George McMillin
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Wang. Pada nama panggung/nama pena, nama belakangnya adalah Jun. Jun Ji-hyunJun Ji-hyun pada 2019.LahirWang Ji-hyun30 Oktober 1981 (umur 42) SeoulNama lainGianna JunAlmamaterUniversitas Dongguk(Teater dan Film)PekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1998–sekarangAgenIHQ (1997–2010)Culture Depot (2012–sekarang)Tinggi173 cm (5 ft 8 in)Suami/istriChoi Joon-hyuk (m. 2012)Anak2[1]Nama KoreaHa...
Kerajaan Tondoᜃᜑᜍᜒᜀᜈ᜔ ᜅ᜔ ᜆᜓᜈᜇᜓ Kaharian ng TondoKayarian ning TundoPagarian ti TondoKahadean merdeka Indonesia/Tondo Kerajaan Tunduns. 900an–1589 BenderaIbu kotaTondo (Sekarang distrik Manila)Bahasa yang umum digunakanTagalog Lama, Kapampangan, Bikol, Ilocano (bahasa lokal) Tionghoa Tengah, Melayu Lama (bahasa bisnis), Sansekerta dan Pali (aktivitas keagamaan)Agama Hindu, Buddha, Kepercayaan asli dan IslamPemerintahanKelakananLakan • Zaman Besi �...

PemberitahuanTemplat ini mendeteksi bahwa artikel bahasa ini masih belum dinilai kualitasnya oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa dan ProyekWiki terkait dengan subjek. Terjadi [[false positive]]? Silakan laporkan kesalahan ini. 07.03, Sabtu, 30 Maret, 2024 (UTC) • hapus singgahan Sebanyak 1.305 artikel belum dinilai Artikel ini belum dinilai oleh ProyekWiki Bahasa Cari artikel bahasa Cari berdasarkan kode ISO 639 (Uji coba) Kolom pencarian ini hanya didukung oleh beberapa antarmuka Hala...
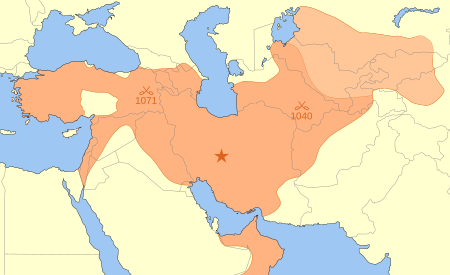
Series of conflicts in the Middle Ages Byzantine–Seljuk warsPart of Decline of the Byzantine EmpireDate1046–1243LocationAnatolia and Northern / Western SyriaResult Military stalemate Seljuks conquer parts of Anatolia prior to their collapse to the MongolsBelligerents Byzantine EmpireEmpire of TrebizondEmpire of NicaeaCrusader States Seljuk EmpireSultanate of RumAbbasid CaliphateStrength c. 1071:Could raise up to 100,000 troops1140:25,000 to 50,000 field troops Unknown vteByzantine–Selju...

Former municipality in DenmarkRudkøbing Municipality Rudkøbing KommuneFormer municipality Coat of armsCountryDenmarkCountyFunenEstablishedApril 1, 1970DissolvedDecember 31, 2006SeatRudkøbingGovernment • Last mayorJohan Norden (A)Area[1] • Total62.94 km2 (24.30 sq mi)Population (2006)[1] • Total6,647 • Density110/km2 (270/sq mi)Time zoneUTC1 (CET) • Summer (DST)UTC2 (CEST)Municipal code475Un...

Summons and deportation of Paris-area foreign-born Jews on 14 May 1941 Green ticket roundupThe roundup taking place on 14 May 1941Native name Rafle du billet vertEnglish nameGreen ticket roundupDate14 May 1941LocationParisTargetForeign jews living in FranceOrganised byNazi Germany, Vichy FranceParticipantsFrench Police and GendarmerieArrests3,747[1] Part of a series onThe HolocaustJews on selection ramp at Auschwitz, May 1944 Responsibility Nazi Germany People Major perpetrators ...

2nd Infantry Regiment2nd Infantry Regiment coat of armsActive1808-presentCountry United StatesBranch United States ArmyTypeInfantryRole1st Battalion – Inactive2nd Battalion – Light InfantryPart of 3rd BCT, 10th Mountain DivisionGarrison/HQ1st Battalion – Inactive2nd Battalion – Fort Johnson, LouisianaNickname(s)1st Battalion Black Scarves2nd Battalion RamrodsMotto(s)Noli Me Tangere(Do Not Touch Me)EngagementsWar of 1812Indian WarsMexican–U.S. WarAmerican Ci...

Salah satu kucing polidaktil milik Ernest Hemingway di rumahnya di Key West. Kucing khusus ini memiliki 26 jari kaki. Anak kucing dengan 23 jari kaki. Kucing polidaktil adalah salah satu jenis kucing yang memiliki enam jari di kaki depan dan lima jari di kaki belakang, sehingga jumlah jarinya adalah 22 atau lebih. Kucing ini memiliki jari yang mirip dengan jempol.[1] Kata polidaktil berasal dari bahasa Yunani yang berarti berkaki banyak. Kucing polidaktil memiliki jari yang lebih dise...

