Hurlford F.C.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Perusahaan / pengembangKaiOS Technologies (Hong Kong) Limited (denganTCL sebagai pemegang saham terbesar)[1]Diprogram dalamHTML, CSS, JavaScriptKeluargaFirefox OS / Open Web (berbasis pada Linux kernel)Status terkiniAktifModel sumberSumber tertutupRilis perdanaOktober 2017Rilis final4.0.5,4.0.6,5.0.0 (Januari 2023) / Oktober 2017Rilis tak-stabil final4.0.5 (November 2017)Target pemasaranTelepon genggamManajer paketKaiStoreDukungan platformARMKernel typeMonolithic (Linux)Antarmuka...

Berkas:Df5 06large.jpg Dongfeng 5 [wǔ] (Tionghoa: 东风 -5, harfiah Eurus 5) atau DF-5 adalah ICBM Tiongkok 3 tahap. Ini memiliki panjang 32,6 m dan diameter 3,35 m. Beratnya mencapai 183.000 kilogram dan memiliki rentang perkiraan 12.000 sampai 15.000 kilometer. DF-5 memiliki penerbangan pertama pada tahun 1971 dan dalam pelayanan operasional 10 tahun kemudian. Salah satu kelemahan dari rudal adalah bahwa hal itu membutuhkan waktu antara 30 dan 60 menit untuk bahan bakar. DF-5 dijadwalkan ...

Artikel ini mungkin terdampak dengan peristiwa terkini: Invasi Rusia ke Ukraina 2022. Informasi di halaman ini bisa berubah setiap saat. Oblast Kherson merupakan sebuah oblast di Ukraina yang diduduki oleh Rusia dalam invasi di tahun 2022. Memiliki luas wilayah 28.461 km² dan populasi 1,016,707 jiwa (2021) dan ibu kotanya ialah Kherson. Referensi lbsPembagian administratif Ukraina Oblast Cherkasy · Chernihiv · Chernivtsi · Krimea · Dnipropetro...

George C. ScottScott pada tahun 1959LahirGeorge Campbell Scott(1927-10-18)18 Oktober 1927Wise, Virginia, U.S.Meninggal22 September 1999(1999-09-22) (umur 71)Westlake Village, California, U.S.PekerjaanActor, director, producerTahun aktif1958–1999Suami/istriCarolyn Hughes (1951–1955)Patricia Reed (1955–1960)Colleen Dewhurst (1960–1965)Colleen Dewhurst (1967–1972)Trish Van Devere (1972–1999) George Campbell Scott (18 Oktober 1927 – 22 September 1999) merupa...

Volume dari United States Reports di rak di perpustakaan hukum. United States Reports adalah catatan resmi (laporan hukum) dari putusan, perintah, tabel kasus (daftar setiap kasus yang diputuskan, dalam urutan abjad baik oleh nama pemohon (pihak yang kalah di pengadilan yang lebih rendah) dan dengan nama responden (pihak yang berlaku di bawah)), dan proses lain dari Mahkamah Agung Amerika Serikat. United States Reports, setelah dicetak dan terikat, adalah versi akhir dari pendapat pengadilan ...

Irish musician and activist, lead vocalist of U2 (born 1960) For other uses, see Bono (disambiguation). Paul Hewson redirects here. For the New Zealand musician and songwriter of the same name, see Dragon (band). BonoBono performing on the Joshua Tree Tour 2017 in IndianapolisBornPaul David Hewson (1960-05-10) 10 May 1960 (age 63)Dublin, IrelandOther namesBono VoxEducationMount Temple Comprehensive SchoolOccupationsSinger-songwriteractivistbusinessmanOrganizationOne CampaignSpouse A...

Scientific study of humans, human behavior, and societies This article is about the study of humans. For the study of human origins, see Anthropogeny. For other uses, see Anthropology (disambiguation). An anthropologist with indigenous American people Part of a series onAnthropology OutlineHistory Types Archaeological Biological Cultural Linguistic Social Archaeological Aerial Aviation Battlefield Biblical Bioarchaeological Environmental Ethnoarchaeological Experiential Feminist Forensic Mari...

Coating that prevents sticking Food in a non-stick pan A non-stick surface is engineered to reduce the ability of other materials to stick to it. Non-stick cookware is a common application, where the non-stick coating allows food to brown without sticking to the pan. Non-stick is often used to refer to surfaces coated with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a well-known brand of which is Teflon. In the twenty-first century, other coatings have been marketed as non-stick, such as anodized alumini...
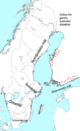
Halländska Halländska är de dialekter inom svenska som talas i landskapet Halland. Södra Halland anses tillhöra det skånska språkområdet, och är sålunda historiskt sett en östdansk, alternativt sydskandinavisk dialekt.[1] Halländskan närmar sig i dialektområdets nordliga delar västgötska och göteborgska. Kännetecken I likhet med andra östdanska/sydsvenska dialekter har konsonanterna p, t, k efter lång vokal i nästan hela landskapet övergått till b, d, g (sv. kaka → ka...

