Media ownership in Canada
|
Read other articles:

Orang Anglo-IndiaIbu dan anak perempuan Anglo-India, sekitar 1920Daerah dengan populasi signifikan India1 juta[1] Bangladesh200,000[butuh rujukan] Britania Raya86,000[2] Australia22,000 Kanada22,000 Amerika Serikat20,000 Myanmar19,200[3] Selandia Baru15,861 Malaysia10,310 Singapura4,800 Pakistan<1,500[4]BahasaInggris (India),[3] Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil, Bengali, Telugu, Oriya dan bahasa...
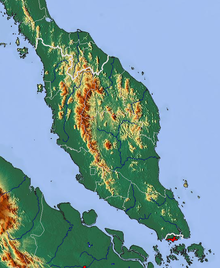
Artikel ini bukan mengenai Semenanjung Malaya. Mosaik Malaysia Semenanjung dengan warna palsu oleh Landsat Topografi Malaysia Semenanjung Malaysia Semenanjung,[note 1] dalam sejarahnya dikenal sebagai Malaya,[note 2] juga dikenal sebagai Malaysia Barat atau Semenanjung Malaysia,[note 3] adalah bagian barat dari Malaysia yang mengisi bagian selatan Semenanjung Malaya di Asia Tenggara Daratan dan pulau di sekitarnya.[1] Luas wilayahnya adalah 132.490 km2 (51...

Planned, socially-cohesive, residential community Collective settlement, Utopian society, and Utopian experiment redirect here. For the legal term, see Settlement (litigation). For the film, see The Utopian Society. For other uses of Utopian experiment, see Utopian experiment (disambiguation). For other uses of Commune and Communal, see Commune (disambiguation) and Communal (disambiguation). Part of a series onLiving spaces MainHouse (detached) • Apartment • Housing projects • Human out...

ExileInformasi latar belakangNama lainEguJ Soul Brothers (1999-2001)Asal TokyoGenreJ-popTahun aktif2001–sekarang (1999-2001 sebagai J Soul Brothers)Labelrhythm zoneSitus webexile.jpAnggotaExile HiroExile MakidaiToshio Matsumoto (Matsu)Exile UsaExile AtsushiExile AkiraExile TakahiroKenchi Tachibana(Kenchi)Keiji Kuroki (Keiji)Exile TetsuyaExile NaotoNaoki Kobayashi (Naoki)Exile NesmithExile ShokichiNaoki KobayashiTakanori IwataAlan ShirahamaMandy SekiguchiSekaiTaiki SatoMantan anggotaShun Exi...

التاريخ الكبير التاريخ الكبير معلومات الكتاب المؤلف محمد بن إسماعيل البخاري(194 هـ - 256 هـ) البلد بخارى اللغة العربية السلسلة علم الجرح والتعديل الموضوع علم التراجم - علم الرجال الفريق فنان الغلاف غلاف كتاب التاريخ الكبير طبعة دار الكتب العلمية.. المواقع ويكي مصدر التاريخ ال...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

County in Missouri, United States County in MissouriLawrence CountyCountyThe Lawrence County Courthouse in Mt. VernonLocation within the U.S. state of MissouriMissouri's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 37°07′N 93°50′W / 37.11°N 93.83°W / 37.11; -93.83Country United StatesState MissouriFoundedFebruary 14, 1845Named forJames LawrenceSeatMount VernonLargest cityMonettArea • Total613 sq mi (1,590 km2) • Land612&...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) كأس المثابرة 2001التاريخ2001 الملعبملعب الشعب الدولي وهي سادس بطولة كأس السوبر في العراق والتي تقام ب...

Yang MuliaGeorg GänsweinPrefek Emeritus Rumah Tangga KepausanKanon Kehormatan Katedral FreiburgGänswein pada tahun 2017GerejaGereja Katolik RomaTakhtaUrbs Salvia (titular)ImamatTahbisan imam31 Mei 1984oleh Oskar SaierTahbisan uskup6 Januari 2013oleh Paus Benediktus XVIPeringkatUskup AgungInformasi pribadiLahir30 Juli 1956 (umur 67)Riedern am Wald, Waldshut, Jerman BaratKewarganegaraanJermanDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaJabatan sebelumnyaSekretaris Pribadi Paus Benediktus XVI (...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant les Côtes-d'Armor et la mer. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Côte de granit rose La Côte de granit rose. Pays France Région Bretagne Département Côtes-d'Armor Communes Perros-Guirec, Pleumeur-Bodou, Trébeurden, Trégastel Coordonnées géographiques 48° 49′ 23″ N, 3° 32′ 02″ O Étendue d'eau Manche (océan Atla...

SMA Santa Ursula Jakarta pada masa Hindia Belanda Biara dan sekolah ordo Santa Ursula di Bogor (tahun 1920-1930) Ordo Santa Ursula adalah suatu ordo keagamaan Katolik yang didirikan tahun 1535 di Brescia (Lombardia) di Italia oleh Santa Angela Merici atau Angela dari Brescia. Kegiatan ordo ini terfokus pada pendidikan anak perempuan. Ursulin juga aktif di Hindia Belanda sejak 1855. Mereka adalah religius wanita pertama di koloni itu, diikuti pada 1859 oleh religius pria pertama, Yesuit. Enam ...

