Juniperus phoenicea
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
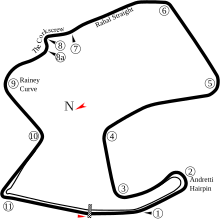
Grand Prix Amerika Serikat 2012Detail lombaLomba ke 10 dari 18Grand Prix Sepeda Motor musim 2012Tanggal29 Juli 2012Nama resmiRed Bull U.S. Grand Prix[1][2][3]LokasiMazda Raceway Laguna SecaSirkuitFasilitas balapan permanen3.610 km (2.240 mi)MotoGPPole positionPembalap Jorge Lorenzo YamahaCatatan waktu 1:20.554 Putaran tercepatPembalap Dani Pedrosa HondaCatatan waktu 1:21.229 PodiumPertama Casey Stoner HondaKedua Jorge Lorenzo YamahaKetiga Dani Ped...

Peta county di Rumania dan Munisipalitas Bukares Rumania Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanRumania Undang-Undang Dasar Referendum 1991 (pengesahan) 2003 (amendemen) 2015 (amendemen) Mahkamah Konstitusi Pemerintah Presiden (daftar) Klaus Iohannis Perdana Menteri (daftar) Nicolae Ciucă Kabinet (saat ini, daftar) Parlemen Senat Presiden: Florin Cîțu Biro Tetap Dewan Perwakilan Presiden: Marcel Ciolacu Biro Tetap Yudikatif Pengadilan Tinggi Kasasi dan Keadilan Mahka...

Konten dan perspektif penulisan artikel ini hanya berpusat pada sudut pandang dari negara Indonesia dan tidak menggambarkan wawasan global pada subjeknya. Silakan bantu mengembangkan atau bicarakan artikel ini di halaman pembicaraannya, atau buat artikel baru, bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel...

Manohar Singh GillDr. M.S. Gill pada Desember 2008 Menteri Statistik dan Pelaksana ProgramMasa jabatan19 Januari 2011 – 12 Juli 2011PresidenPratibha PatilPerdana MenteriManmohan Singh PendahuluShriprakash Jaiswal, Menteri Negara (Penanggung Jawab Independen)PenggantiSrikant Kumar Jena, Menteri Negara (Penanggung Jawab Independen)Menteri Pemuda dan OlahragaMasa jabatan28 Mei 2009 – 19 Januari 2011PresidenPratibha PatilPerdana MenteriManmohan Singh PenggantiAjay Maken, Men...

Untuk wilayah di Karachi, lihat Distrik Keamari. Permainan Kemari di Kuil Tanzan Cetak blok yang menggambarkan pakar Kemari Fujiwara no Narimichi (1097–1162) dan tiga monyet, dewa penjaga permainan tersebut Lapangan Kemari di Istana Kekaisaran Kyoto Kemari (蹴鞠code: ja is deprecated ) adalah sebuah permainan atletik yang populer di Jepang pada zaman Heian. Permainan tersebut mirip dengan permainan sepak bola atau hacky sack. Kemari telah dibangkitkan pada zaman modern. Sejarah Bukti awal...

Augustus De MorganAugustus De Morgan (1806-1871)Lahir(1806-06-27)27 Juni 1806Madurai, Kepresidenan Madras, Kekaisaran Britania (sekarang India)Meninggal18 Maret 1871(1871-03-18) (umur 64)London, InggrisTempat tinggalIndiaInggrisKebangsaanBritaniaAlmamaterTrinity CollegeUniversity of CambridgeDikenal atasHukum De MorganDe Morgan algebraRelation algebraUniversal algebraKarier ilmiahBidangMatematikawan dan logikawanInstitusiUniversity College LondonUniversity College SchoolPembimbing akade...

Chief wife of Hindu god Krishna For other uses, see Rukmini (disambiguation). RukminiMother Goddess[1][2][3]Goddess of Fortune[4][5]Member of Ashtabharya12th-13th century sculpture of Rukmini from Tamil Nadu Museum of ArtOther namesVaidarbhi, Bhaishmi, Rakhumai, DwarikeshwariDevanagariरूक्मिणीVenerated inWarkari, HaridasaAffiliationAshtabharya, Devi, Avatar of Lakshmi, VaishnavismAbodeDvārakā, PandharpurTextsVishnu Purana, Bhagavata Pu...

Bagian dari seriZoroastrianismeFaravahardiyakini sebagai gambaran dari fravashi Topik utama Ahura Mazda Zarathustra aša (asha) / arta Malaikat dan iblis Amesha Spentas · Yazatas Ahuras · Daevas Angra Mainyu Kitab dan penyembahan Avesta Gatha · Yasna Vendidad · Visperad Yashts · Khordeh Avesta Ab-Zohr Selawat Ahuna Vairya Kuil Api Cerita dan legenda Dēnkard · Bundahišn Kitab Arda Viraf Kitab Jamasp Sanjan Sejarah dan kultur Zurvanism Kalender · Festival Pernikahan Eksatologi/Akhirat ...

Ekaterinburg ЕкатеринбургKotaBeberapa tetenger Kota Ekaterinburg. BenderaLambang kebesaranPeta lokasi Ekaterinburg EkaterinburgLokasi EkaterinburgTampilkan peta RusiaEkaterinburgEkaterinburg (Rusia)Tampilkan peta RusiaKoordinat: 56°50′8″N 60°36′46″E / 56.83556°N 60.61278°E / 56.83556; 60.61278Koordinat: 56°50′8″N 60°36′46″E / 56.83556°N 60.61278°E / 56.83556; 60.61278NegaraRusiaSubjek federalSverdlovsk OblastP...

