List of works by Akira Kurosawa
|
Read other articles:

Ini adalah daftar katedral di Papua Nugini diurutkan berdasarkan denominasi. Katedral Santa Maria, Port Moresby Katolik Katedral Gereja Katolik di Papua Nugini:[1][2] Katedral Santo Ignasius, Aitape Katedral Hati Kudus Yesus, Alotau Katedral Bunda Maria dari Hati Kudus, Bereina Katedral Bunda Maria Dikandung Tanpa Noda, Hahela Katedral Santo Gerardus, Kiunga Kon-Katedral Santo Louis de Montfort, Daru Katedral Maria Penolong Umat Kristiani di Kefamo, Goroka Katedral Bunda Maria...

For the song by Sebastián Yatra, Manuel Turizo and Beéle, see Vagabundo (song). 1996 studio album by Robi Dräco RosaVagabundoStudio album by Robi Dräco RosaReleasedJune 18, 1996RecordedNovember 1995 – January 1996GenreGrungehard rockalternative metalLength48:16LabelSony MusicProducerPhil ManzaneraRobi Dräco Rosa chronology Frio(1994) Vagabundo(1996) Mad Love(2004) Singles from Vagabundo Madre TierraReleased: 1996 VagabundoReleased: 1996 Para No OlvidarReleased: 1997 VivirReleas...

American cyberneticist Allenna Leonard at Stafford Beer’s Fifty Years of Applied Epistemology Or, what else besides the VSM? meeting at Hull University Centre for Systems Studies, 2015 Allenna Leonard is an American cyberneticist, consultant and director of Team Syntegrity International, specializing in the application of Stafford Beer's Viable System Model and Syntegration.[1] She was president of the International Society for the Systems Sciences in 2009–2010,[2] and led...

Athenian statesman, orator and general (c. 495 – 429 BC) For other uses, see Pericles (disambiguation). PericlesBust of Pericles bearing the inscription Pericles, son of Xanthippus, Athenian. Marble, Roman copy after a Greek original from c. 430 BC, Museo Pio-Clementino, Vatican Museums,Bornc. 495 BCAthens, GreeceDied429 BC (aged c. 65 – 66)Athens, GreeceAllegianceAthensRankStrategosBattles/wars First Peloponnesian War Battles of Sicyon and Acarnania Second S...

Al-Mustadrak 'ala aṣ-Ṣaḥiḥain PengarangHakim an-NaisaburiBahasaArabSubjekالمستدرك على الصحيحينGenreKumpulan Hadis Al-Mustadrak 'ala ash-Shahihain (Arab: المستدرك على الصحيحينcode: ar is deprecated ) adalah kitab koleksi hadits yang disusun oleh Hakim al-Naisaburi (w. 405 H) setebal lima jilid. Al-Hakim menyusun kitab ini pada tahun 393 H (1002 M) ketika dia berumur 72 tahun. Kitab ini memuat 9045 hadits.[1] Dia menyatakan bahwa seluruh had...

Riedisheimcomune Riedisheim – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Alto Reno ArrondissementMulhouse CantoneRixheim TerritorioCoordinate47°45′N 7°22′E / 47.75°N 7.366667°E47.75; 7.366667 (Riedisheim)Coordinate: 47°45′N 7°22′E / 47.75°N 7.366667°E47.75; 7.366667 (Riedisheim) Superficie6,96 km² Abitanti12 558[1] (2009) Densità1 804,31 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale68400 F...

Gubernur Jawa TimurPetahanaAdhy KaryonoPenjabatsejak 16 Februari 2024KediamanGrahadiMasa jabatan5 tahun, dapat diperpanjang sekaliDibentuk19 Agustus 1945; 78 tahun lalu (1945-08-19)Pejabat pertamaSoerjoSitus webSitus web resmi Gubernur Jawa Timur adalah kepala daerah tingkat I yang memegang pemerintahan di Jawa Timur bersama dengan Wakil Gubernur dan 120 anggota Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Daerah Jawa Timur. Gubernur dan Wakil Gubernur Jawa Timur dipilih melalui pemilihan umum yang dila...

Sailing at the Olympics Sailingat the Games of the XXVII OlympiadRushcutters Bay.VenuesSydneyDatesFirst race: 17 September 2000 (2000-09-17)Last race: 30 September 2000 (2000-09-30)Competitors402 (307 men, 95 women)← 19962004 → Sailing at the2000 Summer OlympicsMistralmenwomenEuropewomenLaseropenFinnmen470menwomen49eropenTornadoopenStaropenSolingopenvte Sailing at the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney was held from 17 to 30 September 2000 at th...
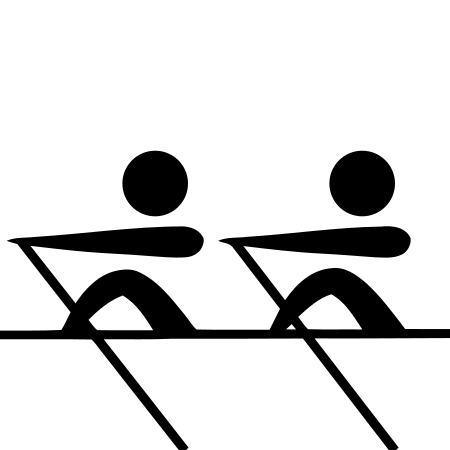
Main article: Rowing at the Summer Olympics Rowingat the Games of the XIV OlympiadVenueHenley Royal Regatta courseDates5–9 August 1948Competitors310 from 27 nations← 19361952 → Rowing at the1948 Summer OlympicsSingle scullsmenDouble scullsmenCoxless pairmenCoxed pairmenCoxless fourmenCoxed fourmenEightmenvte Rowing at the 1948 Summer Olympics featured seven events, for men only. Competitions were held over the Henley Royal Regatta course from 5 to 9 August.&...

