Lever Brothers
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Paweł Brożek Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Paweł Łukasz BrożekTanggal lahir 21 April 1983 (umur 40)Tempat lahir Kielce, PolandiaTinggi 1,80 m (5 ft 11 in)Posisi bermain PenyerangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Wisła KrakówNomor 11Karier junior1992–1998 Polonia Białogon Kielce1998 SMS Zabrze1998–2000 Wisła KrakówKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2001–2010 Wisła Kraków 178 (81)2002 → ŁKS Łódź (pinjaman) 8 (0)2004 → GKS Katowice (pinjaman) 20 (5)2011�...

Damian PriestPriest pada tahun 2017Nama lahirLuis Martínez[1]Lahir26 September 1982 (umur 41)New York City, A.S.[2]Karier gulat profesionalNama ringDamian Martinez[1]Damian PriestLuis Martinez[1]Punisher Martinez[1]Punishment Martinez[1]Tinggi6 ft 5 in (1,96 m)[3]Berat249 pon (113 kg)[3]Asal dariNew York CityDilatih olehMonster Factory[1]Debut25 Maret 2005[4] Luis Martínez[1]...

German extermination camp in Poland during World War II Chełmno / KulmhofExtermination campLocation of the former Chełmno extermination camp in PolandCoordinates52°9′15″N 18°43′23″E / 52.15417°N 18.72306°E / 52.15417; 18.72306Other namesGerman: Vernichtungslager KulmhofLocationNear Chełmno nad Nerem, Reichsgau Wartheland (German-occupied Poland)CommandantHerbert Lange, Christian Wirth, Hans BothmannOperationalDecember 8, 1941 – April 11, 1943 (1st peri...

1974 aviation accident Eastern Air Lines Flight 212Wreckage of N8984E at the crash siteAccidentDateSeptember 11, 1974 7:34 am EDTSummaryControlled flight into terrainSiteNear Douglas Municipal Airport, Charlotte, North Carolina, U.S. 35°09′14″N 80°55′34″W / 35.15389°N 80.92611°W / 35.15389; -80.92611AircraftAircraft typeDouglas DC-9-31OperatorEastern Air LinesIATA flight No.EA212ICAO flight No.EAL212Call signEASTERN 212RegistrationN8984E[1]Flig...

Public university in Chickasha, Oklahoma, US USAO redirects here. For the offices of federal prosecutors in the United States, see United States Attorney. University of Science and Artsof OklahomaFormer namesOklahoma Industrial Institute and College for Girls (1908–1912)Oklahoma College for Women (1912–1965)Oklahoma College of Liberal Arts (1965–1972)MottoCollege for the Curious MindTypePublic liberal arts collegeEstablished1908Endowment$27,000,000[1]PresidentKayla HaleStudents8...

National highway in India, running from Srinagar to Kanyakumari For the oldest National Highway 4, see National Highway 6 (India), National Highway 8 (India), and National Highway 37 (India). National Highway 44National Highway 44 in Red on India mapEntrance of National Highway 44 in Jammu and Kashmir.Route informationPart of AH1 AH2 AH43 Length4,112 km (2,555 mi)GQ: 94 km (58 mi) (Bengaluru – Krishnagiri)NS: 1,828 km (Lakhnadon – Kanyakumari)Major junctionsN...

CRHP redirects here. For the healthcare organization in India, see Comprehensive Rural Health Project. For the register in Columbus, Ohio, see Columbus Register of Historic Properties. Federal list of historic sites of Canada Canadian Register of Historic PlacesType of siteOnline database of historic sites in CanadaAvailable inEnglishFrenchOwnerAdministered by Parks CanadaURLwww.historicplaces.ca CommercialNoRegistrationNoLaunchedMay 2004; 20 years ago (2004-05)Cur...

Peta infrastruktur dan tata guna lahan di Komune Livry-sur-Seine. = Kawasan perkotaan = Lahan subur = Padang rumput = Lahan pertanaman campuran = Hutan = Vegetasi perdu = Lahan basah = Anak sungaiLivry-sur-SeineNegaraPrancisArondisemenMelunKantonMelun-SudAntarkomuneCommunauté d'agglomération Melun-Val de SeinePemerintahan • Wali kota (2008-2014) Michel Le Maoult • Populasi11,880Kode INSEE/pos77255 / 2 Population sa...

1972 funeral and death The grave of Prince Edward, Duke of Windsor in the Royal Burial Ground, Frogmore The funeral of Prince Edward, Duke of Windsor, took place on 5 June 1972. Edward had been King of the United Kingdom from 20 January to 11 December 1936, reigning as Edward VIII before his abdication, and had lived in Paris at the time of his death. His funeral took place at St George's Chapel in Windsor Castle after lying in state for three days and he was buried at the Royal Burial Ground...

Alec John Jeffreys Sir Alec John Jeffreys (Oxford, 9 gennaio 1950) è un genetista britannico. Ha inventato le tecniche di fingerprinting genetico del DNA, rivoluzionando le tecniche di identificazione nella scienza forense.[1] Indice 1 Biografia 2 Fingerprinting genetico 3 Riconoscimenti 4 Onorificenze 5 Note 6 Bibliografia 7 Altri progetti 8 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Jeffreys trascorse i primi sei anni della sua vita a Oxford; nel 1956 la famiglia si trasferì a Luton. Jeffreys...

