Nagapattinam Lok Sabha constituency
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Koordinat: 47°45′26″N 16°37′20″E / 47.75722°N 16.62222°E / 47.75722; 16.62222 Perlintasan batas dimana piknik Pan-Eropa diadakan. Otto von Habsburg Piknik Pan-Eropa (Jerman: Paneuropäisches Picknickcode: de is deprecated ; bahasa Hungaria: páneurópai piknik; bahasa Slowakia: Paneurópsky piknik) adalah sebuah unjuk rasa damai yang diadakan di perbatasan Austria-Hungaria di dekat Sopron, Hungaria pada 19 Agustus 1989. Pembukaan gerbang perbatasan ...

Juan Carlos I adalah kapal serbu amfibi serba guna di Angkatan Laut Spanyol (Armada Española). Serupa dalam peran untuk banyak kapal induk, kapal memiliki lompatan ski untuk operasi STOVL, dan dilengkapi dengan pesawat tempur AV-8B Harrier II. Kapal ini dinamai untuk menghormati Juan Carlos I, mantan Raja Spanyol. Kapal baru memainkan peran penting dalam armada, sebagai platform yang tidak hanya menggantikan LST Newport kelas Hernán Cortés dan Pizarro untuk mendukung mobilitas Marinir dan...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang wilayah administratif di Hindia Belanda dalam kurun waktu 1817–1942. Untuk wilayah administratif di Indonesia sejak 2000, lihat Banten. Untuk tempat lain yang bernama sama, lihat Banten (disambiguasi). Keresidenan Banten1817–1942StatusKeresidenanIbu kotaSerangKelompok etnik SundaJawaAgama Islam (mayoritas)Sejarah • Didirikan 1817• Dibubarkan 1942 Didahului oleh Digantikan oleh kslKesultanan Banten Jawa Barat Sekarang bagian dariBa...

Political party in Mexico National Democratic Front Frente Democrático NacionalLeaderCuauhtémoc CárdenasFounded1988Dissolved1988Merger ofPMSPARMPFCRNPPSCoalición Obrera, Campesina y Estudiantil del IstmoUnión Popular Revolucionaria Emiliano ZapataCentral Campesina CardenistaCentral Independiente de Obreros Agrícolas y CampesinosAsamblea de Barrios de la Ciudad de MéxicoUnión de Colonias PopularesMerged intoParty of the Democratic RevolutionIdeologyDemocratic socialismLef...

Racism against Romani people Not to be confused with Anti-Romanian sentiment. Anti-Romani protest in České Budějovice, Czech Republic, 29 June 2013 Part of a series onDiscrimination Forms Institutional Structural Attributes Age Caste Class Dialect Disability Genetic Hair texture Height Language Looks Mental disorder Race / Ethnicity Skin color Scientific racism Rank Sex Sexual orientation Species Size Viewpoint Social Arophobia Acephobia Adultism Anti-albinism Anti-autism Anti-hom...

Part of the LGBT rights seriesLegal status ofsame-sex unions Marriage Andorra Argentina Australia Austria Belgium Brazil Canada Chile Colombia Costa Rica Cuba Denmark Ecuador Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Iceland Ireland Luxembourg Malta Mexico Netherlands1 New Zealand2 Norway Portugal Slovenia South Africa Spain Sweden Switzerland Taiwan United Kingdom3 United States4 Uruguay Recognized Israel5 Civil unions andregistered partnerships Bolivia Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Hungary Ita...

Loi constitutionnelle du 10 juillet 1940 Données clés Recto de l'acte constitutionnel numéro 2. Présentation Pays État français Type Loi constitutionnelle Branche Droit constitutionnel Adoption et entrée en vigueur Adoption 10 juillet 1940 Abrogation 9 août 1944 Lire en ligne Consulter Lois constitutionnelles de 1875 (IIIe République) Loi constitutionnelle du 2 novembre 1945 (Gouvernement provisoire de la République française) modifier La loi constitutionnelle du 10 jui...

Métropole du Grand Nancy Administration Pays France Région Grand Est Département Meurthe-et-Moselle Forme Métropole Siège Nancy Communes 20 Président Mathieu Klein (PS) Budget 778 150 000 € (2021) Date de création communauté urbaine : 1995 Métropole : 2016 Code SIREN 245400676 Démographie Population 257 412 hab. (2021) Densité 1 809 hab./km2 Géographie Superficie 142,30 km2 Localisation Localisation en Meurthe-et-Moselle. Liens ...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Aldo Fagiuoli Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex difensore) Carriera Squadre di club1 1911-1915 Hellas9 (0)1919-1927 Padova156 (24) Carriera da allenatore 1926-1927 Padova1927-1928 Verona1929-1930 Padova 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le ...

Childhood friend of Adolf Hitler This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: August Kubizek – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) August KubizekAugust Kubizek in his youthBorn(1888-08-03)3 August 1888Linz, Austria-Hungary (now Austria)Died23...

