Heaven & Hell Tour
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
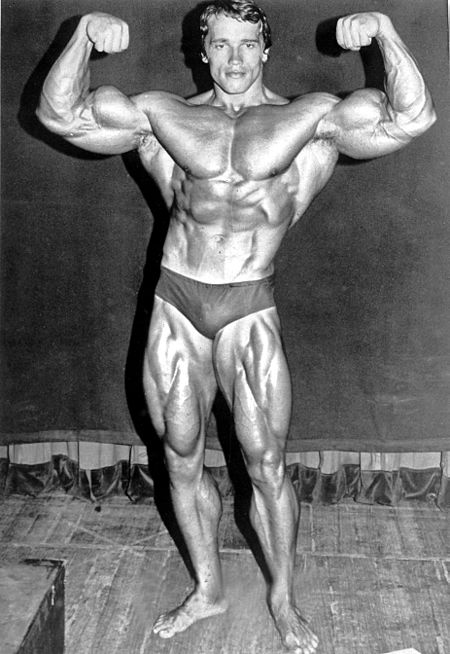

Austrian and American actor and politician (born 1947) Schwarzenegger redirects here. For other people with the name, see Schwarzenegger (surname). Arnold SchwarzeneggerSchwarzenegger in 201938th Governor of CaliforniaIn officeNovember 17, 2003 – January 3, 2011Lieutenant Cruz Bustamante John Garamendi Mona Pasquil (acting) Abel Maldonado Preceded byGray DavisSucceeded byJerry BrownChairman of the President's Councilon Physical Fitness and SportsIn officeJanuary 22, 1990 �...

كفر المنشي البحرى - قرية مصرية - تقسيم إداري البلد مصر المحافظة محافظة كفر الشيخ المركز كفر الشيخ المسؤولون السكان التعداد السكاني 2179 نسمة (إحصاء 2006) معلومات أخرى التوقيت ت ع م+02:00 تعديل مصدري - تعديل قرية كفر المنشي البحرى هي إحدى القرى التابعة لمركز ك...

Hobby A group of spotters at Domodedovo International Airport taking photos of a KrasAir Ilyushin Il-96-300 in 2008. Aircraft spotting, or planespotting, is a hobby consisting of observing and tracking aircraft, which is usually accomplished by photography or videography. Besides monitoring aircraft, planespotting enthusiasts (who are usually called planespotters) also record information regarding airports, air traffic control communications, airline routes, and more. History and evolution Av...

Class of extinct, Paleozoic arthropods For other uses, see Trilobite (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Trilobozoa. TrilobiteTemporal range: Early Cambrian[1][2] – Late Permian, 521–251.9 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Montage of trilobite genera: Top row: Walliserops, Phacops and Cambropallas; bottom row: Isotelus, Kolihapeltis and Ceratarges Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda (unranked): †Artiopoda Subphylum...

For related races, see 1896 United States gubernatorial elections. 1896 North Carolina gubernatorial election ← 1892 November 3, 1896 1900 → Nominee Daniel Lindsay Russell Cyrus B. Watson William A. Guthrie Party Fusion Democratic Populist Popular vote 154,025 145,286 30,943 Percentage 46.5% 43.9% 9.4% Governor before election Elias Carr Democratic Elected Governor Daniel Lindsay Russell Republican Elections in North Carolina Federal government U.S. Presiden...

Lawrence v. TexasMahkamah Agung Amerika SerikatDisidangkan pada March 26, 2003Diputus pada June 26, 2003Nama lengkap kasusJohn Geddes Lawrence and Tyron Garner v TexasDocket nos.02-102Kutipan539 U.S. 558 (lanjut)123 S. Ct. 2472; 156 L. Ed. 2d 508; 2003 U.S. LEXIS 5013; 71 U.S.L.W. 4574; 2003 Cal. Daily Op. Service 5559; 2003 Daily Journal DAR 7036; 16 Fla. L. Weekly Fed. S 427Versi sebelumnyaDefendants convicted, Harris County Criminal Court (1999), rev'd, 2000 WL 729417 (Tex. App. 2000) (dep...

Agostino Pantò Agostino Pantò (Alcamo, 11 settembre 1675 – Palermo, 11 giugno 1735) è stato un teologo, oratore e giurista italiano. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Opere 3 Note 4 Bibliografia 5 Voci correlate 6 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Agostino Pantò nacque ad Alcamo l'11 settembre 1675 e qui fece i primi suoi studi. Era un discendente dei Conti di Pierras in Catalogna;[1] fin da giovane evidenziò alte capacità intellettive. All'età di sedici anni, indossato l'abito talare, si tr...

提示:此条目页的主题不是中華人民共和國最高領導人。 中华人民共和国 中华人民共和国政府与政治系列条目 执政党 中国共产党 党章、党旗党徽 主要负责人、领导核心 领导集体、民主集中制 意识形态、组织 以习近平同志为核心的党中央 两个维护、两个确立 全国代表大会 (二十大) 中央委员会 (二十届) 总书记:习近平 中央政治局 常务委员会 中央书记处 �...

