II Corps (United Kingdom)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
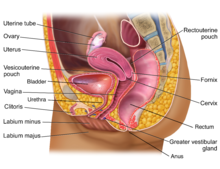
Branch of biology studying reproduction Reproductive biology includes both sexual and asexual reproduction.[1][2] Reproductive biology includes a wide number of fields: Reproductive systems Endocrinology Sexual development (Puberty) Sexual maturity Reproduction Fertility Human reproductive biology Main article: Human reproduction Endocrinology Main article: Endocrinology Human reproductive biology is primarily controlled through hormones, which send signals to the human reprod...

Extinct genus of carnivores ChasmaporthetesTemporal range: Pliocene–Early Pleistocene PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N ↓ C. lunensis skull Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Suborder: Feliformia Family: Hyaenidae Subfamily: Hyaeninae Genus: †ChasmaporthetesHay, 1921 Species See text Synonyms Euryboas Chasmaporthetes, also known as hunting or running hyena, is an extinct genus of hyenas[1][2]&...

Yōjo SenkiGambar sampul novel ringan volume pertama幼女戦記GenreFantasi, militer[1] Seri novelPengarangCarlo ZenPenerbitArcadiaTerbit2012 – 2013 Novel ringanPengarangCarlo ZenIlustratorShinobu ShinotsukiPenerbitEnterbrainPenerbit bahasa InggrisNA Yen PressDemografiPriaTerbit31 Oktober 2013 – sekarangVolume14 (Daftar volume) MangaPengarangCarlo ZenIlustratorChika TōjōPenerbitKadokawa ShotenPenerbit bahasa InggrisNA Yen PressMajalahComp AceDemografiSeinenTerbit26 April 2016 �...

CBS affiliate in Peoria, Illinois This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: WMBD-TV – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) WMBD-TVPeoria–Bloomington–Normal, IllinoisUnited StatesCityPeoria, IllinoisChannelsDigital: 26 (UHF)Virtual:...

GCR Class 11ELNER Class D10No. 2652 Edwin A. Beazley at Northwich MPD in 1947Type and originPower typeSteamDesignerJohn G. RobinsonBuilderGCR, at Gorton WorksBuild date1913Total produced10SpecificationsConfiguration: • Whyte4-4-0 • UIC2'Bh2Gauge4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm)Leading dia.3 ft 6 in (1,070 mm)Driver dia.6 ft 9 in (2,060 mm)Wheelbase48 ft 8+1⁄2 in (14,846 mm)Length58 ft 11+...

American college football season 1974 Texas Tech Red Raiders footballPeach Bowl, T 6–6 vs. VanderbiltConferenceSouthwest ConferenceRecord6–4–2 (3–4 SWC)Head coachJim Carlen (5th season)Offensive schemeNo-huddle optionDefensive coordinatorRichard Bell (5th season)Base defense4–3Home stadiumJones StadiumSeasons← 19731975 → 1974 Southwest Conference football standings vte Conf Overall Team W L T W L T No. 14 Bay...

Chinese-American engineer Statue of Ku at the Gu Yuxiu Memorial in Wuxi Yu Hsiu Ku or Gu Yuxiu (Chinese: 顾毓琇; December 24, 1902 – September 9, 2002) was a Chinese-American electrical engineer, musician, novelist, poet, and politician. A polymathic academic, he was one of the first Chinese people to earn a doctorate from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, in 1928, and became a leader in higher education in China until the fall of the Republic of China in 1949. Afterwards, h...
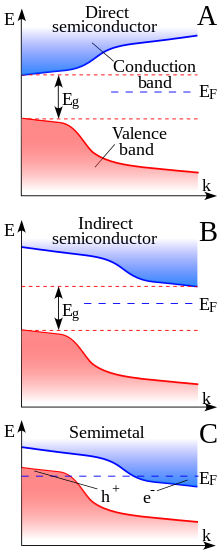
Material with small overlap between conduction and valence bands Not to be confused with Half-metal. For the class of chemical elements on the periodic table, see metalloid. Filling of the electronic states in various types of materials at equilibrium. Here, height is energy while width is the density of available states for a certain energy in the material listed. The shade follows the Fermi–Dirac distribution (black: all states filled, white: no state filled). In metals and semimetals the...

American politician For other people named James Miller, see James Miller (disambiguation). Jim Miller26th Director of the Office of Management and BudgetIn officeOctober 8, 1985 – October 16, 1988PresidentRonald ReaganDeputyJoe WrightPreceded byDavid StockmanSucceeded byJoe WrightChair of the Federal Trade CommissionIn officeSeptember 26, 1981 – October 4, 1985PresidentRonald ReaganPreceded byMichael PertschukSucceeded byDaniel Oliver Personal detailsBornJames Clifford ...