Aspect of Jewish history For the period of Spanish cultural flourishing in the 17th century, see Spanish Golden Age. For broader coverage of this topic, see History of the Jews in Spain and History of the Jews in Portugal. History of Al-Andalus Muslim conquest(711–732) Battle of Guadalete Siege of Córdoba (711) Battle of Toulouse Battle of Tours Umayyad dynasty of Córdoba(756–1031) Emirate of Córdoba Caliphate of Córdoba Al-Mansur Ibn Abi Aamir First Taifa period(1009–1110) Almoravi...

Letusan pada bulan September tahun 1985. Nevado del Ruiz adalah sebuah stratovolcano yang terletak di Kolombia. Gunung ini merupakan gunung yang terletak di bagian paling utara Sabuk vulkanik Andes dan terbentang sekitar 15 mil sebelah tenggara dari Manizales, dengan kota Armero di lembah dekat gunung ini. Gunung ini adalah gunung tertinggi dan gunung yang terletak paling utara di Kolombia. Letusan gunung ini tahun 1985 memproduksi lahar yang mengubur kota dan menyebabkan kematian sebesar 23....

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

MarsangiscomuneMarsangis – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Marna ArrondissementÉpernay CantoneVertus-Plaine Champenoise TerritorioCoordinate48°36′N 3°50′E / 48.6°N 3.833333°E48.6; 3.833333 (Marsangis)Coordinate: 48°36′N 3°50′E / 48.6°N 3.833333°E48.6; 3.833333 (Marsangis) Superficie6,89 km² Abitanti53[1] (2009) Densità7,69 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale51260 Fuso orarioUTC...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il politico omonimo, vedi Edward Douglass White Senior. Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento politici statunitensi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Edward Douglass White 9º Presidente della Corte Suprema degli Stati UnitiDurata mandato19 dicembre 1...

Place in Lower Austria, AustriaBerndorfGeneral view of the town Coat of armsBerndorfLocation within AustriaCoordinates: 47°56′34″N 16°6′13″E / 47.94278°N 16.10361°E / 47.94278; 16.10361CountryAustriaStateLower AustriaDistrictBadenGovernment • MayorFranz Rumpler (ÖVP)Area[1] • Total17.58 km2 (6.79 sq mi)Elevation314 m (1,030 ft)Population (2018-01-01)[2] • Total9,064 •&...

Club of less than arm's length Billy Club redirects here. For the film, see Billy Club (film). Police club redirects here. For the Iraqi football club, see Al-Shorta SC. A 1968-era Chicago Police helmet and billy club A baton (also truncheon, nightstick, billy club, billystick, cosh, lathi, or simply stick) is a roughly cylindrical club made of wood, rubber, plastic, or metal. It is carried as a compliance tool and defensive weapon[1] by law-enforcement officers, correctional staff, s...

History of socialism in Finland The balance scale of the reds: A humour maganize's depicture of Moderates being kicked out of the Social Democratic Party, and being replaced with a pack of dynamite.Socialism in Finland is thought to stretch back to the latter half of the 19th century in the Grand Duchy of Finland, with the increasing industrialization of Finland. History Part of a series onSocialism HistoryOutline Development Age of the Enlightenment French Revolution Revolutions of 1848 Soci...

Microsoft's programming language based on BASIC and COM This article is about the Visual Basic language that shipped with Microsoft Visual Studio pre-.NET. For the current Visual Basic language, based on .NET, see Visual Basic (.NET). Not to be confused with VBScript. Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help improve this article by looking for better, more reliable sources. Unreliable citations may be challenged and removed. (April 2014) (Learn how and when to re...

Questa voce sull'argomento federazioni calcistiche è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Confederation of Independent Football AssociationsLogo Disciplina Calcio Fondazione7 giugno 2013 Federazioni affiliate62 Sede Luleå Presidente Per-Anders Blind Sito ufficialewww.conifa.org/en/ Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La Confederation of Independent Football Associations (CONIFA) è una federazione internazionale di calcio fondata ...

American politician Betsy HollandMember, Georgia House of Representatives, 54th DistrictIncumbentAssumed office January 14, 2019[1]Preceded byBeth Beskin Personal detailsBorn (1976-01-10) January 10, 1976 (age 48)Political partyDemocraticSpouseJason[1]Residence(s)Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.Alma materSmith College[2]OccupationCorporate executive Betsy Holland (born January 10, 1976) is an American politician. She is a Democrat representing the 54th district in the G...

1974 studio album by John HiattHangin' Around the ObservatoryStudio album by John HiattReleased1974RecordedJuly 1973StudioColumbia Studio A, NashvilleGenreRockLength37:44LabelEpicProducerGlen SpreenJohn Hiatt chronology Hangin' Around the Observatory(1974) Overcoats(1975) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllMusic[1]Christgau's Record GuideB[2]Rolling Stone[3]The New Rolling Stone Album Guide[4]Tom HullA−[5] Hangin' Around The Obse...


