Jean Piccard
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Flying Tiger Line IATA ICAO Kode panggil FT FTL TIGER Didirikan1945Mulai beroperasi1945Berhenti beroperasi1989 (diakuisisi oleh Federal Express)Kantor pusatBandara Los AngelesLos Angeles, California, Amerika Serikat Flying Tiger Line, juga dikenal sebagai Flying Tigers, adalah maskapai penerbangan kargo berjadwal pertama di Amerika Serikat dan juga maskapai carter militer terkemuka selama Perang Dingin baik untuk pengangkutan kargo dan personel tentara (yang terakhir dengan pesawat sewaan). F...

Gábor GergelyGábor pada tahun 2019Personal informationNama lengkapGergely GáborKebangsaan HungariaLahir21 Juni 1953 (umur 70) Rekam medali Putra Tenis meja Mewakili Hungaria World Championships 1983 Tokyo Men's Team 1981 Novi Sad Men's Team 1979 Pyongyang Men's Team European Championships 1982 Budapest Singles 1982 Budapest Doubles 1982 Budapest Men's Team 1980 Berne Doubles 1978 Duisburg Singles 1978 Duisburg Doubles 1978 Duisburg Men's Team 1974 Novi Sad Singles 1974 Novi...

American explorer, surveyor, ambassador (1822–1893) Edward Fitzgerald BealeUnited States Minister to Austria In officeJune 1, 1876 – April 20, 1877PresidentUlysses S. GrantPreceded byGodlove S. OrthSucceeded byJohn A. KassonSurveyor General of California and NevadaIn office1861PresidentAbraham LincolnSuperintendent of Indian Affairs for California and NevadaIn office1853–1856PresidentMillard Fillmore Personal detailsBornAustria-Hungary(1822-02-04)February 4, 1822Washington, D.C...

Artikel ini mengenai cerita bergambar dari Jepang; untuk anime, lihat Otogizōshi (anime). Ilustrasi cerita Issun bōshi Otogizōshi (御伽草子, お伽草子, atau おとぎ草子code: ja is deprecated , buku cerita dongeng) adalah sebutan untuk buku-buku cerita bergambar asal Jepang yang disusun mulai abad ke-14 hingga abad ke-17. Isinya berupa cerita pendek (dongeng) yang dilengkapi dengan ilustrasi, dan ditujukan bagi anak-anak sekaligus orang dewasa. Nama pengarang dan ilustrator tidak...

دوري الدرجة الأولى الإماراتي الجهة المنظمة اتحاد الإمارات العربية المتحدة لكرة القدم تاريخ الإنشاء 1974 (منذ 50 سنة) الرياضة كرة قدم البلد الإمارات القارة آسيا النسخة الأولى 1974 (منذ 50 سنة) عدد الفرق 11 أحدث بطل خورفكان (6 ألقاب) الأكثر فوزا اتحاد كلباء (7 ألقاب) الصعود الدو...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Balte. Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’histoire et l’ethnologie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Les Baltes sont un ensemble de peuples indo-européens du nord de l'Europe, identifiés par le fait qu'ils parlent des langues de la branche des langues baltes et qui ont conservé la langue vivante la plus ancienne des Indo-Européens. Ils sont actuelle...

American baseball player (born 1988) Baseball player Dallas KeuchelKeuchel with the Houston Astros in 2015Seattle Mariners PitcherBorn: (1988-01-01) January 1, 1988 (age 36)Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S.Bats: LeftThrows: LeftMLB debutJune 17, 2012, for the Houston AstrosMLB statistics (through 2023 season)Win–loss record103–92Earned run average4.02Strikeouts1,243 Teams Houston Astros (2012–2018) Atlanta Braves (2019) Chicago White Sox (2020–2022) Arizona Diamondbacks (2022)...

Finnish former athlete (born 1941) Juha VäätäinenJuha Väätäinen in 2011.Personal informationBirth nameJuha VäätäinenFull nameToivo Juha VäätäinenNickname(s)Juha the Cruel Julma-Juha in FinnishNationalityFinnishBorn (1941-07-12) 12 July 1941 (age 82)Oulu, FinlandHeight1.72 m (5 ft 8 in)Weight60 kg (132 lb; 9 st 6 lb)Websitewww.juhavaatainen.infoSportCountry FinlandSportRunningEventLong-distanceClubHaapaveden Urheilijat 1958-67 ...

1985 film by Woody Allen The Purple Rose of CairoTheatrical release posterDirected byWoody AllenWritten byWoody AllenProduced byRobert GreenhutStarring Mia Farrow Jeff Daniels Danny Aiello CinematographyGordon WillisEdited bySusan E. MorseMusic byDick HymanDistributed byOrion PicturesRelease date March 1, 1985 (1985-03-01) Running time82 minutes[1]CountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishBudget$15 millionBox office$10.6 million[2] The Purple Rose of Cairo is a 1985 Am...

