Museo Regional de la Ceramica, Tlaquepaque
|
Read other articles:

Hilda ManafeHilda Manafe sebagai Anggota Dewan Perwakilan Daerah Republik Indonesia periode 2019–2024 Senator Dewan Perwakilan DaerahDapil Nusa Tenggara TimurPetahanaMulai menjabat 1 Oktober 2019PresidenJoko WidodoKetua DPDLa Nyalla Mattalitti Informasi pribadiLahir07 Juli 1964 (umur 59)Kupang, Nusa Tenggara TimurSuami/istriDr. Jefirstson Richset Riwu Kore, MM., MHAnak2Orang tuaJosia Nehemia Manafe (ayah)Alma materUniversitas Pendidikan Nasional DenpasarSekolah Tinggi Ilmu Manajeme...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang Bacaan Taurat Mingguan Yudaisme pada parsyah Emor. Untuk album mini Les Savy Fav, lihat Emor: Rome Upside Down. Sang Penista (gambar abad ke-16 karya Niccolò dell'Abbate) Emor (אֱמֹר — Ibrani untuk bicara, kata kelima, dan kata distinsif pertama, dalam parsyah tersebut) adalah bacaan Taurat Mingguan (פָּרָשָׁה, parashah) ke-31 dalam siklus bacaan Taurat Yahudi tahunan dan kedelapan dalam Kitab Imamat. Parsyah tersebut berisi aturan-aturan pe...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Betina (disambiguasi). Simbol untuk dewi Romawi Venus, yang sering digunakan untuk melambangkan jenis kelamin betina dan perempuan. Betina adalah jenis kelamin sesuatu ataupun sebagian organisme yang memiliki vagina untuk menghasilkan ovum. Betina setara dengan perempuan pada jenis kelamin manusia. Perempuan Artikel utama: perempuan Manusia betina disebut sebagai perempuan. Bagi manusia, terdapat banyak komponen (selain dari genetik) yang menentukan jenis kelamin bi...

Genre of newspaper This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Alternative newspaper – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) An alternative newspaper is a type of newspaper that eschews comprehensive coverage of general news in favor...

Township in the American state of Missouri Township in Missouri, United StatesCote Sans Dessein TownshipTownshipCoordinates: 38°38′18″N 092°00′07″W / 38.63833°N 92.00194°W / 38.63833; -92.00194CountryUnited StatesStateMissouriCountyCallawayArea • Total48.82 sq mi (126.43 km2) • Land47.29 sq mi (122.49 km2) • Water1.52 sq mi (3.95 km2) 3.12%Elevation[1]551 ft ...

American mixed martial arts fighter Kendall GroveBornKendall Grove (1982-11-12) November 12, 1982 (age 41)Wailuku, Maui, Hawaii, U.S.Other namesDa SpyderResidenceMaui, HawaiiNationalityAmericanHeight6 ft 6 in (198 cm)Weight185 lb (84 kg; 13 st 3 lb)DivisionLight HeavyweightMiddleweightReach79 in (201 cm)StanceOrthodoxFighting out ofMaui, Hawaii, United StatesTeamCobra Kai (2002–2008)[1] Team Punishment (2006–2008)[2] Misfit...

Pour l’article homonyme, voir Ligne de partage des eaux (segmentation). Ne doit pas être confondu avec Le Partage des Eaux. Principales lignes de partage européennes (lignes rouges) séparant les bassins (régions grisées). La ligne de partage des eaux est une limite géographique qui divise hydrographiquement en plusieurs bassins versants. Plus précisément, de chaque côté de cette ligne, les eaux de pluie s’écoulent vers des exutoires différents. Le plus souvent, cette ligne, l...

Peta Lokasi Provinsi Sulawesi Tengah di Indonesia Peta Lokasi Kabupaten dan kota Sulawesi Tengah di Sulawesi Berikut daftar kabupaten dan/atau kota di Sulawesi Tengah, Indonesia. Provinsi Sulawesi Tengah terdiri atas 12 kabupaten dan 1 kota, 147 kecamatan, 170 kelurahan, dan 1.839 desa dengan ibukota di Kota Palu.. Provinsi ini memiliki luas daratan 61.841,29 km2 (BPS 2015), dengan penduduk 3.021.8 km,79 jiwa (BPS 2022), dengan tingkat kepadatan penduduk 48,86 jiwa/km². Adapun daftar l...

American baseball player (1944–2004) Baseball player Tug McGrawPitcherBorn: (1944-08-30)August 30, 1944Martinez, California, U.S.Died: January 5, 2004(2004-01-05) (aged 59)Brentwood, Tennessee, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: LeftMLB debutApril 18, 1965, for the New York MetsLast MLB appearanceSeptember 25, 1984, for the Philadelphia PhilliesMLB statisticsGames pitched824Win–loss record96–92Earned run average3.14Strikeouts1,109Saves180 Teams New York Mets (196...

