Joseph Jay Pastoriza
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kaseifu no MitaPoster Kaseifu no MitaGenreDrama keluargaDitulis olehKazuhiko YukawaSutradaraRyuichi Inomata, Toya Sato, Jun Ishio, Ken HigurashiPemeran Nanako Matsushima Yumi Shirakawa Hiroki Hasegawa Shiori Kutsuna Taishi Nakagawa Shūto Ayabe Miyu Honda Saki Aibu Penggubah lagu temaYoshihiro Ike,Kazuyoshi SaitoLagu pembukaMain Thema of MitaLagu penutupYasashiku NaritaiPenata musikYoshihiro IkeNegara asal JepangBahasa asliJepangJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode11ProduksiProduser eksekuti...
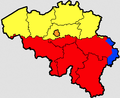
Flanders beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Flanders (disambiguasi). Flemish Region Vlaams GewestRegion of Belgium BenderaLambang kebesaranHimne daerah: De Vlaamse Leeuw [en] Negara BelgiaKursi ParlemenBrusselPemerintahan • Presiden MenteriKris PeetersLuas • Total13.522 km2 (5,221 sq mi)Populasi (2008-01-01)[1] • Total6.161.600Demografik • BahasaBelandaKode ISO 3166BE-VLGHari peringatan11 ...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This biographical article is written like a résumé. Please help improve it by revising it to be neutral and encyclopedic. (November 2017) A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please dis...

Rahul GandhiRahul Gandhi in 2018 Anggota parlemen, Lok SabhaPetahanaMulai menjabat 7 August 2023[1]PendahuluDia sendiriPenggantiPetahanaDaerah pemilihanWayanad, KeralaMasa jabatan23 Mei 2019 – 23 Maret 2023 [9]PendahuluM. I. ShanavasPenggantiDia sendiriDaerah pemilihanWayanad, KeralaMasa jabatan17 Mei 2004 – 23 Mei 2019PendahuluSonia GandhiPenggantiSmriti IraniDaerah pemilihanAmethi, Uttar PradeshPresiden Kongres Nasional IndiaMasa jabatan16 Desember ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Чайки (значения). Чайки Доминиканская чайкаЗападная чайкаКалифорнийская чайкаМорская чайка Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:Вторич...

Era in the history of Lutheranism (1580–1730) For the Eastern Christian reformation movement, see Protestant Eastern Christianity.For the branch of Lutheranism based in the Byzantine Rite of the Eastern Orthodox Church, see Eastern Lutheranism.Part of a series onLutheranism Background Christianity Start of the Reformation Reformation Protestantism Doctrine and theology Bible Old Testament New Testament Creeds Apostles' Creed Nicene Creed Athanasian Creed Book of Concord Augsburg Confession ...

Hybrid rail service in Denton County, Texas A-trainA-train diesel multiple unit train at the Downtown Denton Transit CenterOverviewOwnerDenton County Transportation AuthorityLocaleDenton County, TexasTerminiDowntown Denton Transit CenterTrinity Mills stationStations6Websitedcta.net/a-trainServiceTypeHybrid railSystemDenton County Transportation Authority (DCTA)Operator(s)Rio Grande Pacific (operations)Stadler US (rolling stock maintenance)[1]Rolling stock11 Stadler GTW 2/6Daily riders...

Soviet electrical engineer In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Fedorovych and the family name is Toptunov. Leonid F. ToptunovЛеонід Федорович ТоптуновBorn16 August 1960Mykolaivka, Buryn Raion, Sumy Oblast, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet UnionDied14 May 1986 (aged 25)Moscow, Russian SFSR, Soviet UnionCause of deathAcute radiation syndromeNationalitySoviet UnionOther namesЛеонид Фёдорович Топтунов (in Russ...

Religion originating in Punjab, India Not to be confused with Sikkim. For adherents of Sikhism, see Sikhs. This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. You can assist by editing it. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) SikhismਸਿੱਖੀDarbar Sahib (Golden Temple) in Amritsar, Punjab, the holiest site of the Sikh religionTypeEthnic religion; universal religionClassificationIndian religionScripture Guru Granth Sahib Dasam Grant...

Bệnh lý bẩm sinhTên khácquái thai, dị tật bẩm sinh[1]Một cậu bé bị hội chứng Down, một trong những dị tật bẩm sinh phổ biến nhất [2]Khoa/NgànhDi truyền y học, nhi khoaTriệu chứngKhuyết tật thể chất, khuyết tật trí tuệ, khuyết tật phát triển [3]Khởi phátHiện tại khi sinh[3]LoạiKết cấu, chức năng[4]Nguyên nhânDi truyền, tiếp xúc với một số loại thuốc h...

