Johnny Peirson
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kaukasus KecilGunung Aragats di ArmeniaTitik tertinggiPuncakGunung Aragats[1]Ketinggian4.090 m (13.420 ft)DimensiPanjang600 km (370 mi) NW-SEGeografiNegara Daftar ArmeniaAzerbaijanGeorgiaIranTurki Rentang koordinat41°N 44°E / 41°N 44°E / 41; 44Koordinat: 41°N 44°E / 41°N 44°E / 41; 44PegununganPegunungan KaukasusBerbatasan denganKaukasus Besar Kaukasus Kecil adalah salah satu dari dua pegunungan utama pegu...
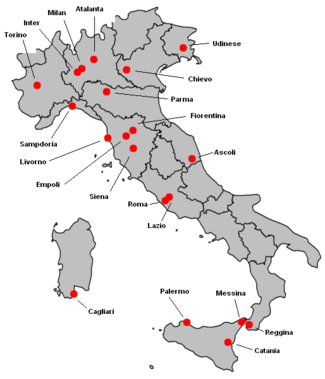
Serie AMusim2006-07JuaraInter MilanDegradasiChievoAscoliMessinaLiga ChampionsInter MilanAS RomaLazioAC MilanPiala UEFAPalermoFiorentinaEmpoliJumlah pertandingan380Jumlah gol969 (2,55 per pertandingan)Pencetak golterbanyakFrancesco Totti(26 gol)Pertandingan terbanyak golAS Roma 7–0 CataniaRata-ratajumlah penonton19,720← 2005–06 2007–08 → Serie A 2006–07 (dikenal juga sebagai Serie A TIM 2006–07) dimulai pada 10 September 2006. Musim ini awalnya dijadwalkan dimulai pada 26 da...

Duke of Aquitaine and Gascony and Count of Poitou William IXMiniature of William from a 13th-century chansonnier now in the Bibliothèque nationale de FranceDuke of AquitaineReign1086–1127PredecessorWilliam VIII, Duke of AquitaineSuccessorWilliam X, Duke of AquitaineBorn22 October 1071Died10 February 1126 (aged 54)SpouseErmengarde of AnjouPhilippa, Countess of ToulouseIssueWilliam X, Duke of AquitaineRaymond of PoitiersAgnes of Aquitaine, Queen of AragonHouseRamnulfidsFatherWilliam VIII, Du...

Un seuil et sa fosse de dissipation Un bassin de dissipation, fosse de dissipation ou bassin d'amortissement est un ouvrage ou parfois une configuration naturelle où plonge une chute d'eau après un déversoir, un seuil, ou une chute à l'intérieur d'une canalisation. On parle également de bassin de tranquillisation. Il est construit en vue de dissiper l'énergie de l'eau et d'éviter l'usure, l'érosion ou la destruction qu'elle pourrait provoquer à l'ouvrage ou à son environnement. Bas...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Конфликт (значения). Драка школьников на Ямайке Протестующие в Ломе (Того) противостоят полиции, 2017 год Драка морских слонов Конфли́кт (лат. conflictus — столкнувшийся) — наиболее острый способ разрешения противоречий в и�...

A manuscript from the early 1800s from central Sumatra, in Batak Toba language, one of many languages from Indonesia. Southeast Asia uses various non-Latin-based writing systems. The writing systems below are listed by language family. Austroasiatic languages Main article: Austroasiatic languages Khmer script (for Khmer language)[1] Khom script (for Bahnaric languages)[2] Chữ Nôm (historical writing for Vietnamese language)[3] Austronesian languages Main article: Au...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir John Brown (homonymie) et Brown. John BrownJohn Brown par Augustus Washington, c. 1846-1847.FonctionCommandant en chefArmée provisoire (d)BiographieNaissance 9 mai 1800TorringtonDécès 2 décembre 1859 (à 59 ans)Charles TownSépulture North ElbaNom de naissance John BrownSurnoms Osawatomie, Isaac SmithNationalité américaineDomiciles John Brown Home (d) (1844-1846), Torrington, North Elba, Hudson, AkronActivités Abolitionniste, maître de poste, ta...

Hindu temple in IndiaThis article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ghuisarnath Temple – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Ghuisarnath Templeघुइसरनाथ (घुश्मेश्वरनाथ) धामGhuisarnath (Ghushmeshwa...

District in American Samoa The Western District of American Samoa is shown in blue. The Western District is one of the three primary divisions of American Samoa. It consists of the western portion of Tutuila Island. It has a land area of 74.781 km2 (28.873 sq mi) and contains 29 villages plus a part of Nuʻuuli village. Among these is the largest village of American Samoa, Tafuna, at its eastern end. The district's total population as of the 2010 census was 31,329. Dental and medical car...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une maison d'édition. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?). Les entreprises étant un sujet propice aux controverses, n’oubliez pas d’indiquer dans l’article les éléments qui le rendent admissible. Les Éditions Bernard Valiquette était une maison d'édition québécoise ayant eu des activités dans des pays libres pendant la Seconde Guerre mondiale. Elle a été enregistrée en 1938 et a cessé de publie...

