Lancer
|
Read other articles:

Katedral MaputoKatedral Bunda Maria Yang Dikandung Tanpa NodaPortugis: Catedral de Nossa Senhora da Imaculada Conceiçãocode: pt is deprecated Katedral Maputo25°58′8.4″S 32°34′30″E / 25.969000°S 32.57500°E / -25.969000; 32.57500Koordinat: 25°58′8.4″S 32°34′30″E / 25.969000°S 32.57500°E / -25.969000; 32.57500LokasiMaputoNegara MozambikDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaSejarahPendiriYang Mulia Mgr. D. Rafael Maria da Asun�...
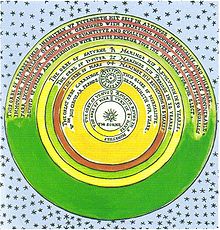
English mathematician and astronomer Thomas DiggesBornc. 1546Wootton, Kent, EnglandDied(1595-08-24)24 August 1595London, EnglandNationalityEnglishKnown forProposing that the universe is infinite in extentScientific careerFieldsAstronomer and mathematicianAcademic advisorsJohn Dee NotesSon of Leonard Digges, and father of Dudley Digges and Leonard Digges (II) Thomas Digges (/dɪɡz/; c. 1546 – 24 August 1595) was an English mathematician and astronomer. He was the first to expound the C...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Luch 5V (Rusia: Луч-5В berarti ray dan kadang-kadang diterjemahkan sebagai Loutch-5B) adalah satelit estafet luch Rusia yang akan mengirimkan data dari Segmen Orbital Rusia dari Stasiun Luar Angkasa Internasional, dan dari satelit lain di orbit Bum...

Turgut Özal Presiden Republik Turki ke-8Masa jabatan9 November 1989 – 17 April 1993PendahuluKenan EvrenPenggantiSüleyman Demirel Informasi pribadiLahir13 Oktober 1927MalatyaMeninggal17 April 1993AnkaraKebangsaanTurkiSuami/istriSemra ÖzalSunting kotak info • L • B Turgut Özal (13 Oktober 1927 – 17 April 1993) adalah pimpinan politik, perdana menteri, dan presiden Turki ke-8. Ia adalah tokoh politik dari Kurdi [1] Diarsipkan 2006-05-13 di Wayback Mac...

Township in Pennsylvania, United StatesBensalem Township, PennsylvaniaTownshipAndalusia, a NRHP site in Bensalem FlagSealLocation of Bensalem Township in Bucks County, PennsylvaniaBensalem TownshipLocation of Bensalem in PennsylvaniaShow map of PennsylvaniaBensalem TownshipBensalem Township (the United States)Show map of the United StatesCoordinates: 40°06′46″N 74°56′36″W / 40.11278°N 74.94333°W / 40.11278; -74.94333CountryUnited StatesStatePennsylvaniaCou...
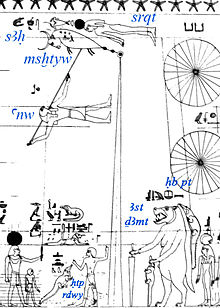
Celestial diagram in ancient Egyptian tomb Top and bottom portions[1] Astronomical ceiling decoration in its earliest form can be traced to the Tomb of Senenmut (Theban tomb no. 353), located at the site of Deir el-Bahri, discovered in Thebes, Upper Egypt. The tomb and the ceiling decorations date back to the XVIII Dynasty of ancient Egypt (circa 1479–1458 BCE). It is closed to the public.[2] Discovery The tomb of Senemut was discovered during the 1925–1927 excavations dir...

Waikino Music FestivalArtwork Gunther CollinsGenreRock, psychedelic rockLocation(s)Waikino and Waihi, New ZealandYears active1977Attendance5,000 Waikino Music Festival was a 1977 music and alternatives event held on Bicknell's farm in the Waitawheta Valley between Waikino and Waihi, New Zealand. Between band set ups; solo artists, poets and storytellers, comedians, yoga demonstrations and ravers would entertain, enabling the show to continue without breaks. These ideas were even further devel...

Professional ice hockey team Atlanta KnightsCityAtlanta, GeorgiaLeagueInternational Hockey LeagueConferenceEasternDivisionCentralFounded1992Folded1996Home arenaOmni ColiseumColorsBlack, blue and gray Owner(s)David Berkman[1]Franchise history1992–1996Atlanta Knights1996–1998Quebec RafalesChampionshipsDivision titles1993, 1994Conference titles1994Turner Cups1994 The Atlanta Knights were a minor league professional ice hockey team in the International Hockey League...

Neighborhood in Virginia Beach, Virginia, United StatesPungoNeighborhoodPungo Pizza in PungoPungoLocation within the state of VirginiaShow map of VirginiaPungoPungo (the United States)Show map of the United StatesCoordinates: 36°43′25″N 76°1′4″W / 36.72361°N 76.01778°W / 36.72361; -76.01778CountryUnited StatesStateVirginiaIndependent cityVirginia BeachTime zoneUTC−5 (Eastern (EST)) • Summer (DST)UTC−4 (EDT)ZIP Code23457Area code757 Pungo is ...