Mathematical model to quantify lift The Lanchester-Prandtl lifting-line theory[1] is a mathematical model in aerodynamics that predicts lift distribution over a three-dimensional wing from the wing's geometry.[2] The theory was expressed independently[3] by Frederick W. Lanchester in 1907,[4] and by Ludwig Prandtl in 1918–1919[5] after working with Albert Betz and Max Munk. In this model, the vortex bound to the wing develops along the whole wingspan ...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Sekop – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Seorang pria membawa sekop Sekop adalah alat untuk menggali, mengangkat, dan memindahkan material curah seperti pasir, tanah, batu kecil, bijih, ...

Serbian-American inventor (1856–1943) For other uses, see Nikola Tesla (disambiguation). Nikola TeslaНикола ТеслаTesla, c. 1890Born(1856-07-10)10 July 1856Smiljan, Austrian Empire (now Croatia)Died7 January 1943(1943-01-07) (aged 86)New York City, U.S.Resting placeNikola Tesla Museum, Belgrade, Serbia44°48′18″N 20°28′15″E / 44.8051°N 20.4707°E / 44.8051; 20.4707Citizenship Austria (1856–1891) United States (1891–1943) Alma&#...

George SilkBornArthur George Silk(1916-11-17)17 November 1916Levin, New ZealandDied23 October 2004(2004-10-23) (aged 87)Norwalk, Connecticut, USAOccupationPhotojournalistSpouseMargery Gray Schieber (1947–2004) George Silk (17 November 1916 – 23 October 2004) was a New Zealand-born Australian photojournalist. He served as a photojournalist for Life for 30 years.[1][2] Early life Silk was born in the New Zealand town of Levin, New Zealand, the fourth child of Arthur Si...

Isola del TinoGeografia fisicaLocalizzazioneMar Ligure Coordinate44°01′38″N 9°51′02″E44°01′38″N, 9°51′02″E ArcipelagoArcipelago Spezzino Superficie0,13 km² Altitudine massima121,8 m s.l.m. Geografia politicaStato Italia Regione Liguria Provincia La Spezia Comune Portovenere Cartografia Isola del Tino voci di isole d'Italia presenti su Wikipedia Bene protetto dall'UNESCOPortovenere, Cinque Terre e Isole (Palmaria, Tino e Tinetto) Patrimo...

1891 Iowa gubernatorial election ← 1889 November 3, 1891 1893 → Nominee Horace Boies Herman C. Wheeler Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 207,594 199,381 Percentage 49.40% 47.45% Governor before election Horace Boies Democratic Elected Governor Horace Boies Democratic Elections in Iowa Federal government U.S. Presidential elections 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 1908 1912 1916 1920 1924 1928 1932 1936 1940 19...
AwardColonial Auxiliary Forces Long Service MedalQueen Victoria versionTypeMilitary long service medalAwarded forTwenty years serviceCountry United KingdomPresented bythe Monarch of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and Empress of IndiaEligibilityAll ranks of part-time Colonial ForcesStatusDiscontinued in 1930Established1899Last awarded1931Ribbon bar Order of WearNext (higher)Colonial Auxiliary Forces Officers' DecorationNext (lower)Medal for Good Shooting (Naval)Rel...

Municipality in Algarve, PortugalFaroMunicipality Clockwise from top: aerial view of Faro; Faro Cathedral; city gates; Castelo de Faro; historic center; and Estói Palace FlagCoat of armsCoordinates: 37°00′58″N 07°56′06″W / 37.01611°N 7.93500°W / 37.01611; -7.93500Country PortugalRegionAlgarveIntermunic. comm.AlgarveDistrictFaroParishes4Government • PresidentRogério Bacalhau (PSD)Area • Total202.57 km2 (78.21 sq ...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «James Callaghan» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 14 de septiembre de 2015. James Callaghan Callaghan en 1975 Primer ministro del Reino UnidoPrimer lord del Tesoro 5 de abril de 1976-4 de mayo de 1979Monarca Isabel IIPredecesor Harold WilsonSucesor Margaret Thatcher Miembro de la Cámara de los LoresLord Temporal 5 de novie...
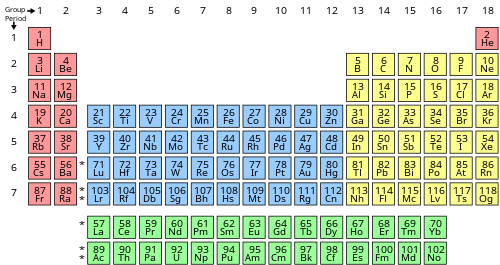
Etymology of chemical elements Part of a series on thePeriodic table Periodic table forms 18-column 32-column Alternative and extended forms Periodic table history D. Mendeleev 1871 table 1869 predictions Discovery of elements Naming and etymology for people for places controversies (in East Asia) Systematic element names Sets of elements By periodic table structure Groups (1–18) 1 (alkali metals) 2 (alkaline earth metals) 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 (pnictogens) 16 (chal...
