Ian Hornak
| |||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pokémon FireRedPokémon LeafGreen Karya seni FireRed (diwakili oleh Charizard) dan LeafGreen (diwakili Venusaur). Tipepaired remakes of Pokémon paired versions (en) BerdasarkanPokémon Red and Green (en) dan Pokémon Red dan Blue Versi pertamaJP: 29 Januari 2004NA: 9 September 2004[1]AU: 23 September 2004EU: 1 Oktober 2004GenreBermain peranKarakterRed (en) Bahasa Daftar Inggris, Italia, Jepang, Jerman, Prancis dan Spanyol 60 Karakteristik teknisPlatformGame Boy Advance Modepermainan...

City in east central Missouri, U.S. City in Missouri, United StatesSt. Peters, MissouriCityCity Centre Park near City Hall SealLocation of St. Peters in MissouriCoordinates: 38°46′44″N 90°36′11″W / 38.77889°N 90.60306°W / 38.77889; -90.60306CountryUnited StatesStateMissouriCountySt. CharlesIncorporated1910Government • MayorLen PaganoArea[1] • Total22.47 sq mi (58.19 km2) • Land22.46 sq mi ...

Venezuelan actor and entertainer This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Amador BendayánBendayán, c. 1960sBorn(1920-11-11)November 11, 1920Villa de Cura, Aragua, VenezuelaDiedAugust 4, 1989(1989-08-04) (aged 68)OccupationtelevisionYears&...

Musalla Fatihova di Bosnia-Herzegovina Ruangan untuk salat umat Muslim di Bandara Internasional Hong Kong, Tiongkok. Musala (takbaku: mushola, mushala), langgar, surau, atau bandarsah (Arab: مصلى, translit: muṣallácode: ar is deprecated ) adalah ruang selain masjid, terutama digunakan untuk ibadah salat di Islam.[1] Kata tersebut berasal dari kata kerja صلى (ṣallā), yang artinya berdoa. Ini secara tradisional digunakan untuk salat Id dan salat Jenazah sesuai anjuran ...

Shawnee leader in the American Revolution For other uses, see Corn Stalk. CornstalkDetail of Cornstalk as illustrated in John Frost’s Pictorial History of Indians (1873)Died(1777-11-10)November 10, 1777Fort Randolph, Virginia (now West Virginia)Cause of deathMurdered while imprisonedBurial placePoint Pleasant, West VirginiaNationalityShawneeOther namesHokoleskwa, Colesquo, KeightughquaKnown forShawnee war leaderRelativesNonhelema (sister) Cornstalk (c. 1727? – Novembe...

Article principal : Chef du gouvernement d'Andorre. Cet article dresse la liste des chefs du gouvernement d'Andorre (Cap de Govern d'Andorra) depuis la création de la fonction le 8 janvier 1982. Liste des titulaires N° Portrait Titulaire(Naissance-mort) Élection Mandat Partipolitique Début Fin Durée Période pré-constitutionnelle (1982-1993) 1 Òscar Ribas Reig(1936-2020) 1981 8 janvier 1982 21 mai 1984 2 ans, 4 mois et 13 jours PNL 2 Josep Pintat-Solans(1925-2007) 1...

Richard Karl von Weizsäcker Presiden Jerman ke-10 Presiden Republik Federal Jerman ke-6Masa jabatan1 Juli 1984 – 30 Juni 1994PendahuluKarl CarstensPenggantiRoman Herzog Informasi pribadiLahir(1920-04-15)15 April 1920 Stuttgart, JermanMeninggal31 Januari 2015(2015-01-31) (umur 94) Berlin, JermanKebangsaanJermanPartai politikCDUSuami/istriMarianne Freifrau (Baroness) von WeizsäckerSunting kotak info • L • B Dr. Richard Karl Freiherr von Weizsäcker dengarkanⓘ (...

提示:此条目页的主题不是中華人民共和國最高領導人。 中华人民共和国 中华人民共和国政府与政治系列条目 执政党 中国共产党 党章、党旗党徽 主要负责人、领导核心 领导集体、民主集中制 意识形态、组织 以习近平同志为核心的党中央 两个维护、两个确立 全国代表大会 (二十大) 中央委员会 (二十届) 总书记:习近平 中央政治局 常务委员会 中央书记处 �...