LighthouseMaryport Lighthouses LocationMaryport, United Kingdom Coordinates54°43′04″N 3°30′38″W / 54.71777°N 3.51069°W / 54.71777; -3.51069Maryport Old Lighthouse Constructed1846 Foundation1-storey stone octagonal prism basementConstructioncast iron (tower) Height11 m (36 ft) Shapetwo-stage octagonal tower with lanternMarkingsunpainted (foundation), white (tower), black (lantern) HeritageGrade II listed building&...
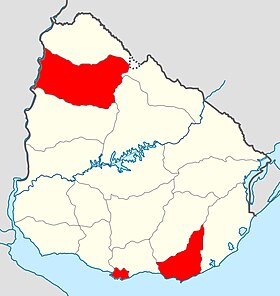
جائحة فيروس كورونا في أوروغواي Map as of 15 March 2020 المرض مرض فيروس كورونا 2019 السلالة فيروس كورونا 2 المرتبط بالمتلازمة التنفسية الحادة الشديدة تاريخ الوقوع 13 مارس 2020(4 سنوات، و2 شهور، و1 أسبوع، و1 يوم) المنشأ لومبارديا، إيطاليا برشلونة، إسبانيا المكان الأوروغواي ال�...

Anglican church in Ireland Church of IrelandEaglais na hÉireann (Irish)Kirk o Airlann (Scots)Holmpatrick St Patrick Church in Skerries, County DublinTypeCommunionClassificationProtestantOrientationAnglican[a]ScriptureBibleTheologyAnglican doctrinePolityEpiscopalPrimatesArchbishop of Armagh – John McDowell Archbishop of Dublin – Michael JacksonAssociationsAnglican CommunionConference of European ChurchesChurches Together in Britain and IrelandIrish Council of ChurchesPor...

Process by which particulates move towards the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment For the human activity, see settler. For the audio drama, see The Settling. Settling pond for iron particles at water works Settling is the process by which particulates move towards the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. Particles that experience a force, either due to gravity or due to centrifugal motion will tend to move in a uniform manner in the direction exerted by that force. For gravity settling...

LIRR beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Lirr (disambiguasi). Long Island Rail RoadLong Island Rail Road menyediakan jasa kereta listrik dan diesel timur-barat di seluruh Long Island, New York.IkhtisarArmadaDE30AC, DM30AC (khusus lokomotif Diesel Elektrik bermode Ganda), M3, M7, dan M9 (khusus KRL)Kantor pusatJamaica Railroad StationJamaica, NY 11435Markah laporanLILokalLong Island, New YorkTanggal beroperasi1834–sekarang(PRR-beroperasi sejak 1928 hingga 1949)TeknisLebar ...

Hindu temple in Kerala, India Sree Maheswara TempleReligionAffiliationHinduismDistrictThrissurDeityShivaFestivalsThaipooya MahotsavamLocationLocationKoorkenchery, City of ThrissurStateKeralaCountry IndiaSree Maheswara Temple, Koorkenchery, Thrissur, KeralaGeographic coordinates10°30′09″N 76°12′45″E / 10.5026°N 76.2125°E / 10.5026; 76.2125ArchitectureTypeArchitecture of KeralaElevation39.51 m (130 ft) Sree Maheswara Temple is a Hindu temple s...

عبد الرحمن علي الحجي معلومات شخصية الميلاد سنة 1935 [1] المقدادية الوفاة 18 يناير 2021 (85–86 سنة)[1] مدريد سبب الوفاة نوبة قلبية مواطنة العراق الحياة العملية المواضيع تاريخ الأندلس، والتَّاريخ الإسلامي المدرسة الأم جامعة كامبريدج (الشهادة:دكت...

US election 1844 Ohio gubernatorial election ← 1842 October 8, 1844 1846 → Nominee Mordecai Bartley David Tod Party Whig Democratic Popular vote 146,333 145,062 Percentage 48.73% 48.31% County Results Bartley 40–50% 50-60% 60-70% Van Buren 40–50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Governor before election Thomas W. Bartley (acting) Democratic Elected Governor Mordecai Bartley Whig...

Campionato europeo di pallanuoto 2020 Competizione Campionato europeo di pallanuoto Sport Pallanuoto Edizione 18ª Organizzatore LEN Date dal 12 gennaioal 25 gennaio 2020 Luogo UngheriaBudapest Partecipanti 12 Formula Fase a gironiEliminazione diretta Impianto/i Duna Aréna Sito web Sito ufficiale Risultati Oro Spagna(2º titolo) Argento Russia Bronzo Ungheria Statistiche Incontri disputati 44 Gol segnati 939 (21,34 per incontro) Cronologia della competizione Barcellona 20...

English churchman and writer (1564–1659) For other people named Thomas Morton, see Thomas Morton (disambiguation). The Right ReverendThomas MortonBishop of DurhamPortrait by Simon LuttichuysDioceseDiocese of DurhamIn office1632–1646 (Episcopacy abolished)[1]PredecessorJohn HowsonSuccessorVacant (Civil War)Other post(s)Dean of Gloucester (June 1607–1609)Dean of Winchester (1609–1616)Bishop of Chester (1616–1619)Bishop of Coventry & Lichfield (February 1619–1632)OrdersOr...

Component city in Camarines Sur, Philippines Not to be confused with Iringa. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Iriga – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Component city in Bicol Region, PhilippinesIrigaComponent cityCity of Iriga ...