See also: Vice President of the United Arab Emirates Prime Minister of the United Arab Emiratesرئيس مجلس الوزراء دولة الإمارات العربية المتحدةEmblem of the UAEFlag of the United Arab EmiratesIncumbentMohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoumsince 11 February 2006Executive branch of the Federal Government of the United Arab EmiratesCabinet of the United Arab EmiratesStyleHis Excellency, SheikhMember ofCabinet of the United Arab EmiratesReports toPresidentRes...

American politician and baseball player (1839–1906) For his son, see Arthur Pue Gorman Jr. Senator Gorman redirects here. For other uses, see Senator Gorman (disambiguation). Arthur P. GormanGorman c. 1899Chairman of the Senate Democratic CaucusIn officeMarch 4, 1903 – June 4, 1906Preceded byJames Kimbrough JonesSucceeded byJoseph Clay Stiles BlackburnIn officeMay 3, 1890 – April 1898Preceded byJames B. BeckSucceeded byDavid TurpieUnited States Senatorfrom MarylandIn o...
U-19 quốc gia AnhBiệt danhTam sưHiệp hộiHiệp hội bóng đá AnhLiên đoàn châu lụcUEFA (Châu Âu)Huấn luyện viên trưởngWill AntwiMã FIFAENG Áo màu chính Áo màu phụ Áo màu khác Giải vô địch bóng đá U-19 châu ÂuSồ lần tham dự46 (Lần đầu vào năm 1948)Kết quả tốt nhấtVô địch : (1948, 1963, 1964, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1975, 1980, 1993, 2017, 2022) U-19 quốc gia AnhBiệt danhTam sưHiệp hộiHiệp hội bóng đá AnhLiên ...

إن حيادية وصحة هذه المقالة محلُّ خلافٍ. ناقش هذه المسألة في صفحة نقاش المقالة، ولا تُزِل هذا القالب من غير توافقٍ على ذلك. (نقاش) (مايو 2016) الصحراء الغربية الجمهورية العربية الصحراوية الديمقراطية República Árabe Saharaui Democrática الجمهورية العربية الصحراوية الديمقراطيةعلم الجمهو�...

كاناجوهاري الإحداثيات 42°54′22″N 74°34′19″W / 42.906111111111°N 74.571944444444°W / 42.906111111111; -74.571944444444 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 1788 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة مونتغومري خصائص جغرافية المساحة 43.10 ميل مربع عدد السكان عد...

Unitary local authority for the district of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole CouncilCouncil logoTypeTypeUnitary authority HistoryFounded1 April 2019Preceded byBournemouth Borough CouncilChristchurch Borough CouncilPoole Borough CouncilDorset County CouncilLeadershipChairLesley Dedman, Christchurch Independents since 23 May 2023 LeaderVikki Slade, Liberal Democrats since 23 May 2023 Chief ExecutiveGraham Farrant since 21 May 2019 StructureSea...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Hôtel de Brancas (homonymie). Hôtel de BrancasL'hôtel de Brancas en 2008.PrésentationType Hôtel particulierArchitecte Pierre BulletConstruction 1710Patrimonialité Classé MH (1970, 2021)LocalisationArrondissement 6e arrondissementCoordonnées 48° 51′ 03″ N, 2° 20′ 13″ ELocalisation sur la carte de ParisLocalisation sur la carte du 6e arrondissement de Parismodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata...

School of early Jewish mysticism Merkavah and Merkabah redirect here. For the Israeli main battle tank, see Merkava. For other uses, see Merkabah (disambiguation). Copy of Matthäus Merian's engraving of Ezekiel's vision (1670) Merkabah (Hebrew: מֶרְכָּבָה, romanized: merkāḇā, lit. 'chariot')[1] or Merkavah mysticism[2] (lit. Chariot mysticism) is a school of early Jewish mysticism, c. 100 BCE – 1000 CE, centered on visions such as those foun...

Danish composer, conductor, and music teacher (1817–1890) Niels Gade Niels Wilhelm Gade (22 February 1817 – 21 December 1890) was a Danish composer, conductor, violinist, organist and teacher. Together with Johan Peter Emilius Hartmann, he was the leading Danish musician of his day, in the period known as the Danish Golden Age.[1] Biography Gade was born in Copenhagen, the son of a joiner and instrument maker. He was intended for his father's trade, but his passion for a music...

Voce principale: Società Sportiva Dilettantistica Calcio San Donà. Società Sportiva San DonàStagione 1993-1994Sport calcio Squadra San Donà Allenatore Ezio Glerean Presidente Alfio Granzotto Campionato Nazionale Dilettanti1º posto nel girone D (promosso in Serie C2) Coppa Italia DilettantiPrimo turno Poule ScudettoSemifinale Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Cecconi (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Meacci (22) 1992-1993 1994-1995 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce racc...

日本の政治結社大政翼賛会大政翼󠄂贊會 大政翼賛会本部1940年11月30日に東京会館の建物を臨時徴用し、1942年1月25日まで本部を設置した[1]。成立年月日 1940年10月12日[2]前身政党 立憲政友会立憲民政党国民同盟社会大衆党解散年月日 1945年6月13日[3]解散理由 国民義勇隊に発展解消のため[4]後継政党 国民義勇隊本部所在地 日本 東京都麹町区政治...