H 10,59 %, O 10,51...

Chemical compound Not to be confused with Cyclexanone. CyclazodoneClinical dataRoutes ofadministrationOralATC codenoneLegal statusLegal status In general: legal Identifiers IUPAC name (RS)-2-(cyclopropylamino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one CAS Number14461-91-7 YPubChem CID26701ChemSpider24875 NUNIIO8U55ZRL9KChEMBLChEMBL2106536 NChemical and physical dataFormulaC12H12N2O2Molar mass216.240 g·mol−13D model (JSmol)Interactive imageChiralityRacemic mixture SMILES C1CC1NC2=N...

Swedish politician (1943–2023) Per GahrtonMember of ParliamentIn office1976 to 1979, 1988 to 1991, 1994 to 1995Member of the European ParliamentIn office1995 to 2004 Personal detailsBorn(1943-02-02)2 February 1943Malmö, SwedenDied19 September 2023(2023-09-19) (aged 80)Hörby, SwedenPolitical partyLiberal PartyGreen Party Carl Per Gunnar Gahrton (2 February 1943 – 19 September 2023) was a Swedish politician. He was a member of Parliament, holding a seat for the Liberal Party from 197...

American baseball player (born 1985) Baseball player Bud NorrisNorris with the Los Angeles Angels in 2017PitcherBorn: (1985-03-02) March 2, 1985 (age 39)Greenbrae, California, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutJuly 29, 2009, for the Houston AstrosLast MLB appearanceSeptember 28, 2018, for the St. Louis CardinalsMLB statisticsWin–loss record67–90Earned run average4.45Strikeouts1,153 Teams Houston Astros (2009–2013) Baltimore Orioles (2013–2015) Sa...

Charles George HerbermannLahir(1840-12-08)8 Desember 1840Saerbeck, PrusiaMeninggal24 Agustus 1916(1916-08-24) (umur 75)New York, New YorkTempat pemakamanCalvary CemeteryPendidikanCollege of St. Francis XavierPekerjaanPengajar, sejarawan The Catholic Encyclopedia; sebuah karya rujukan internasional tentang konstitusi, doktrin, disiplin, dan sejarah Gereja Katolik Charles George Herbermann (8 Desember 1840 – 24 Agustus 1916) adalah seorang profesor dan sejarawan Jerman-Ame...

Country in West Asia and Southeast Europe This article is about the country. For the bird, see Turkey (bird). For other uses, see Turkey (disambiguation). Türkiye redirects here. For other uses, see Türkiye (disambiguation). Republic of TürkiyeTürkiye Cumhuriyeti (Turkish) FlagAnthem: İstiklal MarşıIndependence MarchCapitalAnkara39°55′N 32°51′E / 39.917°N 32.850°E / 39.917; 32.850Largest cityIstanbul41°1′N 28°57′E / 41.017...
In computer and telecommunications networks, presence information is a status indicator that conveys ability and willingness of a potential communication partner—for example a user—to communicate. A user's client provides presence information (presence state) via a network connection to a presence service, which is stored in what constitutes his personal availability record (called a presentity) and can be made available for distribution to other users (called watchers) to convey their av...

1988 live album by Dexter GordonBoth Sides of MidnightLive album by Dexter GordonReleased1988RecordedJuly 20, 1967VenueJazzhus Montmartre, Copenhagen, DenmarkGenreJazzLength53:14LabelBlack LionBLP 60103ProducerAlan BatesDexter Gordon chronology The Squirrel(1967) Both Sides of Midnight(1988) Body and Soul(1967) The Montmartre Collection Vol. 1 cover Both Sides of Midnight is a live album by American saxophonist Dexter Gordon recorded at the Jazzhus Montmartre in Copenhagen, Denmark in...

Private university in New York City, New York, US For other uses, see Columbia University (disambiguation). This article needs editing to comply with Wikipedia's Manual of Style. Please help improve the content. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article may contain improper use of non-free material. Please review their use according to the criteria and guidelines. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Columbia UniversityCoat of armsLatin: Univers...

English novelist (1949–2023) For the landscape and documentary photographer, see Martin Amis (photographer). SirMartin AmisFRSLAmis in 2014BornMartin Louis Amis(1949-08-25)25 August 1949Oxford, EnglandDied19 May 2023(2023-05-19) (aged 73)Lake Worth Beach, Florida, USPen nameHenry TilneyAlma materExeter College, OxfordNotable worksThe Rachel Papers (1973)Money (1984)London Fields (1989)Notable awardsKnight Bachelor 2023 Spouse Antonia Phillips (m. 1984&#...

Football league seasonLiga Primera de NicaraguaSeason2018–19ChampionsApertura:ManaguaClausura: Real EstelíRelegatedUNAN ManaguaCONCACAF LeagueManagua Real EstelíMatches played65Goals scored181 (2.78 per match)Top goalscorerApertura: Lucas Dos Santos (15 goals) – Clausura: TBD –Biggest home winApertura: Real Estelí 5-0 Ocotal Clausura: TBD TBDBiggest away winApertura: Real Madriz 1-6 Managua Clausura: TBD TBDHighest scoringApertura: Ocotal 4-3 Real Estelí Real Madriz 1-6 Managua...

