Manifesto for Walloon culture
|
Read other articles:

Mexican racing driver (born 1990) This article is about the racing driver. For other people with the same name, see Sergio Pérez (disambiguation). In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Pérez and the second or maternal family name is Mendoza. Sergio PérezPérez in 2019BornSergio Michel Pérez Mendoza (1990-01-26) 26 January 1990 (age 34)Guadalajara, Jalisco, MexicoOccupationsRacing driverHeight1.73 m (5 ft 8 in)Formula One World Championship care...

Gakpé Administration Pays Bénin Département Atlantique Démographie Population 6 236 hab.[1] (2013) Géographie Coordonnées 6° 26′ 57″ nord, 2° 06′ 37″ est Localisation Géolocalisation sur la carte : Bénin Gakpé modifier Gakpé Gakpé est un arrondissement de la commune de Ouidah localisé dans le département de l'Atlantique au Sud du Bénin[2],[3]. Histoire et Toponymie Cette section est vide, insuffisamment détaillée ou...
Lombardia region di Italiawilayah budaya Lombardia (it) Dinamakan berdasarkanLangobardia (en) Tempat <mapframe>: Judul Italy/Region/Lombardy.map .map bukan merupakan halaman data peta yang sah Negara berdaulatItalia NegaraItalia Ibu kotaMilan Pembagian administratifProvinsi Bergamo Provinsi Lecco Provinsi Milan (1970-31 Desember 2014)Provinsi Como Provinsi Monza dan Brianza Provinsi Brescia Provinsi Cremona Provinsi Lodi Provinsi Mantova Provinsi Pavia Provinsi Sondrio Provinsi Varese K...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité bulgare. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. General TochevoÉglise Saint Dimitar SolunskiNom officiel (ro) Gheneral Toșevo (depuis 1942)GéographiePays BulgarieOblast DobritchMunicipalité General Toshevo (chef-lieu)Superficie 63,7 km2Altitude 230 mCoordonnées 43° 42′ 01″ N, 28° 02′ 12″ EDémog...

American politician Edward F. McLaughlinMcLaughlin c. 1915Boston Fire CommissionerIn office1934–1938Preceded byEugene M. McSweeneySucceeded byWilliam Arthur ReillyIn office1930–1933Preceded byEugene HultmanSucceeded byEugene M. McSweeneyMember of the Massachusetts Senate from the 4th Suffolk DistrictIn office1916–1918Preceded byJoseph LeonardSucceeded byJohn J. KearneyMember of the Massachusetts House of Representatives from the 12th Suffolk DistrictIn office1913–1915 Personal details...

Rugby union matches played by British and Irish Lions team in South Africa in 1968 1968 British Lions tour to South AfricaDate26 May – 28 AugustCoach(es)Ronnie DawsonTour captain(s) Tom KiernanTest series winners South Africa (3–0)Top test point scorer(s) Tom Kiernan (35)← Australia and New Zealand 1966 New Zealand 1971 → 1968 British Lions tour to South AfricaSummaryP W D L Total20 15 01 04Test match04 00 01 03OpponentP W D L South Africa4 0 1 3 In 1968 the B...

Output of a dynamic system when given a brief input The impulse response from a simple audio system. Showing, from top to bottom, the original impulse, the response after high frequency boosting, and the response after low frequency boosting. In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse (δ(t)). More generally, an impulse response is the reaction ...

Association football club in England Football clubLichfield CityFull nameLichfield City Football ClubFounded1970[1]GroundCity Ground, LichfieldCapacity1,500[1]ChairmanDarren LeaverManagerIvor GreenLeagueMidland League Premier Division2022–23Midland League Premier Division, 11th of 20 Home colours Lichfield City Football Club is a football club based in Lichfield, Staffordshire, England. They are members of the Midland League Premier Division and play at the City Ground. Hist...

Type of engine Engine block of an Elsbett straight-three diesel engine A straight-three engine (also called an inline-triple or inline-three)[1][2][3] is a three-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. Less common than straight-four engines, straight-three engines have nonetheless been used in various motorcycles, cars and agricultural machinery. Design four stroke Straight-three engine with firing order 1-3-2 A cranksha...

Main article: 2008 United States presidential election 2008 United States presidential election in Tennessee ← 2004 November 4, 2008 2012 → Turnout66.34% [1] 0.02 pp Nominee John McCain Barack Obama Party Republican Democratic Home state Arizona Illinois Running mate Sarah Palin Joe Biden Electoral vote 11 0 Popular vote 1,479,178 1,087,437 Percentage 56.85% 41.79% County results Congressional district results Precinct results McCain &...
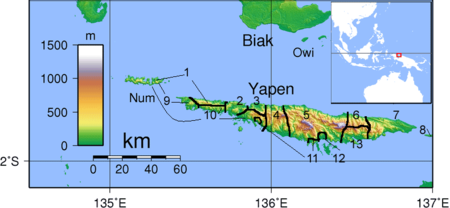
Branch of the Austronesian language family Not to be confused with Yapen languages (Papuan). YapenGeographicdistributionYapen Island, Western New Guinea, IndonesiaLinguistic classificationAustronesianMalayo-PolynesianCentral–EasternSouth Halmahera–West New GuineaCenderawasih BayYapen–WaropenYapenGlottologyape1249 The Yapen languages are the branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken on Yapen Island and the nearby isle of Cenderawasih Bay, both in Papua province of northeastern Indones...