Japanese commercial CubeSat WE WISHA collection of CubeSats at Tsukuba Space Center prior to their launch in 2012, with WE WISH visible on the far leftMission typeTechnology demonstrationAmateur radioEarth observationOperatorMeisei Amateur Radio ClubCOSPAR ID2012-038F (1998-067CS)SATCAT no.38856Mission duration158 days (achieved)100 days (planned) Spacecraft propertiesSpacecraft typeCubeSatBusCubeSatManufacturerMeisei ElectricMeisei Amateur Radio ClubLaunch mass1 kg (2.2 lb)Dimensio...

This article is about the city. For the Saudi Aramco residential compound, see Saudi Aramco Residential Camp in Dhahran. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Dhahran – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) City in Eastern Province, Sau...

15th Army GroupFormation badgeActive1943–45CountryUnited Kingdom & United States, with numerous allies attachedAllegianceAllies of World War IITypeArmy groupRoleArmy Group HeadquartersSize1,200,000CommandersNotablecommandersHarold AlexanderMark W. ClarkMilitary unit The 15th Army Group was an army group in World War II, composed of the British Eighth Army and initially the Seventh United States Army (1943), replaced by the Fifth United States Army (from January 1944), which apart from ...

Grand Prix F1 Jepang 2005 merupakan balapan Formula 1 pada 9 Oktober 2005 di Sirkuit Suzuka. Lomba dimenangkan oleh Kimi Raikkonen yang menyalip Giancarlo Fisichella di lap terakhir lomba.[1] Pembalap tuan rumah dari tim BAR-Honda, yaitu Takuma Sato didiskualifikasi dari hasil akhir lomba karena tabrakan di lap ke-10 dengan Jarno Trulli yang menyebabkan pembalap Italia itu harus mundur dari balapan. Lomba Pos No Pembalap Tim Lap Waktu/Tersingkir Grid Poin 1 9 Kimi Raikkonen McLaren-Me...

Radio station in Springfield, OhioWEECSpringfield, OhioBroadcast areaDayton metropolitan areaFrequency100.7 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingHope 100.7ProgrammingFormatWorship musicOwnershipOwnerStrong Tower Christian Media(World Evangelistic Enterprise Corporation)Sister stationsWFCJHistoryFirst air dateDecember 15, 1961; 62 years ago (December 15, 1961)Call sign meaningWorld Evangelistic Enterprise CorporationTechnical informationLicensing authorityFCCClassBERP50,000 wattsHAAT143 meters (...
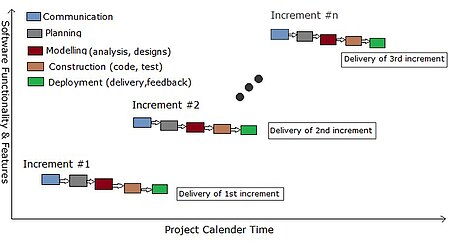
Part of a series onSoftware development Core activities Data modeling Processes Requirements Design Construction Engineering Testing Debugging Deployment Maintenance Paradigms and models Agile Cleanroom Incremental Prototyping Spiral V model Waterfall Methodologies and frameworks ASD DevOps DAD DSDM FDD IID Kanban Lean SD LeSS MDD MSF PSP RAD RUP SAFe Scrum SEMAT TDD TSP UP XP Supporting disciplines Configuration management Deployment management Documentation Software quality assurance Projec...

Greek footballer Nikos Liberopoulos Liberopoulos in 2012Personal informationFull name Nikolaos LiberopoulosDate of birth (1975-08-04) 4 August 1975 (age 48)Place of birth Filiatra, GreeceHeight 1.87 m (6 ft 2 in)Position(s) Forward, attacking midfielderSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1991–1993 Erani Filiatra 53 (33)1993–1996 Kalamata 78 (20)1996–2003 Panathinaikos 185 (72)2003–2008 AEK Athens 142 (66)2008–2010 Eintracht Frankfurt 50 (10)2010–2012 AEK Athens ...

Science education center in Pennsylvania, US The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guidelines for companies and organizations. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted.Find sources: Nurture Nature Center – news&...

33rd professional season of the top-flight football league in Mexico Football league seasonPrimera División de MéxicoSeason1974–75ChampionsToluca (3rd title)RelegatedCiudad MaderoChampions' CupLeónMatches played392Goals scored1,125 (2.87 per match)Top goalscorerHoracio López Salgado (25 goals)← 1973–74 1975–76 → Statistics of the Mexican Primera División for the 1974–75 season. Overview UANL was promoted to Primera División. Segunda División semifinalists, UASLP-Pumas ...

Football clubMSV Duisburg IIFull nameMeidericher Spielverein 02 e.V. DuisburgNickname(s)Die Zebras (The Zebras)Founded1902 (club)1958/1959 (reserve team)Dissolved2016GroundStadion MeiderichCapacity5,000 Home colours Away colours MSV Duisburg II was a German football team located in Duisburg, North Rhine-Westphalia. They were the reserve team of MSV Duisburg. History The reserve team was founded in 1958 by the club direction of Meidericher SV which was the name of MSV Duisburg before the city...