American baseball player (born 1977) Baseball player Brandon IngeInge with the Detroit TigersThird baseman / CatcherBorn: (1977-05-19) May 19, 1977 (age 46)Lynchburg, Virginia, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutApril 3, 2001, for the Detroit TigersLast MLB appearanceJuly 21, 2013, for the Pittsburgh PiratesMLB statisticsBatting average.233Home runs152Runs batted in648 Teams Detroit Tigers (2001–2012) Oakland Athletics (2012) Pittsburgh Pirates (2013) C...

هنودمعلومات عامةنسبة التسمية الهند التعداد الكليالتعداد قرابة 1.21 مليار[1][2]تعداد الهند عام 2011ق. 1.32 مليار[3]تقديرات عام 2017ق. 30.8 مليون[4]مناطق الوجود المميزةبلد الأصل الهند البلد الهند الهند نيبال 4,000,000[5] الولايات المتحدة 3,982,398[6] الإمار...

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 ...

Danish badminton player (born 1994) Badminton playerMathias ChristiansenChristiansen in 2016.Personal informationCountryDenmarkBorn (1994-02-20) 20 February 1994 (age 30)Bornholm, DenmarkResidenceCopenhagen, DenmarkHeight1.86 m (6 ft 1 in)Years active2011–presentHandednessRightMen's & mixed doublesHighest ranking19 (MD with David Daugaard 21 September 2017)4 (XD with Christinna Pedersen 25 October 2018)Current ranking10 (XD with Alexandra Bøje 16 April 2024) Me...

Japanese television series An evil version of Minilla battles the Toho superhero Greenman. Go! Greenman (行け! グリーンマン, Ike! Greenman) is a tokusatsu television series Kyodai Hero kaiju produced by Toho in 1973. It ran from November 12, 1973, to September 27, 1974. It emerged as a follow-up series to Ike! Godman, but the two share no continuity. Compared to the anthology-like storylines of Ike! Godman, Go! Greenman has a single overarching plot. Synopsis Deep beneath Japan, a dem...

2010 single by Norah JonesYoung BloodSingle by Norah Jonesfrom the album The Fall ReleasedFebruary 16, 2010[1]Length3:38LabelBlue NoteSongwriter(s)Norah JonesProducer(s)Jacquire KingNorah Jones singles chronology Chasing Pirates (2009) Young Blood (2010) It's Gonna Be (2010) Music videoYoung Blood on YouTube Young Blood is the second single by American singer Norah Jones from her fourth album, The Fall.[2] It was released exclusively on February 16, 2010, for North America, Eu...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Albert. Albert L'ancien quai de la ligne 51 vers Uccle. Localisation Pays Belgique Ville Bruxelles Communes Saint-GillesForest Coordonnéesgéographiques 50° 49′ 17″ nord, 4° 20′ 31″ est Caractéristiques Position parrapport au sol souterraine Voies 2 passantes2 en impasse Quais 2 (+ 2 inutilisés) sur les voies passantes1 sur les voies en impasse Nombre d'accès 3 Accessibilité Non Historique Mise en service 3 décem...

French playwright Jules-Henri Vernoy de Saint-Georges Jules-Henri Vernoy de Saint-Georges (7 November 1799 – 23 December 1875) was a French playwright, who was born and died in Paris. He was one of the most prolific librettists of the 19th century, often working in collaboration with others.[1] Saint-Georges' first work, Saint-Louis ou les deux dîners (1823), a comédie en vaudeville written in collaboration with Alexandre Tardif, was followed by a series of operas and ballets. In ...

Epistemology without sure premises Not to be confused with Philosophical skepticism. This article needs more complete citations for verification. Please help add missing citation information so that sources are clearly identifiable. (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Anti-foundationalism (also called nonfoundationalism) is any philosophy which rejects a foundationalist approach. An anti-foundationalist is one who does not believe that there is some fundamental belief or p...

Map of seismic hazard in Texas as of 2014[update], as determined using the peak ground acceleration with 2% probability of exceedance in 50 years Earthquakes intense enough to be perceptible occur annually in the U.S. state of Texas. Most earthquakes in the state have been small or have produced minimal impacts. No earthquake-related fatalities have been reported in the state, though one earthquake in Texas caused a death in the neighboring Mexican state of Chihuahua in 1923. The ear...

King of Anuradhapura Aggabodhi IIKing of AnuradhapuraReign608–618PredecessorAggabodhi ISuccessorSangha Tissa IIDynastyHouse of Moriya Aggabodhi II was King of Anuradhapura (in modern-day Sri Lanka) in the 7th century CE. His reign lasted from 608 to 618 CE.[1][2] He was the nephew (the son of a sister) of the previous king, Aggabodhi I, and had acted as viceroy during this king's reign.[2] Upon coming to the throne, Aggabodhi II continued the work his uncle had begun...