拉吉夫·甘地राजीव गांधीRajiv Gandhi1987年10月21日,拉吉夫·甘地在阿姆斯特丹斯希普霍尔机场 第6任印度总理任期1984年10月31日—1989年12月2日总统吉亞尼·宰爾·辛格拉马斯瓦米·文卡塔拉曼前任英迪拉·甘地继任維什瓦納特·普拉塔普·辛格印度對外事務部部長任期1987年7月25日—1988年6月25日前任Narayan Dutt Tiwari(英语:Narayan Dutt Tiwari)继任納拉辛哈·拉奥任期1984年10�...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2019) منتخب رومانيا لكرة الطائرة للسيدات كونفدرالية الاتحاد الأوروبي لكرة الطائرة [الإنجليزية] مراتب تصنيف فيف...
Rape case leading to anti-American movement in China (1946) You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (January 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wi...

Pemilihan Member Single ke-17 JKT48Logo Pemilihan Member Single ke-17 JKT48 Siapa yang akan membuat zaman baru? bersama Honda The Power of DreamsTanggal8 Maret - 20 April 2017 (pemungutan suara)22 April 2017 (pengumuman hasil)LokasiBalai Sarbini, Jakarta Selatan, JakartaJl. Jenderal Sudirman Kav. 52, Jakarta 12930 (pengumuman hasil pemilu)Peserta/Pihak terlibat64 anggota JKT48Hasil Anggota Senbatsu untuk single ke-17 JKT48 Indahnya Senyum Manismu dst. Shani terpilih menjadi center pada lagu t...

Active stratovolcano in the Gulf of Naples, Italy Vesuvius redirects here. For other uses, see Vesuvius (disambiguation). Mount VesuviusMount VesuviusHighest pointElevation1,281 m (4,203 ft) Prominence1,232 m (4,042 ft) Coordinates40°49′17″N 14°25′34″E / 40.82139°N 14.42611°E / 40.82139; 14.42611NamingNative nameVesuvio (Italian)Vesuvio (Neapolitan)GeographyMount VesuviusCampania, Italy LocationCampania, ItalyGeo...

ليرة عثمانيةمعلومات عامةالبلد الدولة العثمانية تاريخ الإصدار 1844 عوض قرش رمز العملة £L.T. المصرف المركزي البنك العثماني تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات الليرة العثمانية هي عملة الدولة العثمانية، للفترة ما بين 1844 و29 أكتوبر 1923. والتي حلت محل القروش التركية كوحدة عملة ...

Cette page a pour objectif de retracer toutes les modifications communales dans le département de la Haute-Loire : les anciennes communes qui ont existé depuis la Révolution française, ainsi que les créations, les modifications officielles de nom, ainsi que les échanges de territoires entre communes. En 1800, le territoire du département de la Haute-Loire comptait 277 communes. Très tôt la vague de fusions imposées aux toutes petites communes au début du XIXe siècle va e...

US-2 beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk Untuk kapal terbang US-2 Jepang, lihat ShinMaywa US-2, lihat US-2 (disambiguasi). U.S. Route 2US 2 berwarna merahInformasi rutePanjang:2.579 mi[2] (4.150 km)Berdiri:November 11, 1926[1] – sekarangBagian baratPanjang:2.119 mi[2] (3.410 km)Barat: I-5 / SR 529 di Everett, WAPersimpanganbesar: US 395 di Spokane, WA I-15 di Shelby, MT US 87 dekat Havre, MT US 83 di Minot, ND I-29 / US 81 di Grand Forks, ...
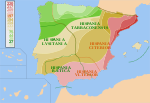
Aspect of Portuguese history Part of a series on the History of Portugal Ancient Prehistoric Iberia Pre-Roman Peoples Roman conquest of Hispania Romanization of Hispania Lusitania Gallaecia Suebic Kingdom Visigothic Kingdom Spania Medieval Umayyad conquest of Hispania Al-Andalus Gharb Al-Andalus Almoravid dynasty County of Portugal Reconquista Portuguese House of Burgundy 1383–1385 Crisis Age of Discovery Imperial expansion House of Aviz Portuguese Renaissance Portuguese Empire War of the P...

Canadian politician Napoléon Champagne31st Mayor of OttawaIn office1908–1909Preceded byD'Arcy ScottSucceeded byCharles HopewellConstituencyOttawa EastIn office1924–1925Preceded byHenry WattersSucceeded byJohn P. BalharrieMLA for Ottawa EastIn officeDecember 11, 1911 – May 29, 1914Preceded byDonald McDougalSucceeded byJoseph Pinard Personal detailsBornMay 4, 1861Lower Town, OttawaDiedNovember 17, 1925OttawaPolitical partyConservative Party of Ontario Napoléon Champagne (May 4,...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (أكتوبر 2019) دخلت أكثر من 1500 غواصة للخدمة في مختلف أساطيل ألمانيا البحرية المختلفة من عام 1906 إلى يومنا هذا. عادة ما يتم...


