Itty Achudan
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Bintang seri televisi – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Bintang (disambiguasi). BintangGenre Roman Remaja PembuatSinemArtDitulis olehAlberthiene EndahSke...

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Heo. Heo Kyung-hwanLahir16 Februari 1981 (umur 43)Tongyeong, South KoreaMediaStand-up, TelevisiKebangsaanKorea SelatanTahun aktif2006–sekarangGenreObservational, Sketch, Wit, Parodi, Slapstick, Dramatic, SitcomNama KoreaHangul허경환 Hanja許卿煥 Alih AksaraHeo Gyeong-hwanMcCune–ReischauerHŏ Kyŏng-hwan Heo Kyung-hwan (Hangul: 허경환; lahir 16 Februari 1981), adalah komedian asal Korea Selatan. Ia memulai debut sebagai komedian ...

Ali Mukhni Bupati Padang Pariaman ke-19Masa jabatan17 Februari 2016 – 17 Februari 2021WakilSuhatri Bur PendahuluRosnini Savitri (Pj.)PenggantiJonpriadi (Plh.)Suhatri BurMasa jabatan25 Oktober 2010 – 25 Oktober 2015WakilDamsuar PendahuluFebri Erizon (Pj.)PenggantiJonpriadi (Plh.)Wakil Bupati Padang Pariaman ke-2Masa jabatan5 September 2005 – 5 September 2010BupatiMuslim Kasim PendahuluMartias MahyuddinPenggantiDamsuar Informasi pribadiLahir(1956-09-16)1...

Alpine mountain pass in Switzerland Fuorn PassFuorn PassElevation2,149 m (7,051 ft)Traversed byRoad 28LocationGraubünden, SwitzerlandRangeAlpsCoordinates46°38′23″N 10°17′32″E / 46.63972°N 10.29222°E / 46.63972; 10.29222Fuorn PassLocation in Switzerland Fuorn Pass or Ofen Pass (Romansh: Pass dal Fuorn, German: Ofenpass, Italian: Passo del Forno) (el. 2149 m.) is a high alpine mountain pass in the canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. The name is based on th...

Queen of Denmark and Norway from 1699 to 1721 Louise of Mecklenburg-GüstrowPortrait by Johann Salomon Wahl, c. 1720Queen consort of Denmark and NorwayTenure25 August 1699 – 15 March 1721Coronation15 April 1700Born(1667-08-28)28 August 1667GüstrowDied15 March 1721(1721-03-15) (aged 53)CopenhagenBurialRoskilde CathedralSpouse Frederick IV of Denmark (m. 1695)IssueChristian VIPrincess Charlotte AmalieHouseMecklenburgFatherGustav Adolph, Duke of Mec...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Advanced Technology Program – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The NIST Advanced Technology Program (ATP, or NIST ATP) is a United States government (U.S. Department of Commerce, Nat...
Historic house in New York, United States United States historic placeHancock HouseU.S. National Register of Historic Places Hancock House, Ticonderoga (rear view)Show map of New YorkShow map of the United StatesLocationMontcalm and Wicker Sts., Ticonderoga, New YorkCoordinates43°50′54″N 73°26′6″W / 43.84833°N 73.43500°W / 43.84833; -73.43500Area1.4 acres (0.57 ha)Built1925–1926 (1926)Built byEdward F. MinorArchitectMax H. WesthoffArchitectural&...
American college football stadium in Massachusetts For other uses, see Alumni Stadium (disambiguation). Alumni StadiumAlumniThe stadium from above in 2023Alumni StadiumLocation in MassachusettsShow map of MassachusettsAlumni StadiumLocation in the United StatesShow map of the United StatesLocation140 Commonwealth Avenue, Chestnut Hill, MA 02467Coordinates42°20′6″N 71°09′59″W / 42.33500°N 71.16639°W / 42.33500; -71.16639OwnerBoston CollegeOperatorBoston Coll...

Election for the governorship of the U.S. state of Virginia 1869 Virginia gubernatorial election ← 1863 July 6, 1869 1873 → Nominee Gilbert Carlton Walker Henry H. Wells Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 119,535 101,204 Percentage 54.15% 45.85% Governor before election Henry H. Wells Republican Elected Governor Gilbert C. Walker Democratic Virginia's elections of 1869 occurred during the post-American Civil War Reconstruction Era and included African-A...

State in northern India For the Bollywood film, see Haryana (film). State in North India, IndiaHaryanaStateState of Haryana From top, left to right: Cyber City in Gurgaon, Pinjore Gardens, bronze chariot of Krishna and Arjuna at Kurukshetra, Asigarh Fort, Ghaggar river, Lake in Surajkund. Emblem of HaryanaEtymology: Abode of God or Green ForestMotto(s): Satyameva Jayate (Truth alone triumphs)Location of Haryana in IndiaCoordinates: 30°44′N 76°47′E / 30.73°N 76.78°...
Bus station in Roseville, Minnesota, United States Snelling & County Road B Metro bus rapid transit stationGeneral informationCoordinates45°0′19.08″N 93°9′59.04″W / 45.0053000°N 93.1664000°W / 45.0053000; -93.1664000Owned byMetro TransitLine(s) A Line Connections65ConstructionStructure typeMedium shelterParkingNoAccessibleYesHistoryOpenedJune 11, 2016Passengers2018371 (average daily)[1] 1.92% Services Preceding station Met...