Association football competition in Scotland For other uses, see Scottish Cup (disambiguation). Football tournamentScottish CupFounded1873; 151 years ago (1873)RegionScotlandEngland (1 team)Number of teams131 (2023–24)Qualifier forUEFA Europa LeagueCurrent championsCeltic(42nd title)Most successful club(s)Celtic(42 titles)Websitescottishfa.co.uk 2023–24 Scottish Cup The Scottish Football Association Challenge Cup,[1] commonly known as the Scottish Cup&#...

Francesco MoriniMorini in allenamento per la Juventus al Campo Combi nella stagione 1972-1973Nazionalità Italia Altezza185 cm Peso78 kg Calcio RuoloStopper Termine carriera1º dicembre 1980 CarrieraGiovanili 19??-1963 Sampdoria Squadre di club1 1963-1969 Sampdoria162 (0)[1]1969-1980 Juventus256 (0)1980 Toronto Blizzard22 (0) Nazionale 1973-1975 Italia11 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo →...

Curling competition at Kamloops, British Columbia 2014 Tim Hortons BrierHost cityKamloops, British ColumbiaArenaInterior Savings CentreDatesMarch 1–9Attendance65,005Winner AlbertaCurling clubGlencoe CC, CalgarySkipKevin KoeThirdPat SimmonsSecondCarter RycroftLeadNolan ThiessenAlternateJamie KingCoachJohn DunnFinalist British Columbia (John Morris)« 2013 2015 » The 2014 Tim Hortons Brier was held from March 1 to 9 at the Interior Savings Centre in Kamloops, British ...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang klub sepak bola wanita. Untuk klub sepak bola pria, lihat Brisbane Roar FC. Brisbane RoarNama lengkapBrisbane Roar Women Football ClubBerdiri2008; 16 tahun lalu (2008)StadionLions Stadium(Kapasitas: 5.000)KetuaRahim SoekasahManajerGarrath McPhersonLigaA-League Women2021–20226 dari 10 Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Brisbane Roar Women Football Club, dahulu bernama Queensland Roar Women, adalah klub sepak bola wanita profesional yang berasal dari Brisban...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir XGA. Cet article est une ébauche concernant l’informatique. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Carte graphique de type IBM XGA-2. Le XGA ou Extended Graphics Array désigne aussi bien un type de carte graphique (XGA Display Adapter/A), produite par IBM au mois d'octobre 1990[1] pour l’IBM-PS/2, que la norme d’affichage dont la définition est de 1 024×7...

Group of science education and research institutes in India Not to be confused with Indian Institute of Science or National Institute of Science Education and Research. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Indian Institutes of Science Education and Research – news · newspapers · books · scholar · ...

本模板依照頁面品質評定標準无需评级。本Template属于下列维基专题范畴: ACG专题 (获评模板級、不适用重要度) ACGPJ:ACGTemplate:ACG專題ACG条目 动漫主题查论编本條目屬於ACG專題的範疇,一個旨在改善中文維基百科日系ACGN類條目內容的專案。如果您有意參與,請瀏覽專題首頁,參與其討論並完成相應的開放性任務。 模板 根据专题质量评级标准,本Template�...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati del Wisconsin è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. OneidaUnincorporated community(EN) Oneida, Wisconsin LocalizzazioneStato Stati Uniti Stato federato Wisconsin ConteaOutagamie TerritorioCoordinate44°29′54.96″N 88°10′58.08″W44°29′54.96″N, 88°10′58.08″W (Oneida) Altitudine207 m s.l.m. Superficie157,6 km² Abit...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della provincia di Cremona è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Castel Gabbianocomune Castel Gabbiano – VedutaVilla Griffoni Sant'Angelo LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Cremona AmministrazioneSindacoGiorgio Sonzogni (lista civica) dal 27-5-2019 (2º mandato dal 9-6-2024) TerritorioCoordinate45°28′N 9°42′E45°28′N, 9°42′E (Castel...
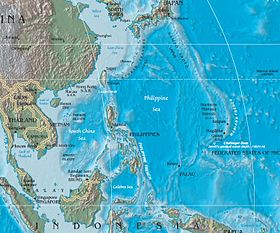
Филиппинское море Характеристики Площадь5 726 000 км² Объём23 522 000 км³ Наибольшая глубина10 994 ± 40[1] м Средняя глубина4108 м Расположение 20°23′09″ с. ш. 133°48′48″ в. д.HGЯO Страны Федеративные Штаты Микронезии Гуам Индонезия Япония С...
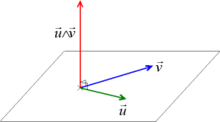
Coefficients of an algebra over a field Using the cross product as a Lie bracket, the algebra of 3-dimensional real vectors is a Lie algebra isomorphic to the Lie algebras of SU(2) and SO(3). The structure constants are f a b c = ϵ a b c {\displaystyle f^{abc}=\epsilon ^{abc}} , where ϵ a b c {\displaystyle \epsilon ^{abc}} is the antisymmetric Levi-Civita symbol. In mathematics, the structure constants or structure coefficients of an algebra over a field are the coefficients of...