Cortevaix L'église, sous le vocable de saint Jean-Baptiste. Blason Administration Pays France Région Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Département Saône-et-Loire Arrondissement Mâcon Intercommunalité Communauté de communes du Clunisois Maire Mandat Aymar de Camas 2020-2026 Code postal 71460 Code commune 71147 Démographie Gentilé Cortevaisien[1], Cortevajons, Cortevayons[2] Populationmunicipale 251 hab. (2021 ) Densité 24 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 46° 32′ 13″...

دوميترو ستانغاسيو معلومات شخصية الميلاد 9 أغسطس 1964 (العمر 59 سنة)براشوف الطول 1.93 م (6 قدم 4 بوصة) مركز اللعب حارس مرمى الجنسية رومانيا مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق OJT Predeal المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 1982–1984 براشوف1 5 (0) 1984–1995 Steaua București football records dispute [الإ�...

Book by Palle Huld A Boy Scout Around the World Danish cover (2012 reprint)AuthorPalle HuldTranslatorEleanor Hard[1]Cover artistAxel MathiesenLanguageDanish (translated to 11 languages)GenreTravel bookPublished1928Publication placeDenmarkPublished in English1929Media typePrintPages178 (Danish original) A Boy Scout Around the World (Danish: Jorden Rundt i 44 dage, literally: Around the World in 44 Days) is a travel description published in October 1928[2] and wri...

Multi-purpose arena in Columbus, Ohio, United States The Schottenstein CenterThe SchottExterior view in 2014Full nameValue City Arena at the Jerome Schottenstein CenterAddress555 Borror DriveLocationColumbus, Ohio, U.S.Coordinates40°00′27″N 83°01′30″W / 40.007511°N 83.025102°W / 40.007511; -83.025102Public transit 1OwnerThe Ohio State UniversityOperatorColumbus Arena ManagementCapacity17,500 (ice hockey)19,500 (basketball)20,000+ (concerts)[1]Constr...

American NBC crime drama series created by John Wells (1999–2005) This article is about the television show. For information about naval watches, see Watch system. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Third Watch – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2015) (Learn how and when to rem...

此条目或其章节有關正在連載或尚未完結的作品。維基百科不是新聞的收集处。請留心記載正確資訊,在信息相對明确之後進行編輯更新。 关于電視動畫,请见「OVERLORD (動畫)」。 OVERLORD オーバーロード Overlord 罗马字 Ōbārōdo 類型 黑暗奇幻[1]、異世界[2] 常用譯名 不死者之王 小说 作者 丸山黃金 插圖 so-bin 出版社 KADOKAWA 台灣角川 次元書館(代理)�...
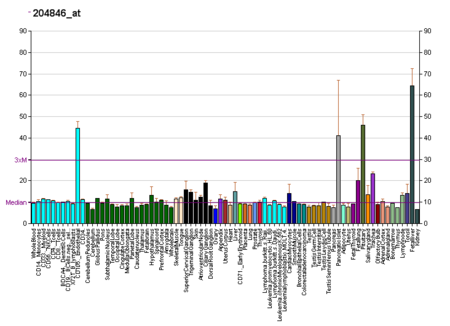
Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens CPAvailable structuresPDBOrtholog search: PDBe RCSB List of PDB id codes1KCW, 2J5W, 4EJX, 4ENZIdentifiersAliasesCP, CP-2, ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase), Ceruloplasmin, AB073614External IDsOMIM: 117700; MGI: 88476; HomoloGene: 75; GeneCards: CP; OMA:CP - orthologsEC number1.16.3.1Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 3 (human)[1]Band3q24-q25.1Start149,162,410 bp[1]End149,221,829 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 3 (mouse)[2...

Cette page contient des caractères spéciaux ou non latins. S’ils s’affichent mal (▯, ?, etc.), consultez la page d’aide Unicode. Ѫ Graphies Capitale Ѫ Bas de casse ѫ Utilisation Alphabets Cyrillique Phonèmes principaux /ɔ̃/ modifier Le grand ious (Ѫ en majuscule, ѫ en minuscule), aussi écrit grand yousse[1] est une lettre de l’alphabet cyrillique utilisée en slavon. Elle a aussi été utilisée jusqu’en 1945 en bulgare et officiellement jusqu’en 1860...

Logotipo similar al de las últimas 2 ediciones de los Goodwill Games Los Goodwill Games (en español, «Juegos de la Buena Voluntad» o «Juegos de la Amistad») fueron un evento deportivo multidisciplinario en el que participaban atletas de diversas partes del mundo. Se crearon en 1985 por iniciativa del empresario estadounidense Ted Turner, quien pretendía aliviar las tensiones existentes durante la Guerra Fría a través de una competición amistosa.[1] Con el fin de la Guerra Fr�...