English footballer and manager For the Leicester City and Brentford player, see Dean Smith (footballer, born 1958). Dean Smith Smith in 2011Personal informationFull name Dean Smith[1]Date of birth (1971-03-19) 19 March 1971 (age 53)Place of birth West Bromwich, EnglandHeight 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)[2]Position(s) Centre-backTeam informationCurrent team Charlotte FC (head coach)Youth career1986–1989 Newcastle UnitedSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1989–1994 ...

Type of beer For other uses, see Saison (disambiguation). Saison Dupont Vieille Provision, the archetype for modern saisons Saison (French, season, French pronunciation: [sɛzɔ̃]) is a pale-colored ale that is highly carbonated, dry, fruity, spicy, and often bottle conditioned.[1][2] It was historically brewed with low alcohol levels, but modern productions of the style have moderate to high levels of alcohol. Along with several other varieties, it is generally class...

Bahasa Akkadia 𒀝𒅗𒁺𒌑akkadû Prasasti Air bah tentang epos Gilgames dalam bahasa Akkadia. WilayahMesopotamiaKepunahan100 SM Rumpun bahasaSemit Semit TimurAkkadia Sistem penulisanHuruf paku Sumero-AkkadiaStatus resmiBahasa resmi dimulanya Akkad (Mesopotamia Utara); lingua franca di Timur Tengah dan Mesir pada akhir Zaman Perunggu dan awal Zaman Besi.Kode bahasaISO 639-2akkISO 639-3akkGlottologakka1240[1]IETFakk Status pemertahanan Punah EXSingkatan dari Extinct (Punah)Te...

Prusia OrientalOstpreußen Provincia prusiana 1773-18291878-1945BanderaEscudo Prusia Oriental (en rojo) como provincia del Reino de Prusia (amarillo), dentro del Imperio alemán. Prusia Oriental (en rojo) como provincia del Estado Libre de Prusia (amarillo), dentro de la República de Weimar.Coordenadas 54°44′00″N 20°29′00″E / 54.733333333333, 20.483333333333Capital KönigsbergEntidad Provincia prusianaSuperficie • Total 36 993,89 km² Poblaci...

Bone of the neurocranium Occiput redirects here. For entomology term, see occiput (insect). Occipital bonePosition of occipital boneAnimation of the occipital boneDetailsArticulationsThe two parietals, the two temporals, the sphenoid, and the atlasIdentifiersLatinos occipitaleMeSHD009777TA98A02.1.04.001TA2552FMA52735Anatomical terms of bone[edit on Wikidata] The occipital bone (⫽ˌɒkˈsɪpɪtəl⫽) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the s...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati dell'Aragona è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Morata de Jilocacomune Morata de Jiloca – VedutaMorata de Jiloca LocalizzazioneStato Spagna Comunità autonoma Aragona Provincia Saragozza TerritorioCoordinate41°15′18.72″N 1°35′08.88″W41°15′18.72″N, 1°35′08.88″W (Morata de Jiloca) Altitudine619 m s.l.m. Superficie23 km² Abitanti300 (2001) Densità...

Toàn cảnh cầu Lư Câu Một sư tử đá với một sư tử con Các sư tử đá trên cầu Cầu Lư Câu (chữ Hán giản thể: 卢沟桥, phồn thể: 盧溝橋, bính âm phổ thông: Lúgōu Qiáo) là một cây cầu vòm được xây bằng đá granite vào cuối thế kỷ 12, bắc qua sông Vĩnh Định (永定河, Yǒngdìng Hé), thuộc địa phận quận Phong Đài (丰台区), thành phố Bắc Kinh, Trung Quốc. Đầu phía Đông của cầu Lư C�...

Đối với các định nghĩa khác, xem Ferrara (định hướng). Ferrara— Comune —Comune di Ferrara Theo chiều kim đồng hồ từ trên xuống: Quảng trường Ariostea, Nhà thờ chính tòa Ferrara, Corso Martiri della Libertà, Nhà hát thành phố Ferrara, Nhà tế bần Ferrara, Tượng đài tháp nước, và Lâu đài Estense. Hiệu kỳHuy hiệuVị trí tại tỉnh FerraraVị trí của Ferrara Lỗi Lua trong Mô_đun:Infob...
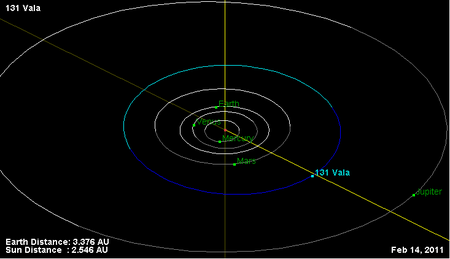
Main-belt asteroid 131 ValaOrbital diagramDiscovery[1]Discovered byChristian Heinrich Friedrich PetersDiscovery date24 May 1873DesignationsMPC designation(131) ValaPronunciation/ˈvɑːlə/[2]Named aftervǫlvaAlternative designationsA873 KA; 1945 KA;1952 DS3; 1953 QEMinor planet categoryMain belt[1]Orbital characteristics[1]Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5)Uncertainty parameter 0Observation arc142.88 yr (52187 d)Aphelion2.60 AU (388.64&...