Les départements de la Côte d'Ivoire sont une division administrative et une ancienne collectivité territoriale. Le pays est subdivisé en 111 départements, regroupés en 31 régions et 14 districts autonomes[1]. Les départements sont à leur tour subdivisés en 509 sous-préfectures[1]. Carte des départements, régions et districts autonomes de la Côte d'Ivoire. Les fonds et noms de couleurs indiquent les régions et districts autonomes (fond rouge, nom magenta). Liste des départemen...

7th to 11th-century Mon kingdom This article is about a historical Mon kingdom. For the Dvaravati in the Hindu epic Mahabharata, see Dvārakā. Dvaravati Kingdom6th–11th centurySIND800UYGHUR KHAGANATEGURJARA-PRATIHARASRASHTRA-KUTASPALAEMPIRECHAM-PANAN-ZHAOTURKSHAHISTANGDYNASTYSILLAKhitansJurchensTungusKARLUKYABGHUTatarsCHENLADVARA-VATISRIVIJAYAKyrgyzsPaleo-SiberiansSamoyedsKimeksTangutsShatuosABBASID CALIPHATEKHAZARKHAGANATEBYZANTINEEMPIREOGHUZ-YABGUSTIBETANEMPIRE ◁ ▷ The Dvaravati King...
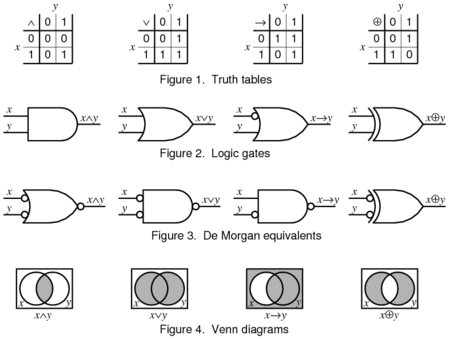
Process by which desired circuit behavior is turned into a schematic of logic gates Not to be confused with Synthetic programming. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Logic synthesis – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) In comput...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une personnalité française. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Jacqueline JanetJacqueline Janet dans Paris-Soir du 10 octobre 1937.BiographieNaissance 21 décembre 191916e arrondissement de ParisDécès 11 mars 2016 (à 96 ans)Neuilly-sur-SeineNationalité françaiseFormation Lycée Victor Duruy de ParisActivités Mannequin, participante à un concours ...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bukit Tengah railway station – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Bukit Tengah | Commuter rail stationGeneral informationLocationBukit Tengah, Penang, Malaysia.Owned byKeretapi Tanah MelayuLine(s) 1 ...

1972 arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Anti-Ballistic Missile TreatyLaunch of a U.S. Army Nike Ze...

Russieau Concours Eurovision 2020 Données clés Pays Russie Chanson Uno Interprète Little Big Langue Anglais Sélection nationale Radiodiffuseur Pervi Kanal Type de sélection Sélection interne Date 2 mars 2020 (artiste)12 mars 2020 (chanson) Concours Eurovision de la chanson 2020 2019 2021 modifier La Russie était l'un des quarante et un pays participants prévus du Concours Eurovision de la chanson 2020, qui aurait dû se dérouler à Rotterdam aux Pays-Bas. Le pays aurait été ...

Eastern European fortifications made of earth Trajan's Wall depicted on Moldovan stamps Trajan's Wall (Romanian: Valul lui Traian) is the name used for several linear earthen fortifications (Latin: valla) found across Eastern Europe, Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine. Contrary to the name and popular belief, evidence shows the ramparts were likely not built under the reign of Trajan, but later, in the period of Late Antiquity. The association with the Roman Emperor Trajan may be a recent scholarl...

「Gガンダム」はこの項目へ転送されています。この作品に登場する後期主役メカについては「ゴッドガンダム」をご覧ください。 機動武闘伝Gガンダム ジャンル ロボットアニメ[1]、子供向けアニメ[2][要ページ番号] アニメ 原作 矢立肇、富野由悠季(『機動戦士ガンダム』より) 総監督 今川泰宏 シリーズ構成 五武冬史 キャラクターデザイン 逢坂浩...

Музей американского искусства Уитниангл. Whitney Museum of American Art Основан 1931[1][2] Открыт 1931 Основатель Гертруда Вандербильт[1] Местонахождение Манхэттен Адрес 99 Gansevoort Street, Lower Manhattan, New York City Посетителей в год 492 500 чел. (2021)[3] Директор Adam D. Weinberg[вд][4] Сайт w...

نهر أركنساس المنطقة البلد الولايات المتحدة الخصائص الطول 2364 كيلومتر المصب نهر المسيسيبي مساحة الحوض 505000 كيلومتر مربع الروافد نهر سيمارون، ونهر نيوشو، ونهر كنديان، ونهر فيرديكريس [لغات أخرى] تعديل مصدري - تعديل نهر أركنساس (بالإ�...


