List of adjectivals and demonyms of astronomical bodies
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Формула условного крещения в Требнике Петра Могилы Усло́вное креще́ние или креще́ние под конди́цией (лат. baptismum conditionalis, baptismum sub conditione) — крещение в католицизме[1] над человеком, о предыдущем крещении которого есть сомнение — было ли оно совершено или нет; при ...

2010 song by Kanye West featuring Jay-Z, Pusha T, Cyhi the Prynce, Swizz Beatz and RZASo AppalledSong by Kanye West featuring Jay-Z, Pusha T, Cyhi the Prynce, Swizz Beatz and RZAfrom the album My Beautiful Dark Twisted Fantasy ReleasedSeptember 24, 2010Recorded2009–10GenreHip hopLength6:38LabelRoc-A-FellaDef JamSongwriter(s)Kanye WestErnest WilsonMike DeanShawn Corey CarterTerrence ThorntonCydell YoungKaseem DeanRobert DiggsManfred MannProducer(s)Kanye WestNo I.D.Mike Dean So Appalled is a ...

Excalibur Hotel and Casino Fakta dan statistik Alamat 3850 Las Vegas Boulevard South Las Vegas, Nevada 89109Tanggal pembukaan 19 Juni 1990Nama sebelumnya Proyek Xanadu (tak pernah dibangun)Jenis kasino Berdasarkan TanahTema Abad Pertengahan / CamelotPemilik MGM MirageJumlah kamar 4,008Luas perjudian 100,000 ft² (9,290 m²)Acara permanen Tournament of KingsThunder Down UnderAtraksi menarik Merlin Versus The Dragon (sekarang ditutup)Restoran terkenal The Ste...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Capcir – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Capcir (Catalan: [kəpˈsi]; French: [kapsiʁ]) is a historical Catalan comarca of Northern Catalonia, now part of the French department of Pyr...

Pementasan Ludruk Ludruk adalah suatu kesenian drama tradisional dari Jawa Timur. Ludruk merupakan suatu drama tradisional yang diperagakan oleh sebuah grup kesenian yang dipergelarkan di sebuah panggung dengan mengambil cerita tentang kehidupan rakyat sehari-hari, cerita perjuangan, dan sebagainya yang diselingi dengan lawakan dan diiringi dengan gamelan sebagai musik. Ludruk termasuk dalam drama [1][2][3] Karakter pertunjukan Tari Remo, diperagakan sebagai pembuka pe...

1911 license plates in the United States Vehicle registration plates of the United States by year Vehicle registration plates of the United States for 1910 Events of 1911 Vehicle registration plates of the United States for 1912 In 1911 Alabama, Arkansas, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, North Dakota, and Oregon joined the list of states and territories providing license plates to vehicle owners, and no new states entered the prestate era. There were now 26 states and 2 territories that were issuing...

Peta menunjukkan lokasi Santo Tomas Data sensus penduduk di Santo Tomas Tahun Populasi Persentase 199529.628—200032.6952.14%200737.8662.05% Santo Tomas adalah munisipalitas yang terletak di provinsi Pampanga, Filipina. Pada tahun 2010, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 37.866 jiwa dan 7.573 rumah tangga. Pembagian wilayah Secara administratif Santo Tomas terbagi menjadi 7 barangay, yaitu: Moras De La Paz Poblacion San Bartolome San Matias San Vicente Santo Rosario (Pau) Sapa (Sant...

Public house in Sully, Vale of Glamorgan, Wales The Captain's Wife The Captain's Wife is a public house in the former fishing hamlet of Swanbridge in Sully, between Barry and Penarth, Vale of Glamorgan, south Wales.[1] The pub was established in 1977 from a row of three sea houses. Notable smuggling operations and dove culling once took place here and a tunnel connected the sea to what was known as Sully House.[2] It takes its name from the wife of a sea captain who lived here...

Publicly owned mixed-use development in Toronto The Princes' Gates are the eastern entrance of Exhibition Place. Exhibition Place is a publicly owned mixed-use district in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located by the shoreline of Lake Ontario, just west of downtown. The 197-acre (80 ha) site includes exhibit, trade, and banquet centres, theatre and music buildings, monuments, parkland, sports facilities, and a number of civic, provincial, and national historic sites. The district's faciliti...