MegavolleyPallavolo Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Nome sponsorizzatoMegabox Ondulati Del Savio Vallefoglia Colori sociali Bianco e verde Dati societariCittàVallefoglia Nazione Italia ConfederazioneCEV FederazioneFIPAV CampionatoSerie A1 Fondazione2019 Presidente Ivano Angeli Allenatore Andrea Pistola ImpiantoPalaCampanara(2 000 posti) Palmarès Stagione in corso Si invita a seguire le direttive del Progetto Pallavolo La Megavolley è una società pallavolistica fe...

الانتخابات التشريعية الإسرائيلية 2022نسبة المشاركة70.63% وبارتفاع 3.19% الحزب الزعيم % عدد المقاعد ± ليكود 23.24 32 يش عتيد 17.92 24 المعسكر الرسمي 8.92 12 شاس 8.4 11 Labor 3.57 4 UTJ 6.2 7 إسرائيل بيتنا 4.33 6 الصهيونية المتدينة 10.32 14 ميرتس 3.2 0 الجبهة–العربية للتغيير 3.91 5 Ra'am 4.33 5 Jewish Home 0 التجمع الوطني الدي...

2018 single by Post Malone featuring Ty Dolla Sign PsychoSingle by Post Malone featuring Ty Dolla $ignfrom the album Beerbongs & Bentleys ReleasedFebruary 23, 2018 (2018-02-23)GenrePop rap[1]Length3:41 3:27 (radio edit) LabelRepublicSongwriter(s) Austin Post Tyrone Griffin Louis Bell Producer(s) Post Malone Louis Bell Post Malone singles chronology Candy Paint (2017) Psycho (2018) Ball for Me (2018) Ty Dolla Sign singles chronology What You Think(2018) Psych...

Medal Commemorating Naval Engagements in the West Indies AwardSampson MedalObverseTypeCampaign medalAwarded forCombat operations in the waters of the West Indies and Cuba.Presented byDepartment of the NavyEligibilityPersonnel who were assigned in the fleet of Rear Admiral William T. Sampson during the Spanish–American WarStatusObsoleteEstablished1901First awarded1901Retroactive to 1898Sampson Medal ribbon Order of Wear (1972)Next (higher)Dewey Medal[1]Next (lower)Peary Pol...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Wiz 'n' Liz – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1993 video gameWiz 'n' Liz The Frantic Wabbit WescueDeveloper(s)Raising Hell SoftwarePublisher(s)PsygnosisDesigner(s)Martyn R. Chudley Mike Wat...

Cet article concerne le peuple ingouche. Pour la langue ingouche, voir Ingouche. Ingouches Populations importantes par région Russie 517,186[1] Turquie 85,000[2][3] Kazakhstan 18,000[4] Belgique 8,000 France 3,000[5] Population totale c. 1 million[6] Autres Langues Ingouche Religions Islam sunnite Ethnies liées Tchétchènes, Bats, Kistines modifier Les Ingouches (en ingouche: ГIалгIай, en russe: Ингуши), sont un peuple de Ciscaucasie habitant majoritairement la République...

Kawasan Konservasi Perairan Daerah Kabupaten Bantul (KKPD Kabupaten Bantul) adalah salah satu kawasan konservasi perairan daerah yang ada di Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta. Dalam pembagian administratif Indonesia, KKPD Kabupaten Bantul masuk dalam wilayah administratif Kabupaten Bantul. Nama lainnya adalah Taman Pesisir Kabupaten Bantul. Dasar hukum penetapannya adalah Surat Keputusan Bupati Bantul Nomor 284 Tahun 2014. Luas KKPD Kabupaten Bantul adalah 182 Hektare.[1] KKPD Kabupaten Bant...

American women's basketball franchise This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Columbus Quest – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Columbus QuestFounded1996Folded1998LeagueAmerican Basketball LeagueTeam history1996–1998Based inColu...

Этель Смит Этель Смит на Олимпийских играх 1928 года Общая информация Полное имя Этель Мэй Смит Дата и место рождения 5 июля 1907(1907-07-05)Торонто, Канада Дата и место смерти 31 декабря 1979(1979-12-31) (72 года)Торонто, Канада Гражданство Канада Рост 165 см Вес 54 кг Клуб Parkdale Ladies' Athletic C...
هذه المقالة بحاجة لصندوق معلومات. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة صندوق معلومات مخصص إليها. هو مسجد أثري يقع في منطقة السيدة زينب بمحافظة القاهرة بمصر، بناه الأمير سيف الدين بشتاك الناصري ، وهو أحد أمراء المماليك في عهد السلطان قلاوون ، وبنى بقربه كُتّابا عٌرف باسمه...

SBT Sistema Brasileiro de TelevisãoLogotipo usado desde 2014 Sistema Brasileiro de TelevisãoA entrada para a sede do CDT da Anhanguera, localizado em Osasco Tipo Rede de televisão comercial aberta País Brasil Fundação 19 de agosto de 1981 (43 anos)por Silvio Santos Pertence a Grupo Silvio Santos Proprietário Família Abravanel Antigo proprietário Silvio Santos (1981–2024) Presidente Daniela Beyruti Sede Osasco, SP Estúdios CDT da Anhanguera Slogan É coisa nossa[1] Format...