IsauriaRegion kuno di AnatoliaLetakAnatolia Selatan-BaratBahasaIsauriaKota terbesarIsaura PalaeaSatrap PersiaFrigia/Secara intermiten merdeka bersama PisidiaProvinsi (Romawi)GalatiaAsia Kecil/Anatolia pada zaman Yunanu-Romawi. Wilayah klasik dan pemukiman utama mereka, termasuk Isauria. Isauria (/aɪˈzɔːriə/ atau /aɪˈsɔːriə/; bahasa Yunani Kuno: Ἰσαυρία), dalam geografi kuno, adalah sebuah distrik terisolasi yang keras di pedalaman Asia Kecil Selatan, dengan luas yang san...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Mad (disambiguasi). Untuk mad dalam tajwid, lihat Hukum mad. Mad adalah majalah humor dari Amerika Serikat yang didirikan oleh editor Harvey Kurtzman dan pertama kali diterbitkan oleh William Gaines pada tahun 1952. Majalah ini memparodikan segala aspek kehidupan Amerika Serikat. Artikel bertopik jurnalisme ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia dengan mengembangkannya.lbs

Sochi 2014 XXII Juegos Olímpicos de Invierno Logo oficial de los Juegos Olímpicos de Invierno de 2014.Localización Sochi Federación RusaParticipantes • Países • Deportistas 882871Eventos 98 en 15 deportes olímpicosLema «Жаркие. Зимние. Твои» (en español: «Calientes. Fríos. Tuyos»)CeremoniasApertura 7 de febrero de 2014Clausura 23 de febrero de 2014Inaugurado por Vladímir PutinJuramentos • Deportista • Juez...
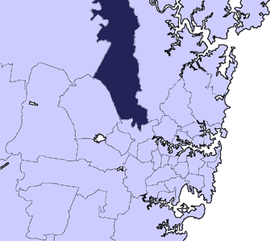
The Hills ShireNew South WalesJumlah penduduk170,965 • Kepadatan385/km2 (1.000/sq mi)Luas401 km2 (154,8 sq mi)WalikotaClr Peter DimbrowskyIbu kota dewanCastle HillDaerahMetropolitan SydneyDaerah pemilihan negara bagianBaulkham Hills, Castle Hill, Hawkesbury, ParramattaDivisi FederalBerowra, Mitchell, ParramattaSitus webThe Hills Shire Wilayah Pemerintah Daerah di Australia di sekitar The Hills Shire: City of Hawkesbury City of Gosford Hornsby Shire City of Blac...

List of events ← 1918 1917 1916 1919 in Portugal → 1920 1921 1922 Centuries: 18th 19th 20th 21st Decades: 1890s 1900s 1910s 1920s 1930s See also:List of years in Portugal Events in the year 1919 in Portugal. Incumbents President: João do Canto e Castro; António José de Almeida Prime Minister: João Tamagnini de Sousa Barbosa; José Relvas; Domingos Leite Pereira; Alfredo de Sá Cardoso Events 11 May – Portuguese legislative election, 1919.[1] Establishment of the ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Gera (homonymie). Gera Hôtel de ville, édifié entre 1573 et 1576 dans le style Renaissance allemande avec les remarquables fenêtres diagonales de la tour Armoiries Drapeau Administration Pays Allemagne Land Thuringe Arrondissement(Landkreis) Gera (ville-arrondissement) Nombre de quartiers(Ortsteile) 40 Bourgmestre(Oberbürgermeister) Julian Vonarb Partis au pouvoir rien Code postal 07545 - 07557 Code communal(Gemeindeschlüssel) 16 0 52 000 Indicat...

Transfer of the meaning of something in one language into another This article is about language translation. For other uses, see Translation (disambiguation). Translator redirects here. For other uses, see Translator (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Transliteration. King Charles V the Wise commissions a translation of Aristotle. First square shows his ordering the translation; second square, the translation being made. Third and fourth squares show the finished translation being bro...

Giovanni I del Palatinato-ZweibrückenGiovanni I in un dipinto di Julius ZimmermannConte palatino e Duca di ZweibrückenStemma In carica11 giugno 1569 –12 agosto 1604 PredecessoreVolfango SuccessoreGiovanni II (Zweibrücken)Federico Casimiro (Landsberg)Giovanni Casimiro (Kleeburg) NascitaMeisenheim, 8 maggio 1550 MorteGermersheim, 12 agosto 1604 (54 anni) Luogo di sepolturaAlexanderkirche, Zweibrücken Casa realeWittelsbach PadreVolfango del Palatinato-Zweibrücken MadreAnna...
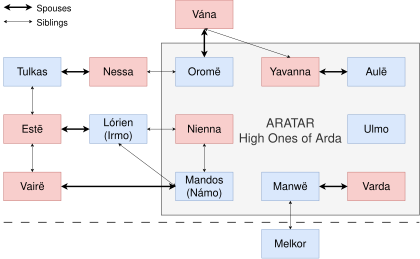
Divine or angelic race in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium For other uses, see Valar (disambiguation). Relationships between the Valar. The Valar (['valar]; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are angelic powers or gods[T 1] subordinate to the one God (Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how some of the Ainur choose to enter the world (Arda) to complete its material development after its form is determined by the Music of the Ainur. The ...
この項目では、FMいかるの愛称で運営しているコミュニティ放送局について説明しています。函館のコミュニティ放送局「FMいるか」とは異なります。 株式会社エフエムあやべ愛称 FMいかるコールサイン JOZZ7AM-FM周波数/送信出力 76.3 MHz/20 W本社・所在地 〒623-0016京都府綾部市〒623-0016 綾部市西町1丁目65番設立日 1997年8月21日開局日 1998年4月17日演奏所 本社と同じ送信所 綾...