American equestrian (1900–1971) For other people with similar names, see Earl Thompson. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Earl Foster Thomson – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Earl Foster Thomson At West Point in 1922 Med...
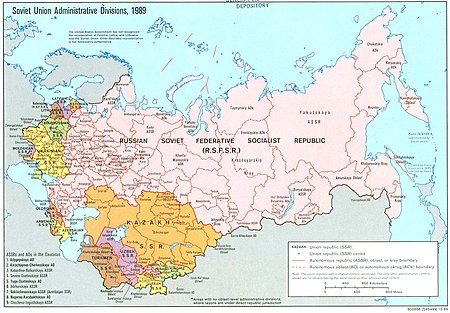
Citizens and nationals of the Soviet Union Soviets redirects here. For the bygone political organizations in Russia, see Soviet (council). For other uses, see Soviet (disambiguation). Ethnic group Soviet peopleСоветский народFlag of the Soviet UnionMap of the country's constituent Union Republics in 1989Total population286,730,819 (1989 census)LanguagesRussian,[1] Ukrainian, Belarusian, Kazakh, Azerbaijani, Georgian, Armenian, Uzbek, Kyrgyz, Tajik, Turkmen, Latvian, Esto...

Spanish philosopher, theologian, Catholic apologist, sociologist and political writer Balmes redirects here. For other uses, see Balmes (disambiguation). Jaime BalmesBornJaime Luciano Antonio Balmes y Urpiá28 August 1810Vic, Catalonia, SpainDied9 July 1848 (1848-07-10) (aged 37)Vic, Catalonia, SpainBurial placeCathedral of St Peter of VicNationalitySpanishAlma materUniversity of CerveraOccupation(s)Theologian, presbyter and writerEra19th-century philosophyRegionWestern philoso...

Method of execution Execution by shootingMethod ofCapital punishment Execution by shooting is a method of capital punishment in which a person is shot to death by one or more firearms. It is the most common method of execution worldwide, used in about 70 countries,[1] with execution by firing squad being one particular form. In most countries, execution by a firing squad has historically been considered a more honorable death and was used primarily for military personnel, though in so...

Djasri Marin Komandan Puspomad ke-20Masa jabatan2000–2002PendahuluMayjen TNI Syamsu DjalalPenggantiMayjen TNI Sulaiman AB Informasi pribadiLahir30 Agustus 1950 (umur 73)Payakumbuh, Sumatera BaratSuami/istriR. Mulyati (alm)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan DaratPangkat Mayor Jenderal TNISatuanPolisi Militer (CPM)Sunting kotak info • L • B Mayjen TNI (Purn) Djasri Marin (lahir 30 Agustus 1950) adalah seorang tokoh militer Indonesia dari TNI-AD....

Head of the US independent space agency Administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space AdministrationNASA SealConstituent part of the administrator's standardIncumbentBill Nelsonsince May 3, 2021Reports toPresidentSeatWashington, D.C.NominatorPresident with Senate advice and consentTerm lengthAt the pleasure of the PresidentConstituting instrument51 U.S.C. § 20111Inaugural holderThomas Keith GlennanSalary$221,900 annually (Executive Schedule II)WebsiteBill Nelson, NA...

Former state electoral district of New South Wales, Australia Phillip was an electoral district of the Legislative Assembly in the Australian state of New South Wales, in central Sydney and named after Arthur Phillip. It was originally created in the 1904 re-distribution of electorates following the 1903 New South Wales referendum, which required the number of members of the Legislative Assembly to be reduced from 125 to 90.[1] It consisted of part of the abolished seats of Sydney-Phi...

Russian politician (born 1989) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Vasilievna and the family name is Ogloblina. Yulia OgloblinaЮлия Оглоблинаofficial portrait, circa 2021Member of the State Duma for MordoviaIncumbentAssumed office 12 October 2021Preceded byVitaly EfimovConstituencyMordovia-at-large (No. 23) Personal detailsBorn (1989-11-01) 1 November 1989 (age 34)Torbeyevo, Torbeyevsky District, Mordovian ASSR, RSFSR, USSRPolit...

ديرك تير هار (بالهولندية: Dik ter Haar)[1] معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة (بالهولندية: Dirk ter Haar)[1] الميلاد 19 أبريل 1919(1919-04-19)المملكة المتحدة الوفاة 3 سبتمبر 2002 (83 سنة)دراختن[1] مواطنة مملكة هولندا[1] عضو في الجمعية الملكية في إدنبرة، والأكاديمية الملك...

British Liberal politician (1826–1904) His Excellency The Right HonourableThe Earl of NorthbrookGCSI PC FRSThe 1st Earl of Northbrook, c. 1889Lord Lieutenant of HampshireIn office7 November 1890 – 15 November 1904MonarchVictoriaPreceded byThe Lord CarnarvonSucceeded byThe Lord WinchesterViceroy and Governor-General of IndiaIn office3 May 1872 – 12 April 1876MonarchVictoriaPreceded byThe Lord NapierSucceeded byThe Lord LyttonMember of Parliament for Penryn...

Den här artikeln behöver fler eller bättre källhänvisningar för att kunna verifieras. (2016-12) Åtgärda genom att lägga till pålitliga källor (gärna som fotnoter). Uppgifter utan källhänvisning kan ifrågasättas och tas bort utan att det behöver diskuteras på diskussionssidan. Naguib Mahfouz نجيب محفوظ Född11 december 1911 Kairo, EgyptenDöd30 augusti 2006 (94 år) Kairo, EgyptenYrkeFörfattareNationalitetEgyptier Språkarabiska[1]Verksam1932 - 2006Genrerroman...

German Catholic theologian and historian Franz Xaver Funk, 1900 Franz Xaver von Funk (22 October 1840 – 24 February 1907) was a German Catholic theologian and historian. Biography Funk was born at Abts-Gmünd, Württemberg, and educated at Tübingen, at the seminary of Rottenburg am Neckar, and in Paris, where he studied economics. In 1870 he was appointed professor of theology at Tübingen and in 1876 became an editor of the Tübingen Theologische Quartalschrift.[1] Though he is pe...