Song performed by Kelly Clarkson Save YouSong by Kelly Clarksonfrom the album All I Ever Wanted Recorded2008Studio Henson Recording, Los Angeles Mansfield, Los Angeles Ocean Way, Nashville Blackbird, Nashville GenreRock[1]Length4:03LabelRCASongwriter(s)Ryan Tedder, Aimée ProalProducer(s)Ryan Tedder Save You is a song by American recording artist Kelly Clarkson, from her fourth studio album, All I Ever Wanted (2009). Written by Ryan Tedder and Aimée Proal, and produced by Tedder, Sav...

Russian blogger (born 1986) Kristina PotupchikPotupchik in 2017Born (1986-01-19) 19 January 1986 (age 38)Murom, USSROccupation(s)Blogger[1]Spokesperson, Nashi[2][3][4] Kristina Andreyevna Potupchik (Russian: Кристи́на Андре́евна Поту́пчик; born 19 January 1986) is a Russian blogger, a public figure,[5] and the head of the Foundation for the Open New Democracy (FOND), engaged in the support of non-profit social projects o...

هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. قانون التوحيد والتعريب والمغربة هو قانون صدر في المغرب بعد نيل الاستقلال[1] وهو ينقسم إلى ثلاثة أقسام هي: 1 التوحيد:وهو توحيد القوانين في المغرب حيت كانت مناطق المغرب تحكم ...

Two peaks in the Elk Mountains, USA Maroon BellsMaroon BellsHighest pointPeakMaroon PeakElevation4317 m (14163 ft)[1][2]NAVD88Prominence712 m (2336 ft)[3]Isolation12.97 km (8.06 mi)[3]ListingNorth America highest peaks 49thUS highest major peaks 35thColorado highest major peaks 17thColorado fourteeners 24thCoordinates39°04′15″N 106°59′20″W / 39.0708492°N 106.9889921°W / 39.0708492; -106.9889921[1]GeographyMaroon ...
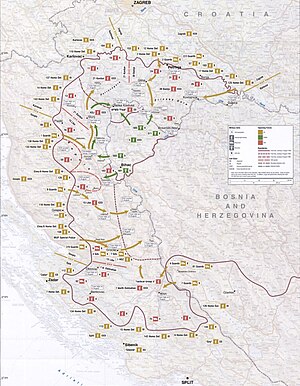
Operasi BadaiBagian dari Perang Kroasiadan Perang BosniaPeta Operasi BadaiForces: Kroasia RKS Bosnia dan HerzegovinaTanggal4–7 Agustus 1995LokasiKroasia dan Bosnia dan HerzegovinaHasil Kemenangan Kroasia Pertempuran dalam perang kemerdekaan berakhir Sebagian besar teritori Krajina diambil alih Kroasia Eksodus warga sipil Serbia Perjanjian Erdut, berakhirnya perang Kemenangan strategis Bosnia: Bosnia Barat dihapuskan Berakhirnya pengepungan BihaćPerubahan...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (أغسطس 2019) الدوري الفنلندي الممتاز 1996 تفاصيل الموسم الدوري الفنلندي الممتاز النسخة 87&#...
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (يناير 2018) الدوري البحريني الممتاز 1970–71معلومات عامةالرياضة كرة القدم البطولة الدوري الب...

كأس الرابطة الفرنسية 2003–04 تفاصيل الموسم كأس الرابطة الفرنسية، وكأس الرابطة الفرنسية النسخة 10 البلد فرنسا التاريخ بداية:23 سبتمبر 2003 نهاية:17 أبريل 2004 المنظم رابطة كرة القدم الفرنسية للمحترفين البطل نادي سوشو مباريات ملعوبة 43 عدد المشاركين 44 &#...

Than Phu YingBusba Kitiyakara Sathanapongบุษบา กิติยากร สธนพงศ์BornMom Rajawongse Busba Kitiyakara (1934-08-02) 2 August 1934 (age 89)Bangkok, ThailandSpousesThawisan Ladawan (div.)Surayud SathanapongChildrenSuthawan SathirathaiParentsNakkhatra Mangala Kitiyakara (father)Bua Kitiyakara (mother) Than Phu Ying Busba Kitiyakara Sathanapong (Thai: บุษบา กิติยากร สธนพงศ์; RTGS: Butsaba Kitiyakon Sathanaphong,...

Dutch speed skater (1981–2019) In this Dutch name, the surname is van Deutekom, not Deutekom. Paulien van DeutekomPaulien van DeutekomPersonal informationBirth namePaulien van DeutekomBorn(1981-02-04)4 February 1981The Hague, NetherlandsDied2 January 2019(2019-01-02) (aged 37)NetherlandsSportCountryNetherlandsSportSpeed skatingTurned pro1998Retired2012 Medal record Women's Speed Skating Representing the Netherlands World Allround Championships 2008 Berlin Allround World Sing...

Como 1907Calcio Lariani, Azzurri, Biancoblù, Voltiani Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Blu reale[1] SimboliOnde del Lario,[2] svasso[3] InnoComasco dal cuore ubriaco[4] Dati societariCittàComo Nazione Italia ConfederazioneUEFA Federazione FIGC CampionatoSerie A Fondazione1907 Rifondazione2005Rifondazione2017Proprietario Robert Budi Hartono (gruppo Djarum)[5] Allenatore Francesc Fàbregas Soler StadioGiuseppe Sinigagl...