Église Elevation Elevation Ballantyne campus Mouvement Christianisme évangélique Courant Baptisme Lieu Matthews (Caroline du Nord), États-Unis Langue(s) Anglais Dirigeant Steven Furtick et Holly Furtick Fondateur Steven Furtick Fondation 2006 Assistance hebdomadaire 14,000 Campus 16 Logo Site Web elevationchurch.org modifier L’Église Elevation (anglais : Elevation Church) est une megachurch chrétienne évangélique baptiste multisite basée à Matthews (Caroline du Nord). ...

Chris BrownAlbum studio karya Chris BrownDirilis29 November 2005Direkam2005GenreR&B, hip-hop soulDurasi55:04LabelJive RecordsProduserScott Storch, Jermaine Dupri, Bryan-Michael Cox, WyldCard, The Underdogs, Dre & Vidal, Shea Taylor, Tyler Matthews, Cool & Dre, Sean Garrett, Nick Pope, Hunter AtkinsKronologi Chris Brown Chris Brown(2005) Exclusive(2007)Exclusive2007 Templat:Extra album cover 2 Singel dalam album Chris Brown Run It!Dirilis: 25 Juli 2005 Yo (Excuse Me Miss)Dirili...

Jean Marie FarinaJean Marie FarinaBiographieNaissance 8 décembre 1685Santa Maria MaggioreDécès 25 novembre 1766 (à 80 ans)CologneSépulture Cimetière de MelatenNom dans la langue maternelle Giovanni Maria FarinaActivités Parfumeur, homme d'affaires, inventeur, chimistemodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata carte de visite 1747 lettre 1716 Facture de Jean Marie Farina 1760 La tour de l'hôtel de ville sur laquelle se trouve une statue du parfumeur, côté gauche, 2d étage ...

Cloud collaboration service Not to be confused with air table. Formagrid, Inc.Type of siteCollaborative softwareFounded2012HeadquartersSan Francisco, California, USFounder(s)Howie LiuAndrew OfstadEmmett NicholasIndustryInternetURLairtable.comRegistrationRequiredCurrent statusActive Airtable is a cloud collaboration service headquartered in San Francisco. It was founded in 2012 by Howie Liu, Andrew Ofstad, and Emmett Nicholas. Airtable is a spreadsheet-database hybrid, with the features o...

The OthersGrace Stewart (Nicole Kidman) in una scena del filmLingua originaleinglese Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America, Spagna, Francia, Italia Anno2001 Durata104 min Rapporto1,85:1 Genereorrore, thriller, drammatico RegiaAlejandro Amenábar SoggettoAlejandro Amenábar SceneggiaturaAlejandro Amenábar ProduttoreFernando Bovaira, Sunmin Park, José Luis Cuerda Produttore esecutivoBob Weinstein, Harvey Weinstein, Tom Cruise, Paula Wagner, Rick Schwartz Casa di produzi...

Financially motivated nonviolent crime committed by business and government professionals This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (September 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message)...

Small form-factor PC running Chrome OS This article is about the variant of the Google Chromebook. For the CD box set, see Chrome Box. ChromeboxSamsung Chromebox from frontManufacturerAcer; AOpen; Asus; CTL; Dell; Google (as a bundler); Hewlett-Packard; Lenovo; Promethian, Samsung; SMARTIntroducedMay 29, 2012; 11 years ago (2012-05-29)Cost$179-$999ProcessorARM, Intel Celeron, Core i3, Core i5, Core i7Memory2, 4, 8, or 16 GBPortsUSB 2.0/3.0/3.2 Gen 1 Type-A & C, Ethernet,...

2023 film directed by Mani Ratnam Ponniyin Selvan: IITheatrical release posterDirected byMani RatnamScreenplay byMani RatnamElango KumaravelB. JeyamohanBased onPonniyin Selvanby Kalki KrishnamurthyProduced byMani RatnamSubaskaran AllirajahStarring Vikram Jayam Ravi Karthi Aishwarya Rai Trisha Aishwarya Lekshmi Sobhita Dhulipala CinematographyRavi VarmanEdited byA. Sreekar PrasadMusic byA. R. RahmanProductioncompaniesMadras TalkiesLyca ProductionsDistributed byRed Giant MoviesRelease date 28&#...

Dutch footballer (born 1994) Andries Noppert Noppert with Heerenveen in 2023.Personal informationFull name Andries Noppert[1]Date of birth (1994-04-07) 7 April 1994 (age 30)[2]Place of birth Heerenveen, NetherlandsHeight 2.03 m (6 ft 8 in)[3]Position(s) GoalkeeperTeam informationCurrent team HeerenveenNumber 44Youth career0000–2013 HeerenveenSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2013–2014 Heerenveen 0 (0)2014–2018 NAC Breda 6 (0)2018–2019 Foggi...