King of France from 1643 to 1715 For other uses, see Louis XIV (disambiguation). Sun King and Le Roi Soleil redirect here. For the French musical about him, see Le Roi Soleil (musical). For other uses, see Sun King (disambiguation). Louis XIVPortrait of Louis XIV, 1701King of France (more...) Reign14 May 1643 – 1 September 1715Coronation7 June 1654Reims CathedralPredecessorLouis XIIISuccessorLouis XVRegentAnne of Austria (1643–1651)Chief ministers See list Cardinal Mazarin(1643–1661) Je...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Baird. Maggie BairdMaggie Baird en 2014.BiographieNaissance 29 mars 1959 (65 ans)FruitaNom de naissance Maggie May BairdNationalité américaineDomicile Los AngelesFormation Université d'UtahActivités Actrice, auteure-compositrice-interprète, professeur d'art dramatiquePériode d'activité Depuis 1981Père William Norton Baird (d)Fratrie Brian Baird (en)Conjoint Patrick O'Connell (d) (depuis 1995)Enfants Finneas O'ConnellBillie Eilishmodifier - modif...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع حادث (توضيح). حادثمعلومات عامةصنف فرعي من حادثةطريقة الوفاةcalamity (en) الأسباب cause of accident (en) تسبب في إصابةموت يدرسه accidentology (en) ممثلة بـ type of accident (en) يتم التعامل معها أو تخفيفها أو إدارتها accident prevention (en) accident insurance (en) [1] تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بي...

Words that imitate the sound they describe This article is about the category of words. For other uses, see Onomatopoeia (disambiguation). A sign in a shop window in Italy proclaims these silent clocks make No Tic Tac, in imitation of the sound of a clock. Onomatopoeia (or rarely echoism)[1] is a type of word, or the process of creating a word, that phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Common onomatopoeias in English include animal noises such as ...

East German politician and diplomat Peter FlorinFlorin and Kurt Waldheim in 1973President of the United Nations General AssemblyIn office1987–1988Preceded byHumayun Rashid ChoudhurySucceeded byDante Caputo Personal detailsBorn(1921-10-02)2 October 1921Cologne, GermanyDied17 February 2014(2014-02-17) (aged 92)Berlin, GermanyPolitical partySocialist Unity Party of GermanyParent(s)Wilhelm Florin (1894–1944)Therese Althammer/Florin (1902–1990)Alma materD. Mendeleev University of Chemic...

Spain's New World Empire coastal possessions surrounding the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico Province of Tierra FirmeProvincia de Tierra Firme1498–1542 Cross of BurgundySpanish map of the Tierra FirmeStatusProvince of the Crown of CastileCapitalSanta María la Antigua del DariénPanama CityCommon languagesSpanishReligion CatholicismGovernmentMonarchyKing • 1492-1516 Ferdinand II and Isabella I• 1516–1556 Charles I Historical eraSpanish Empire• Established 1...

Removal of the human foreskin Not to be confused with female circumcision. For the paintings, see The Circumcision. CircumcisionCircumcision surgery with hemostats and scissorsICD-10-PCSZ41.2ICD-9-CMV50.2MeSHD002944OPS-301 code5–640.2MedlinePlus002998eMedicine1015820[edit on Wikidata] Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, a...

سينيكا غاردينز الإحداثيات 38°13′35″N 85°40′41″W / 38.2264°N 85.6781°W / 38.2264; -85.6781 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 1941 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة جيفيرسون خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.396924 كيلومتر مربع0.396581 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010)&...
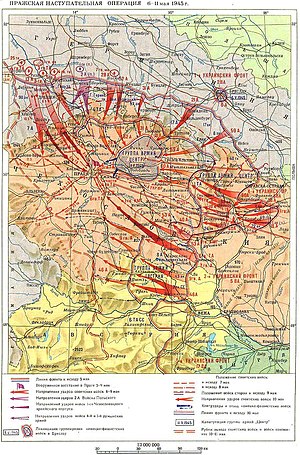
Пражская наступательная операцияОсновной конфликт: Вторая мировая война Бойцы Красной армии вступили в Прагу Дата 6—11 мая 1945 года Место Прага, Чехословакия Итог победа СССР Противники СССР Румыния Чехословакия Польша Германия Восстание: РОА Чехословацкое Сопротив�...

拉斐尔·奥苏纳出生1938年9月15日 墨西哥城 逝世1969年6月4日 (30歲)蒙特雷 母校南加州大学 职业網球運動員 拉斐尔·奥苏纳(西班牙語:Rafael Osuna,1938年9月15日—1969年6月4日),墨西哥男子网球运动员。他曾获得温布尔登网球锦标赛男子双打冠军、美国网球公开赛男子单打冠军、男子双打冠军。[1] 参考资料 ^ Rafael Osuna. ATP Tour. [2023-06-10]. ...