Commune in Hauts-de-France, FranceRoubaix RobaaisCommuneThe city hall Coat of armsMotto: Probitas et IndustriaLocation of Roubaix RoubaixShow map of FranceRoubaixShow map of Hauts-de-FranceCoordinates: 50°41′24″N 3°10′54″E / 50.6901°N 3.18167°E / 50.6901; 3.18167CountryFranceRegionHauts-de-FranceDepartmentNordArrondissementLilleCantonRoubaix-1 and Roubaix-2IntercommunalityMétropole Européenne de LilleGovernment • Mayor (2020–2026) ...

Zona Coordenadas 45°30′N 9°00′E / 45.5, 9Entidad Zona • País ItaliaSubdivisiones 4 regiones: Liguria Lombardía Piamonte Valle de AostaSuperficie • Total 57.950 km²Población (30-04-2010) • Total 16,045,039 hab. • Densidad 276,88 hab./km²[editar datos en Wikidata] La Italia noroccidental es aquella parte del territorio de Italia que comprende las regiones de Valle de Aosta, Piamo...

American baseball player (1925–2006) Baseball player Jack BantaPitcherBorn: (1925-06-24)June 24, 1925Hutchinson, Kansas, U.S.Died: September 17, 2006(2006-09-17) (aged 81)Hutchinson, Kansas, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: RightMLB debutSeptember 18, 1947, for the Brooklyn DodgersLast MLB appearanceJune 21, 1950, for the Brooklyn DodgersMLB statisticsWin–loss record14–12Earned run average3.78Strikeouts116 Teams Brooklyn Dodgers (1947–1950) Jackie Kay Banta (J...

Retired class of New York City Subway car R26R26s 7774 and 7775 at Concourse YardIn service1959–2002ManufacturerAmerican Car and FoundryFamily nameRedbirdsReplacedMany Steinway Lo-VsAll Flivver Lo-VsMany Standard Lo-VsConstructed1959–1960Entered serviceOctober 12, 1959Refurbished1985–1987 (General Overhaul program)1991 (SMS program (H2C coupler to link bar replacement at B ends))Scrapped2001–2003Number built110Number preserved2Number scrapped108SuccessorR142 and R142AFormationSemi-Mar...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

River in North Carolina, the United States of America Pamlico RiverThe Pamlico Sound watershedLocation of mouthLocationCountryUnited StatesStateNorth CarolinaCountiesPamlico, Hyde, BeaufortPhysical characteristicsSource • coordinates35°33′09″N 77°05′05″W / 35.5523849°N 77.0846757°W / 35.5523849; -77.0846757 Mouth • coordinates35°19′6″N 76°25′58″W / 35.31833°N 76.43278°W / 3...

Ethnic group native to Bangladesh and India This article is about the ethnic group. For the citizens of Bangladesh, see Bangladeshis. This article contains Bengali text. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols. Ethnic group Bengalisবাঙ্গালীবাঙালিTotal populationc. 285 million[1][2][3]Regions with significant populations Bangladesh175,000,000[4][5][6] India9...

See also: Lists of mountains of the Caribbean Further information: Geography of the Caribbean and Geology of the Caribbean Pico Duarte is the highest point in the Dominican Republic, the island of Hispaniola, and the entire Caribbean. This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaks[1] of the islands of the Caribbean Sea. The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal ways: The topographic elevation of a summit measures the height of the summi...

نهائي كأس ملك إسبانيا 2000الحدثكأس ملك إسبانيا 1999–00 إسبانيول أتلتيكو مدريد 2 1 التاريخ2000 الملعبملعب ميستايا ، بلنسيةالحكمأنتونيو خيسوس لوبيز نييتو → 1999 2001 ← نهائي كأس ملك إسبانيا 2000 هو النهائي رقم 98 في إطار بطولة كأس ملك إسبانيا ، جمعت المباراة النهائية بين ناديي ...
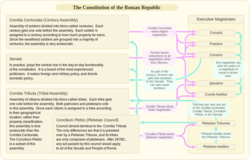
Government practice of having three legislative chambers This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Tricameralism – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Legislature Chambers Unicameralism Bicameralism Tricameralism Multicameralism Upper hou...

Imperatore ZurgZurg nel secondo film UniversoDisney Nome orig.in inglese Emperor Zurg Lingua orig.Inglese AutoreJohn Lasseter StudioWalt Disney Studios 1ª app. inToy Story 2 - Woody e Buzz alla riscossa Voci orig.Andrew Stanton (Toy Story 2 - Woody e Buzz alla riscossa) Wayne Knight (Buzz Lightyear da Comando Stellare - Si parte!, Buzz Lightyear da Comando Stellare) James Brolin (Lightyear - La vera storia di Buzz) Voci italianeMichele Kalamera (in Toy Story 2 - Woody e Buzz al...